Every four months or so, Tezos releases a new version of its protocol. On the one hand, such regularity ensures thorough and well-planned improvements that can benefit both Tezos and projects built on top of it in the long run. On the other hand, developers need to keep an eye on every change and understand how it will affect the project under development.
In this article, we briefly overview the history of Tezos, analyzing how recently introduced functionality can benefit different blockchain projects. Apart from the latest changes to Tezos, we explore new features that are planned for future updates. This article will be helpful for development leaders who are considering using Tezos for their next project and want to learn about the most important changes to this platform and how exactly they can impact their products.
Contents:
Why consider Tezos for your blockchain project development?
What is Tezos?
Tezos is a popular blockchain platform that became famous among the development community thanks to its many benefits, which include a self-amendment protocol, on-chain governance, and formal verification of smart contracts.
Tezos offers developers a rich feature set to help your team create efficient products for various purposes and industries. For example, you can use this blockchain platform to build:
- Non-fungible token (NFT) products. According to the State of Tezos Q1 2023 report, popular NFT platforms like Rarible and Wert.io have added Tezos support to their marketplaces.
- Decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions. The State of Tezos Q1 2023 report mentions that DeFi saw a noticeable 24% increase in users compared to the previous quarter, reaching its highest level in a year.
- Video games. According to the Tezos Foundation Biannual Update [PDF], many developers have been building and launching games in 2022, and they expect more interest in this area in 2023 as well.
- Decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. Many blockchain projects choose to build their projects on Tezos, as this platform supports smart contracts and dApps that can’t be censored or shut down by third parties. Also, Tezos facilitates formal verification, which, if used properly, can help you avoid costly bugs and spending resources to fix them.
You can explore more details about different ways to create smart contracts on Tezos in our previous article, where we also provided a comprehensive overview of the essence of the Tezos blockchain.
Another valid reason to choose Tezos as the basis for your blockchain project is the ease of use. For example, Tezos doesn’t require your team to know only one specific programming language. At the moment, to create smart contracts for Tezos, your developers can use several high-level languages that provide an easy-to-read syntax that will be compiled into Michelson before deployment to the blockchain.
The three popular languages supported are the following:
- SmartPy uses Python syntax to implement smart contract logic. It also provides a simulated environment for development and testing.
- LIGO is a functional language that has two options for smart contract syntax: JavaScript-like JsLIGO and Caml-like CameLIGO.
- Archetype is a general-purpose language that allows for designing a smart contract as a state machine.
Each of these languages has its own specifics, but you won’t lose functionality by choosing either of two. Just choose the language your developers are most comfortable working with.
Last but not least, Tezos introduces a protocol change every four months, ensuring continuous improvement of its ecosystem and offering more and more opportunities for blockchain developers. Let’s explore what updates Tezos has gone through over the past few years and how these changes can impact your blockchain development.
Looking to leverage blockchain technology for your solution?
Benefit from the ability of Apriorit’s blockchain engineers to solve even the most complex challenges for your business!
Brief history of Tezos evolution: protocol versioning
To continuously improve the platform, the Tezos team introduces changes via protocol upgrades. First, on-chain governance approves the suggested changes, and only after that can the new protocol be implemented. Such a mechanism enables integration of amendments without the risk of hard forks, ensuring smooth blockchain evolution.
At the time of writing, Tezos has had 14 protocol updates named in alphabetical order. Let’s overview the main changes each protocol introduced to the platform:
| Protocol | Release Date | Main Changes |
|---|---|---|
| Athens | May 2019 | – Increased block size limit to 8,000,000 gas – Reduced toll size |
| Babylon | October 2019 | – Introduced changes to the consensus algorithm – Added entry points support – Introduced changes to the proposal quorum |
| Carthage | March 2020 | – Increased block size limit to 10,400,000 gas – Improved reward calculations – Optimized Michelson |
| Delphi | November 2020 | – Recomputed gas costs for instructions and storage |
| Edo | February 2021 | – Integrated the Sapling protocol – Added new hash functions – Added tickets mechanism – Introduced changes to the voting procedure |
| Florence | May 2021 | – Changed order of inter-contract calls – Doubled maximum size of operations – Optimized gas cost |
| Granada | August 2021 | – Reduced the block time – Introduced changes to the consensus algorithm – Improved the Michelson performance – Optimized gas cost |
| Hangzhou | December 2021 | – Added on-chain views – Added timelock – Added cache for frequently used data |
| Ithaca | April 2022 | – Introduced the new consensus algorithm |
| Jakarta | June 2022 | – Added optimistic transaction rollups – Optimized gas cost |
| Kathmandu | September 2022 | – Updated randomness generation – Added event logging |
| Lima | December 2022 | – Added the consensus key feature – Removed timelock |
| Mumbai | March 2023 | – Reduced block time – Added smart rollups – Added several instructions to work with bytes |
| Nairobi | June 2023 | – Improved smart rollups – Optimized gas usage |
Knowing all the changes and keeping track of all protocol documentation is vital for blockchain development teams.
Some updates might require your team to change the way they create smart contracts and even double-check and amend already created smart contracts. Others show you what new opportunities to look for. For example, at the moment of writing, Nairobi is the newest Tezos protocol. It’s expected to provide the ability to complete up to eight times more operations per second compared to the previous protocol while decreasing the cost per transaction for most operations.
At Apriorit, we keep an eye on Tezos upgrades to make sure we build and maintain blockchain projects in the most efficient and secure way, leveraging all opportunities this platform provides.
Read also
Tezos Blockchain and Smart Contract Overview
Leverage a new-generation blockchain system. Discover Tezos’s core principles and possibilities and master writing smart contracts for it in Liquidity and Michelson.
4 key Tezos updates that are worth your attention
Regular changes are one of the things that sets Tezos apart from other blockchain platforms. Over the years of Tezos’ evolution, this platform has undergone over 14 protocol upgrades, bringing both big and small changes to improve the platform.
While all of these changes are important, some will affect the progress of Tezos development projects more than others. In this article, we cover in detail the categories of changes that can impact your blockchain development projects the most.
Let’s look at some of the key updates and see how they can help enhance your solution.

1. Consensus algorithm changes
First, let’s quickly go over some key terms to make sure we’re on the same page:
- A consensus algorithm is a set of rules that determine how new blocks are produced and validated.
- Baking is the process of creating blocks, and block creators are called bakers. Participants that are not selected for baking of the current block can validate and endorse it to receive some reward.
- Endorsement is the process of confirming blocks mined by other bakers.
Tezos uses the liquid proof of stake (LPoS) consensus algorithm, which is primarily focused on decentralization. Its initial algorithm — Emmy — had issues with bakers not including all endorsers or withholding their endorsement to produce a more profitable block.
To address this problem and improve the way the consensus algorithm works, the Tezos team introduced a series of changes via protocol upgrades:
- The Babylon protocol introduced several improvements to this algorithm, regrouped under the name Emmy+. These improvements included changed rewards and validation formulas.
- The Granada protocol added a new set of changes to the consensus algorithm called Emmy*, which was an updated version of Emmy+. It increased the number of endorsement slots from 32 to 256, adjusted reward formulas, and changed block delay logic.
- The Ithaca protocol introduced Tenderbake, which is now the current algorithm version promising to provide deterministic finality.
The Tenderbake algorithm modifies block creation logic that is now done in rounds, with each round consisting of three phases: block proposal, pre-endorsement, and endorsement.
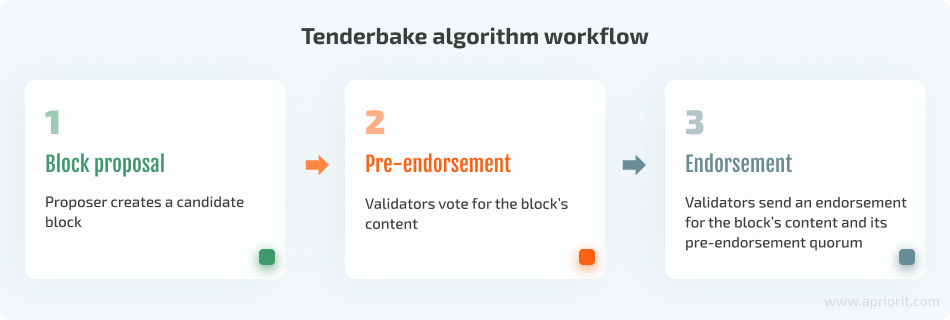
In short, when implementing the Tenderbake algorithm, the Tezos team managed to:
- Reduce the roll size to 6,000 tez, making it easier to become a validator
- Introduce consensus algorithm updates that aim to create a fair set of rules with a focus on security, decentralization, and productivity
- Enforce requirements on block creators that help ensure stability of the blockchain network and dApps built upon it
Why do these changes matter?
The consensus mechanism is what a blockchain platform relies on. Therefore, it affects all solutions built upon this platform. By knowing all details about how the Tezos consensus algorithm works and changes, you can evaluate how well your solution will operate and how to adjust the development process accordingly.
The story of continuous algorithm improvements shows us that the Tezos team strives for constant optimization, which is definitely a competitive advantage of this platform.
Related project
Developing a Decentralized Asset Market on the Tezos Blockchain
Discover how Apriorit blockchain experts created and tested multiple smart contracts to help our client choose the right vector for the future Tezos-based product.
2. Block size and block time improvements
In the initial Tezos version, a new block was produced every minute with a size limit of 4,000,000 gas, where gas refers to the cost necessary to perform a transaction on the network. This size limit severely restricted the number of operations that a smart contract can perform.
Here’s how Tezos improved the speed of handling operations over time by optimizing both block size limits and block time:
- Increased the block size to 8,000,000 gas via the Athens protocol and ensured a further increase to 10,400,000 gas via the Carthage protocol.
- Reduced the delay in block production to 30 seconds via the Granada protocol and then optimized it to 15 seconds via the Mumbai protocol. These changes accelerated the transaction processing speed, but the gas limit per minute remained the same.
- Ensured continuous optimization of instructions, allowing the Tezos team to reduce the gas cost and greatly increased the number of operations included in a block.
Why do these changes matter?
Block time measures how much time it takes for validators within a network to verify transactions within one block and produce a new block in that blockchain. If it’s important for your application to quickly add information to the blockchain, the shorter the block time is and the less the delay time is, the better. The optimized block size helps your developers ensure a larger number of processed operations and minimize delays.
3. Smart contract features
Smart contracts execute themselves automatically once predefined conditions are met, which significantly simplifies and accelerates processes for parties involved in the contract. Thanks to such wide application capabilities, smart contracts are probably one of the most widespread blockchain use cases.
The more helpful features for smart contract development a platform provides, the more opportunities your project has. To ensure those opportunities, Tezos introduced improvements such as various optimizations that reduce the gas cost. Let’s explore the most significant changes made over the years:
- The Babylon protocol introduced support for entry points and provided the ability to store multiple big maps, which made it simpler and faster for developers to create complex smart contracts.
- The Edo protocol integrated the Sapling protocol into the Michelson language, enabling support for shielded transactions that encrypt its content. This also provided the ability to authenticate data with respect to a Tezos address and add new instructions, including new KECCAK and SHA3 hash functions.
- The Hangzhou protocol changed the communication between smart contracts, which previously was done using a callback passing values to the calling contract. The problem with this approach was that the context in which the transaction originated could be lost, creating possibilities to exploit the contract’s logic. Hangzhou introduced on-chain views to mitigate this problem, allowing the external call to be executed at the exact moment it is present in the code and return a value to the current execution context.
- The Kathmandu protocol added the ability to emit events, allowing for the creation of off-chain logic via event listeners by subscribing to selected contract events instead of manually polling every transaction.
Why do these changes matter?
Knowing what opportunities a blockchain platform provides helps your team develop even more efficient smart contracts and expand the number of scenarios for them. Apriorit specialists create different smart contracts to help our clients achieve various goals such as enhancing application licensing, minting and selling NFTs, and powering a decentralized asset market, to name a few. From our experience, we know that high-quality smart contracts should be thoroughly planned, carefully developed, and tested. And the more features a blockchain platform like Tezos provides for these activities, the faster developers can deliver quality smart contracts for your project.
4. Security improvements
The Tezos team introduced numerous security improvements, both minor and significant, over the years via protocol updates. Let’s outline the three most significant changes related to cybersecurity:
- Modified the reward formula in the Carthage protocol to eliminate scenarios when bakers could have more profit with slower block production
- Added a partial stake deposit freeze in the Ithaca protocol to prevent over-delegation and double signing
- Improved randomness in the Kathmandu protocol to make sure that the random seed value can’t be computed before a specific timestamp selected by consensus participants
Why do these changes matter?
Such security updates focus on preventing an intentional slowdown in block creation, which guarantees that block speed will show promised values for all Tezos projects. These changes also improve decentralization of the Tezos network and help minimize fraud-related risks.
Updates in this category aim to ensure smooth blockchain work. Yet, there were no severe security issues detected in Tezos, except for the possibility (that existed earlier) for validators to work unfairly and slow down the network. Therefore, teams that started developing their products on Tezos a while ago might have noticed that the network used to be a little slower before the Carthage protocol.
Read also
Tezos Token Standards: Practical Examples of Implementing FA1.2 and FA2 Tokens
Manage your assets in blockchain! Learn everything about Tezos tokens, their types and standards to attribute value and manage ownership in the blockchain environment effectively.

What’s next? Upcoming Tezos updates
At the time of writing, the next protocol, Oxford, is being tested, promising to bring helpful new features and exciting capabilities.
The four most important improvements the upcoming Oxford protocol will introduce are:

1. A new staking mechanism will provide the ability to stake funds instead of liquid delegation. These funds will be frozen, and it will take several cycles to enroll for staking or unstaking to prevent misbehavior. Staked funds will be subject to both reward accrual and the possibility of slashing in case of rule violations.
2. Adaptive issuance is a feature aimed at dynamically adjusting the issuance of tez in response to inflation. It will adjust the regular issuance at the end of each blockchain cycle to encourage participants to engage in staking.
3. Re-enabled cryptographic timelocks. This update will re-enable cryptographic timelocks after addressing pre-existing security concerns. It allows developers to submit encrypted timelock values sensitive to the order of included operations, preventing maximal extracted value attacks.
4. Improved smart rollups as Layer 2 is promised to allow for running an application written in any programming language that can be compiled to WebAssembly (Wasm), including Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)-compatible smart contracts. Tezos Layer 2 blockchains will greatly increase the network’s capabilities, providing a wide variety of tools.
To sum up, the Oxford protocol will bring valuable improvements to Tezos and offer even more opportunities for blockchain teams who decide to build their products on this platform. From our point of view, the improved smart rollups as Layer 2 is the most exciting news, as this change will significantly simplify the importing of smart contracts from other networks if it’s possible to compile these smart contracts in Wasm.
Moreover, in 2023, Google Cloud partnered with the Tezos Foundation with an aim to enhance Web3 application development and services for Google Cloud customers by providing enhanced infrastructure and helpful tools. Thus, it will be easier for institutions to join the Tezos ecosystem and for developers to build on the Tezos blockchain. So more opportunities and features are yet to come.
Conclusion
Tezos is a popular choice for different projects and industries. You can leverage this platform’s offerings whether your projects involve building an NFT marketplace, developing DeFi products, or creating smart contracts for any purpose. Thanks to the continuous evolution of the Tezos blockchain, this platform can offer a vast range of tools to create various dApps, providing great performance at a low cost.
Thanks to regular updates and upgrades, Tezos keeps improving its services, attracting more and more developers to build projects on the platform. This relatively mature blockchain platform has not had any major security incidents.
However, developers need to keep an eye on every change to both get the most out of Tezos and be aware of what issues to expect. At Apriorit, we have experienced specialists who keep up with all changes and know how to leverage Tezos capabilities to the fullest. Our specialists are ready to help with both blockchain development and security audits for your project.
Looking for secure and decentralized solutions for your industry?
Partner with Aprioirt to build a reliable blockchain system that will set you apart from the competition and enhance your operations!



