Cloud services provide lots of advantages: they’re cheaper, easier, and faster to use than building your own network from scratch. For example, Amazon Web Services provides cloud computing tools and resources for storing data, creating databases, communicating with customers, managing identities and access, and more.
Cloud services provide lots of advantages for your business: they’re cheaper, easier, and faster to deploy than building your own network from scratch. However, responsibility for data protection is usually divided between you and your cloud vendor. To keep your data fully secure, you need to thoroughly audit your cloud infrastructure and all of its components on a regular basis.
In this article, we explore the key points you should consider when conducting an AWS infrastructure security audit of the top Amazon Web Services products. We also share Apriorit’s insights on dividing the security responsibility for cloud infrastructure with your cloud services provider. In the end, you will learn how to audit AWS infrastructure security, what tools to pay attention to, and how to share responsibility for security with your cloud provider.
Contents:
Root causes of security risks in the cloud
More and more organizations are leveraging the public cloud by placing their data and infrastructure on remote servers. The public cloud offers many benefits, including improved efficiency, agility, and quick integration of new technologies. However, concerns arise regarding the security and accessibility of data stored in someone else’s data center.
By recognizing the potential risks associated with cloud solutions, you can proactively protect your cloud infrastructure. Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to security risks in cloud environments is very important for protecting your valuable data as well. Instead of focusing only on data breaches, it’s important to explore all potential vulnerabilities of your system. This includes analyzing the root causes of a hypothetical security risk and identifying weak spots in your cloud solution.
There are a few ways of analyzing the causes of security risks. For example, your team can use a framework like the MITRE matrix, which is designed to prevent, detect, and remediate a cyber intrusion. MITRE breaks down security risks into 11 stages and provides you with ways of strengthening weak spots.
You can also navigate the most critical cybersecurity risks based on recent statistics and apply this knowledge to improve the security of your cloud infrastructure. Here at Apriorit, we navigate The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) Top 10, which is a well-known index of web app security vulnerabilities. This list is formed by a team of security experts from all around the world.
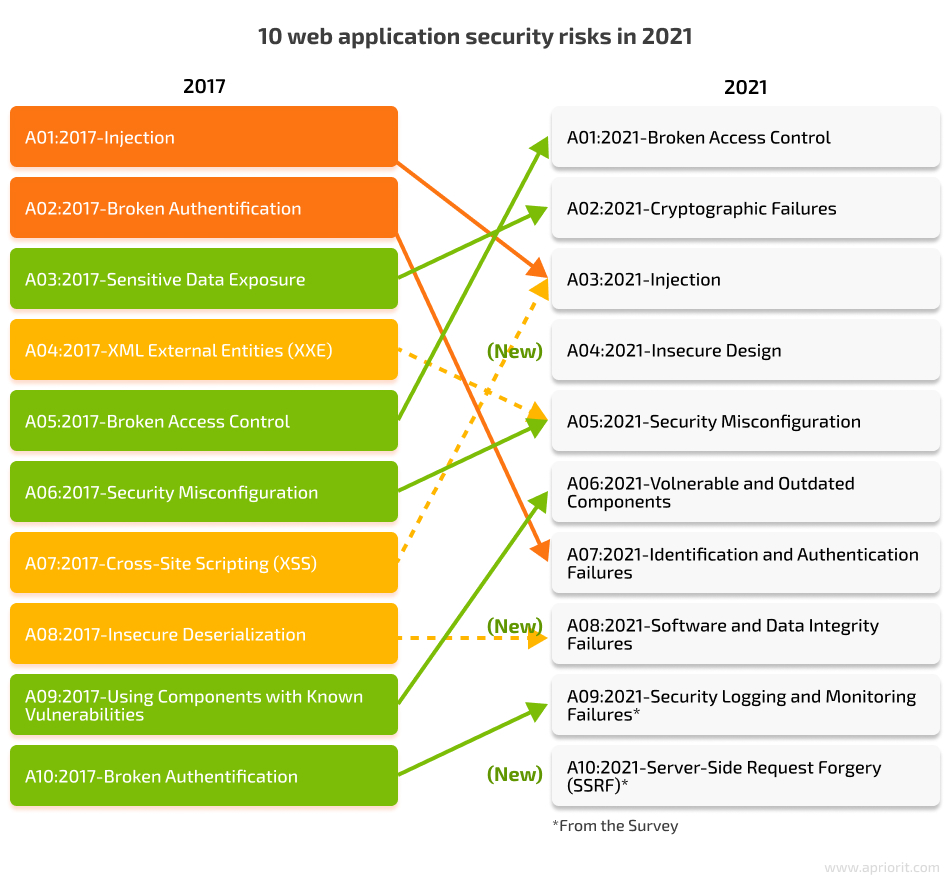
The 2021 edition of the Top 10 shows that the most critical web application security risks are mostly the same as in previous years. However, some new trends are worth noting. The application security risk landscape in 2021 saw several new risks in addition to the previous most critical:
- Insecure design
- Software and data integrity failures
- Server-side request forgery
These changes underscore the continuous evolution of security threats and the necessity for dynamic security measures. Taking into account the nature of these cybersecurity problems, it isn’t surprising that most data breaches are accidental and not the result of a deliberate, targeted attack.
Let’s take a look at the fundamentals of cloud infrastructure security based on the example of Amazon Web Services. To reduce data security risks in your cloud infrastructure, it’s necessary to understand your role in the AWS cloud security audit process.
Want to fortify your AWS infrastructure?
Let’s discuss how our software architects can safeguard your cloud environment.
Overview of AWS cloud infrastructure security
To choose a cloud service for your business, you need to know about types of cloud services, security implications, and the level of control you will have. Knowing this will allow you to make an informed decision about which type of cloud service is most suitable for your needs in terms of services and security. Currently, there are several types of cloud solutions you can use: software as a service, platform as a service, and infrastructure as a service. The main difference between them in terms of security is the number of parameters you have to manage by yourself.
Unlike on-premises software, with cloud services, you can outsource data storage, servers, networking, and security to a cloud services provider.
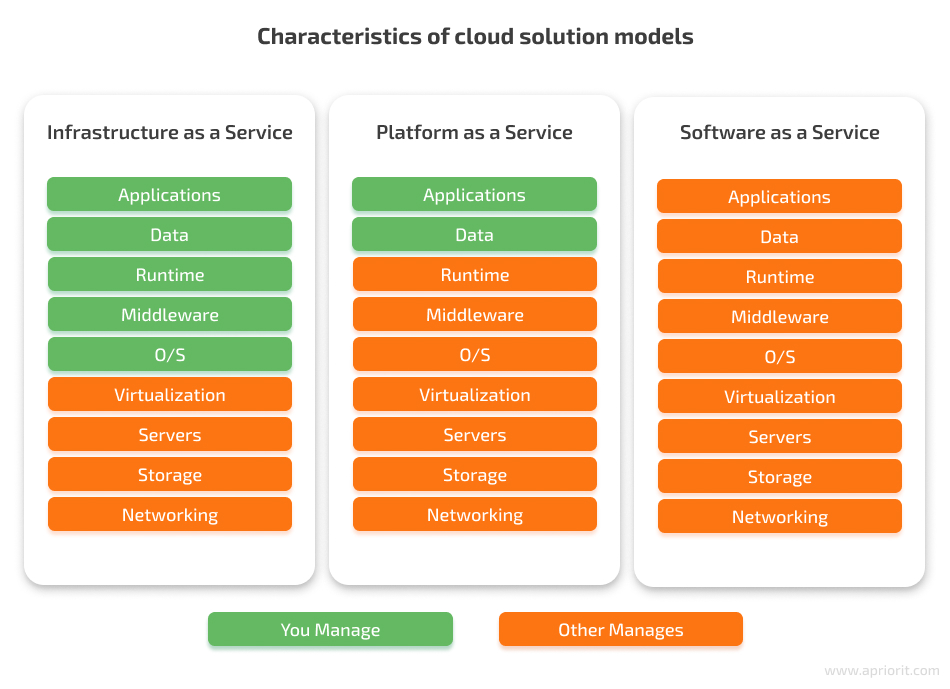
If you’re looking for good configurability and want to create server virtual machines (VMs) from scratch, it will be better to choose an IaaS solution. This cloud service model provides optimal duty separation between client and vendor. In IaaS, you’re responsible for the operating system and applications installed on the virtual machine, stored data, runtimes, and middleware. The service provider is responsible only for the infrastructure, which includes servers, storage, networking, and virtualization.Amazon Web Services (AWS) is one of the best IaaS platforms that provides a variety of tools in five domains: application services, computing and networking, databases, deployment, and management. AWS offers cloud computing tools and resources for storing data, creating databases, communicating with customers, managing identities and access, and more.
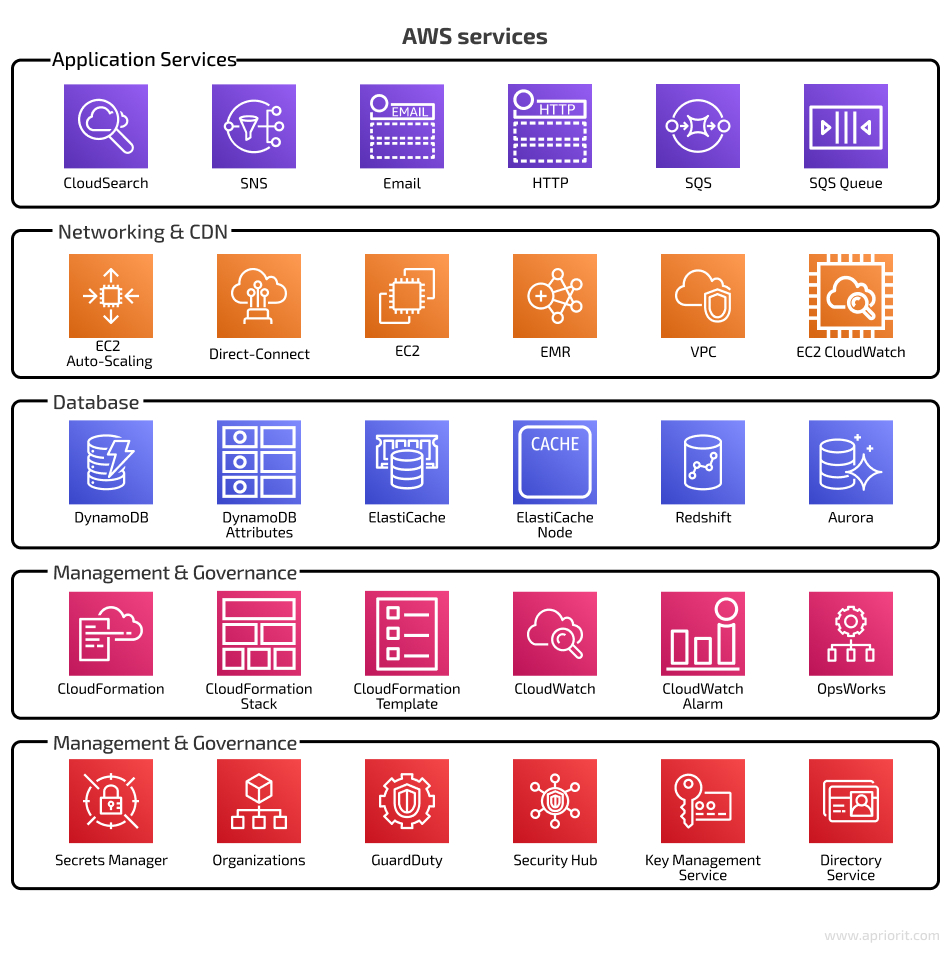
Using cloud infrastructure for your product, and AWS in particular, comes with some security concerns. If you use AWS products, you’re responsible for the AWS security configuration of your server virtual machine, the services on it, and your own app, which includes running AWS application security audits. When it comes to compliance, AWS institutes a shared responsibility model for data security. According to this model, AWS is only responsible for the security of the cloud platform itself; you, as the customer, are responsible for the security of whatever you have in the AWS cloud. Let’s see who audits AWS infrastructure security.
| Area of responsibility | AWS | Customer |
| Infrastructure security | Secure global infrastructure, including data centers, physical security, and network security. | Utilize AWS infrastructure services in a secure manner, following best practices. |
| Compute | Secure the underlying compute infrastructure (Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda). | Manage the security of the operating system, applications, and data running on compute instances. |
| Storage | Secure the underlying storage infrastructure (Amazon S3, Amazon EBS, Amazon RDS). | Configure access controls and encrypt data stored in AWS storage services. |
| Database | Maintain the security of managed database services (Amazon RDS, Amazon DynamoDB). | Manage access controls, data encryption, and data backups for databases. |
| Networking | Secure the underlying network infrastructure (Amazon VPC, AWS Direct Connect). | Configure network security, including VPCs, subnets, security groups, and NACLs. |
| Application-level security | Provide tools and services to help customers secure their applications (AWS WAF). | Implement application-level security measures, such as input validation and secure coding practices. |
| Data encryption | Offer data encryption services and tools (AWS KMS, AWS CloudHSM). | Use encryption features provided by AWS services and manage encryption keys. |
| Identity and access management | Provide IAM services and tools to manage user access and permissions (AWS IAM, AWS Organizations). | Implement and manage user access, roles, and policies according to the principle of least privilege. |
| Operating system and network configuration | N/A (AWS does not manage customer operating systems or network configurations.) | Maintain security for operating systems and network configurations (patch management, hardening). |
| Data classification and compliance | Provide tools to help customers meet their compliance requirements (AWS Artifact, AWS Config). | Classify data and ensure compliance with relevant regulations, laws, and standards (GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS). |
| Incident response and monitoring | Provide monitoring and logging services (Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail). | Provide monitoring and logging services (Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail). |
After checking the security of your cloud infrastructure, it’s time to focus on assessing the security of AWS products to perform a complete audit. The problem is that poorly configured security settings and controls inside your cloud environment can leave open doors for attackers. Let’s see what you need to check in your most frequently used AWS services.
Read also
What Is Serverless Computing: Architecture, Challenges, and Benefits
Discover how serverless computing can revolutionize your business operations, driving efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.

Auditing the security of top AWS products
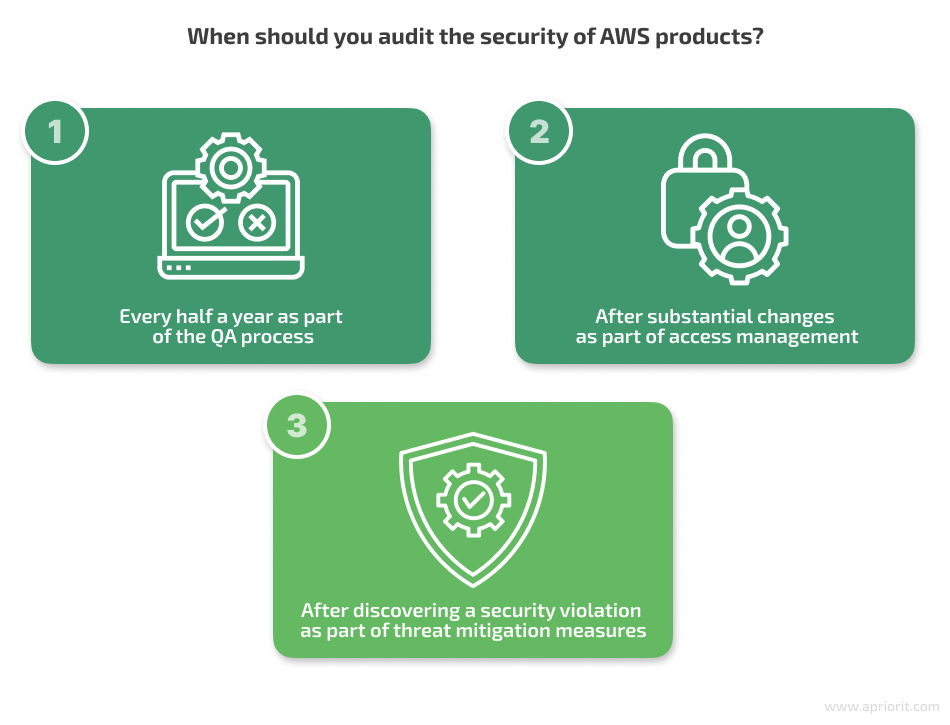
An AWS cloud infrastructure security audit should be a routine task by your security team to guarantee the safety and integrity of your cloud environment. A regular security audit will help you identify and address potential vulnerabilities in AWS cloud infrastructure as well as mitigate risks before they are exploited. Our Apriorit experts recommend performing such an audit in the following three cases:
There are many tools for auditing the security of AWS products. Some of them are developed by Amazon, and others are custom-made. Here are the most popular:
- AWS Config
- AWS CloudTrail
- AWS Inspector
- AWS Trusted Advisor
- AWS Security Hub
As you can see, most of these tools provide some sort of security measures, audits, or evaluations of AWS resources. You can use Amazon’s AWS Security Audit Guidelines as a basic internal security audit checklist. However, to achieve a high security posture, you need to regularly conduct more in-depth checks. We recommend running an audit of these tools as well to see how they function and whether they are configured correctly.
Here is a list of the most frequently used AWS services that should be audited regularly. You can use it as an AWS infrastructure security audit checklist:
Read also
Internal Security Audit Checklist for Increasing Product Quality
Discover how our comprehensive internal security audit checklist can enhance your product quality, and ensure the robust security measures to gain customer trust!
Identity and Access Management Service
The AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) service is created to govern users, user groups, and permissions to access AWS resources. We recommend using the credentials report feature in IAM for listing all users and the status of their passwords, access keys, and MFA devices.
Here is what you need to do during an IAM security audit:
- Disable active keys for the AWS root user account.
- Avoid using the root account for day-to-day tasks and create separate accounts with appropriate permissions.
- Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) for the root account.
- Implement MFA for each user who has access to the AWS Console.
- Configure service users — for example, for continuous integration and continuous deployment — to have only programmatic access without any unnecessary privileges.
- Make sure that all users have only one active access key.
- Regularly change access keys, preferably every 180 days or less.
- Remove any unused security groups.
- Strengthen password policies for each user with access to the AWS Console.
Elastic Compute Cloud
The AWS Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) service is used for provisioning and managing virtual machines. EC2 provides access to Amazon’s proven computing environment and allows for fast scaling and configuration of VMs. The main recommendation for AWS EC2 auditing is to make sure that all powered instances are really needed. Don’t forget to stop instances that were created for testing or development purposes.
Key points to pay attention to during an EC2 security audit:
- Make sure there are no default security groups in use.
- Regularly review and remove any unused security groups.
- Make sure only allowed ports are open to everyone.
- Provide a clear description for each opened port/port range.
- Keep a record of whitelisted IPs with a description.
Simple Storage Service
The simplest description of the Simple Storage Service (S3) bucket is that it’s a cloud folder. S3 is a storage service that supplies you with a variety of settings: region exceptions, versioning, access logging, encryption, and access permission configuration.
Key points to pay attention to during an S3 bucket security audit:
- Enable permissions to list, get, put, delete, and manage data only for specific users.
- Enable bucket versioning.
- Open bucket access logging.
- Configure granted permissions for a specific user, not for everyone.
Virtual Private Cloud
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is an isolated part of the network infrastructure where you can deploy AWS resources. You can fully configure the IP address line, subnets, route tables, and network gateways for each network segment. This service is great for separating different environments. For example, you can isolate the production environment from the staging and test environments.
Key points to pay attention to during a Private Cloud security audit:
- Make sure that the network access control lists (ACLs) are configured according to your framework type.
- Remove any unused network ACLs.
- Enable flow logs for all subnets in use.
CloudTrail
CloudTrail is a service to help you manage AWS accounts and run operational, risk, and compliance audits. It logs, monitors, and saves all account activity within the AWS infrastructure, such as actions performed in AWS SDKs, command-line tools, and the AWS Management Console. This service data is helpful for conducting an audit, as it allows you to analyze any event within the cloud environment. When configured correctly, CloudTrail simplifies security analysis, resource change tracking, and troubleshooting.
Key points to pay attention to during a CloudTrail security audit:
- CloudTrail should be turned on and configured correctly, not by default.
- Enable global services logging.
- Allow write access to S3 buckets with logs only for the CloudTrail service.
Simple Notification Service
Simple Notification Service (SNS) is a solution for sending messages to a large number of subscriber endpoints via SMS, push notifications, and email. This service will be helpful if, for instance, you have a mobile travel app with an AWS backend on AWS Lambda and you need to send push notifications to all users about a new deal.
Key points to pay attention to during an SNS security audit:
- Make sure that permissions to Add, DeleteTopic, Publish, Receive, Remove, SetTopicAttributes, and Subscribe aren’t granted to all entities and identities.
- A separate IAM user with programmatic access should be used only for working with the SNS service.
Related project
Building AWS-based Blockchain Infrastructure for International Banking
Explore how Apriorit transformed international banking operations by building a cutting-edge AWS blockchain infrastructure that made our client’s product more secure, scalable, and efficient!

Relational Database Service
The Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS) makes it easy to set up, use, and scale a relational database in the cloud. It manages database administration processes and provides resizable capacity for an industry-standard database. RDS is used for allocating resources, creating backups, updating software, and monitoring and scaling hardware resources.
Key points to pay attention to during an RDS security audit:
- Enable data backups.
- Set the backup retention period to more than seven days.
- Utilize a multi-availability zone deployment.
- Make sure that your instance storage is encrypted.
- The security group should allow access only to specified IP addresses.
- Database snapshots should not be publicly accessible.
There’s no default possibility to encrypt an existing database, but you can encrypt a copy of the original database instance.
Amazon Inspector
Amazon Inspector is an automated security assessment service that helps you identify vulnerabilities and deviations from best practices in your AWS resources. It evaluates your applications and infrastructure for potential issues and provides recommendations to improve your security posture.
Key points to pay attention to during an Amazon Inspector security audit:
- Ensure you select the correct rules packages for each assessment target.
- Apply overrides where they are necessary and appropriate.
- Regularly review and validate all permissions granted to IAM roles.
Conclusion
A security audit for cloud infrastructure is an important activity that cannot be neglected by your team. Thus, a cloud computing security audit should become a regular task in your QA routine. Apart from following the security measures and using the tools provided by Amazon, you also need to check the configuration of AWS tools during infrastructure security audits.
There is a set of specific features that should be taken into account when auditing Amazon Web Services products. You might need an experienced testing team for infrastructure security auditing in cloud computing. Here at Apriorit, our security experts will assist you in discovering and fixing vulnerabilities in your systems.
Looking for a dedicated team of cloud experts?
Leverage Apriorit’s expertise to optimize performance and drive business growth with confidence!




