Adopting artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare can help doctors and patients improve the level of care, perfect diagnoses, and assist in medical research. At the same time, building a quality product and implementing AI in it can be challenging. Though the healthcare industry is actively adopting innovative AI technologies, developing AI-powered healthcare solutions requires specific skills, resources, and knowledge of the peculiarities of such software and systems.
Even though researchers and developers are still collecting data and figuring out regulations for using artificial intelligence in healthcare, the technology is here to stay. In this article, we explore the benefits of artificial intelligence in healthcare, how current software can improve the healthcare industry, and the risks and challenges of AI adoption. We also discuss what steps you need to take to build a successful medical AI solution.
This article will be useful for business executives, entrepreneurs, and decision-makers in the healthcare software development sector who are looking for ways to upgrade their products.
Contents:
What is artificial intelligence in healthcare?
Artificial intelligence in healthcare refers to the use of advanced algorithms and data analysis techniques to assist medical professionals, improve patient care, and streamline administrative tasks. At its core, AI in the healthcare industry involves systems that can process massive amounts of medical data — such as patient records, diagnostic images, and research findings — to provide insights that aid in diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient management.
AI adoption in healthcare is driven by the need to solve critical challenges unique to the industry. As a response to heavy workloads, an overwhelming amount of patient data, and demand for faster and more accurate diagnoses, healthcare professionals increasingly rely on artificial intelligence. AI applications are designed to:
- Automate time-consuming tasks, reducing doctors’ administrative loads
- Quickly process and analyze vast amounts of patient data
- Provide decision support for more precise diagnostics and treatment plans
These solutions make daily operations more efficient and patient-centered. Alongside ongoing advancements in machine learning algorithms, data processing power, affordable hardware, and 5G technology, AI applications are now more accessible and practical for the healthcare industry. AI is helping organizations better manage data, improve the accuracy of diagnoses, and support personalized patient care.
The AI healthcare market is projected to reach $188 billion by 2030. Widespread AI adoption is poised to cause a leap in medical technology and change how healthcare providers and institutions approach patient care. It will also most likely result in massive changes in how medical providers, hospitals, and healthcare software development companies operate.
Let’s take a closer look at the specific benefits that AI offers to healthcare solutions and how it is transforming the industry.
Need to enhance your healthcare solution?
Take advantage of AI algorithms and models to improve your services and attract new customers. Let expert Apriorit developers take care of all the technical tasks.
Benefits of AI in healthcare
The application of AI in healthcare is expected to accelerate further in the coming years. This is how the healthcare industry improves itself — by embracing innovative technologies. Artificial intelligence takes a special place among innovations that can revolutionize healthcare, as it can bring significant improvements in various areas.
Here is what AI implementation can do for the healthcare industry:
- Improve data management
- Automate routine tasks
- Reduce healthcare costs
- Improve accessibility
- Prevent fraud
- Support health equity
It’s apparent that AI technologies can be of great help to both medical professionals and patients. Let’s explore some examples of how AI can ensure such benefits.
Use cases of AI in healthcare
Today, you can use AI to optimize processes in healthcare facilities, helping doctors automate routine tasks and improve testing accuracy. By streamlining these tasks, AI allows medical staff to focus more on patient care, significantly enhancing the patient experience. So, how does AI contribute to healthcare? With AI-powered software, your healthcare team can:
- Increase the speed of diagnosis
- Improve patient engagement
- Help patients manage chronic diseases
- Boost overall patient comfort
To fully understand the role of AI in healthcare, let’s take a look at some of the key areas where AI can shine alongside doctors and researchers.
1. Provide actionable insights from unstructured data. Healthcare organizations accumulate tons of data every day — too much to be processed and analyzed by a human. AI in healthcare projects can help medical specialists analyze and interpret vast amounts of data, such as doctors’ notes, research papers, and patient records.
Watson for Oncology from IBM processes large amounts of medical literature and suggests personalized treatment options for cancer patients. Merative is a health data management tool that organizes and assesses large volumes of health-related data to provide some structure to doctors.
2. Assist in making medical decisions. This is one of the biggest benefits of AI in healthcare, as it helps medical professionals make quality evidence-based decisions by presenting relevant data and treatment options. Doctors can use it to choose a more fitting procedure or examination, prescribe a better drug, etc. At Apriorit, we’ve recently developed a complex AI-powered system that can detect and measure follicles in ultrasound videos with as high as 90% precision and a recall rate of 97%.
Google’s DeepMind has developed AI models that predict the likelihood of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients, allowing doctors to intervene before the disease progresses. Hippocratic AI looks through symptoms and suggests a second opinion on a patient’s diagnosis or possible treatment.
3. Personalize patient care and assistance. Applying generative AI in healthcare allows for the development of AI-powered medical wearables, medical AI chatbots, and telemedicine applications that increase the personalization of patient care. AI systems can also analyze patients’ health data, behaviors, and preferences to offer more personalized health recommendations.
For example, Ada Health’s AI chatbot and the AI-powered eMed chatbot assess symptoms and offer advice on potential health issues, helping patients understand their conditions and decide on appropriate next steps. Twill Health offers digital-led care and AI-driven recommendations for tailored treatment plans and interventions.
Related project
Leveraging NLP in Medicine with Custom Model for Scientific Reports Analysis
Explore how our AI-powered NLP integration enabled a medical research client to extract critical information from clinical text, accelerating their scientific research process. This software allows their analysts to concentrate on more complex tasks and improve diagnosis accuracy.

4. Improve the accuracy of diagnoses. While AI systems aren’t going to replace medical professionals completely, they can outperform clinicians at specific tasks. In most cases, artificial intelligence is used for identifying patterns and anomalies in decimal images: for example, in detecting skin and breast cancer, brain tumors, and tuberculosis. Apriorit’s AI engineers have explored the possibilities of creating and training deep learning networks capable of performing complex tasks like classifying skin cancer lesions.
For example, Viz.ai uses AI to detect signs of a stroke in CT scans. PathAI assists pathologists in analyzing tissue samples and helps to produce more accurate diagnoses.
5. Enable predictive analytics for early intervention. Insights detected with the help of AI systems enable medical professionals to not only make more accurate diagnoses but to predict potential health issues a particular patient may encounter in the future. By analyzing vital signs and medical data, AI can also help predict patient deterioration.
For instance, the FDA-approved LumineticsCore software uses AI to analyze retinal images and diagnose diabetic retinopathy, enabling early intervention to prevent vision loss. Verily, an application created by Google, can forecast eye disease, diabetes, and some genetic diseases. Regard analyzes patient data and identifies areas for potential health issues and timely interventions.
6. Assist in surgery and patient care. In patient care, AI-powered exoskeleton robots can assist caretakers working with people who are paralyzed or have limited mobility. In complex surgeries, dedicated AI systems can help doctors ensure the absolute accuracy of the tiniest movements, reducing the risk of extensive blood loss and complications.
The da Vinci Surgical System enables minimally invasive surgery while reducing patient trauma and recovery time. VirtuSense focuses on fall prevention with the help of AI-enabled sensors and tracking of movement patterns.
7. Speed up clinical research and drug development. Developing new drugs and treatments is a long, multi-stage process. The common reason for that is the inability of medical professionals to ensure timely matching of patients with clinical trials. AI has the potential to significantly speed up this process. AI also reduces the costs of clinical trials and streamlines drug development.
Deep 6 AI extracts and analyzes patient EHR records to choose the most fitting participants for a particular trial. Freenome uses AI for cancer detection by analyzing blood samples for early signs of cancer-related biomarkers and cancer research.
8. Prevent human error. Every year, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) receives many reports on potential medication errors. Making the wrong diagnosis, choosing the wrong drug, or miscalculating the dosage may all have devastating effects on people’s lives. AI technologies can identify inconsistencies in treatment plans and prescriptions, reducing the risk of human errors that might harm patients.
For example, the HealtheIntent system from Cerner detects mistakes in medication orders and enhances patient safety. Another AI-powered medication safety system, MedEye, assists nurses by verifying the accuracy of both a medication itself and its dosage using machine learning and visual recognition. Medaware can detect if a prescribed drug doesn’t match typical treatment patterns for similar cases and alert the physician of a possible error.
While practitioners have already been actively using AI in the healthcare industry, there are still challenges of AI in healthcare related to its adoption and implementation. In the next section, we go over some of the biggest pitfalls you may face when working on a medical AI project.
Read also
How to Build an EHR System with SaaS: Trends, Challenges, and Prospects
Explore best practices for building SaaS-based EHR systems, emphasizing features and compliance for patient data protection.

Challenges and considerations of implementing AI in healthcare
When developing AI-based solutions, your team might encounter technical challenges as well as non-technical pitfalls, which should be addressed by your research and discovery managers, business analysts, or legal team.
Let’s start with exploring key technical issues of implementing AI in healthcare.
Not enough quality data. Healthcare organizations accumulate lots of data, including health records and images, insurance claims, population information, and clinical trial data. The problem is that this data is often poorly organized and spread across multiple organizations and siloed systems. Finding or generating a relevant dataset that is well-structured and accurately labeled is a challenge.
How to solve it: Look for open-access datasets relevant to your specific task. Start with datasets provided by Medicare, Open Access Series of Imaging Studies (OASIS), or dataset aggregators like Kaggle and Health Catalyst.
Data security concerns. When it comes to patient data privacy, there are two common problems: nonconsensual use of patient data and use of personally identifiable information (PII), such as medical histories, identity data, and payment details. This data is protected by various regulations and rules under the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA). It’s important that patients know who uses their medical records and for what purposes.
How to solve it: Data anonymization techniques can help you ensure there’s no way to link sensitive information used to train an AI system to a particular person based on identifying data such as names, dates of birth, or timestamps on medical records. This is a complex task that requires joint efforts from users (medical staff and patients), developers, designers, and software architects.
Errors and biases in AI. Developers may accidentally implement their cultural prejudices and misconceptions into the algorithms they write. AI systems trained on unbalanced datasets with overrepresented gender, age, or racial groups can provide biased outcomes when faced with data on patients from groups who are underrepresented in the training dataset.
How to solve it: Make sure to use well-balanced datasets filled with diverse data and cross-check the algorithms your AI system relies on. Also, run regular audits and tests of your AI system to ensure timely detection and eliminate possible biases.
Now, let’s talk about some of the key non-technical issues of solving tasks with the help of AI in healthcare projects.
High implementation costs. AI solutions are cost-intensive to build. An initial MVP version of an app powered by off-the-shelf AI and ML solutions in healthcare can set you back $150K. There are several factors that contribute to such high costs, including complex development, the need for rare talents, the high demand for computing resources, and the acquisition of pre-processed quality data.
How to solve it: You may try looking for ready-to-go AI models, pretrained algorithms, and open-access datasets that can be applied to your project. However, be prepared to spend time improving these solutions and adjusting them to your needs.
Lack of public trust. Even though AI solutions are gaining popularity, the general public is not yet ready to trust their private medical data to these apps. A study by the University of Arizona Health Sciences shows that more than 50% of respondents don’t have full trust in AI-powered medical advice. At the same time, many people have faith in AI if it’s monitored and verified by human experts.
How to solve it: Trust is built over time. Through continuous education and training, both patients and doctors can better understand how AI works and grow to trust it. You need to be transparent about how you plan to use AI. By understanding what your users want, you can provide exactly what they need and increase their trust.
No clear rules. AI technologies are progressing faster than relevant laws and regulations. Even though healthcare is a strictly regulated industry, it lacks clear, unified standards for building an AI- or ML-based medical system. For example, in the US, the FDA sees AI and ML systems as software as a medical device (SaMD). In the UK, there is no clear legislation governing the use of AI in healthcare.
How to solve it: Start with following the requirements of relevant industry- and region-specific laws, regulations, and data security standards, including HIPAA and the GDPR. And watch for changes in local requirements regarding the use of artificial intelligence in the medical field.
Don’t let these challenges stop you from maximizing your use of artificial intelligence in your projects. Let’s explore what you need to consider and how you can prepare before starting an AI healthcare project.
Related project
Building an AI-based Healthcare Solution
Discover how our AI-based system revolutionized ovarian follicle tracking for a US healthcare center, achieving 90% precision and a 97% recall rate. Find out how Apriorit’s work helped our client improve patient care and accelerate fertility treatments.
Where to begin your AI journey
Now you know exactly what pros and cons to expect when integrating AI into a healthcare solution. But what should be your first step on the long journey toward creating a successful and efficient AI-powered healthcare product?
Technologies powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning solutions transform the way healthcare is delivered, enabling beneficial collaboration between humans and technology. However, without proper software and hardware, you can’t harness the power of AI and ML to the fullest. Right now, there is a need to upgrade current systems to make the most of AI. Artificial intelligence systems rely on huge amounts of data to learn, and outdated software might not be able to handle this load.
We can outline three major points that can help you make the right decision and ensure the success of your AI-based medical project:
1. To what extent should you use AI?
While many healthcare projects may benefit from implementing AI, not all of them have to do it to achieve their goals. Sometimes, it’s best to save both time and money by choosing a solution that doesn’t leverage costly AI technologies.
Before making the final decision on updating your product with the help of AI, think about these aspects:
- Average data processing volumes
- Task complexity
- Resource sufficiency
Let’s explore each of these aspects in detail.
Average data processing volumes
The more data your solution has to process on a regular basis, the more benefits you’ll get from enhancing it with AI capabilities. If your project doesn’t involve the daily processing of thousands of files, you’d better look for a non-AI alternative: data analytics tools, cloud-based services, and so on.
Task complexity
AI solutions are excellent at automating repetitive tasks of any kind, from filtering patient data to extracting specific patterns in MRI scans. AI- and ML-based solutions work better for cases that can’t be described with simple rules and require making intelligent decisions. In other cases, you might want to consider simpler, rule-based automation solutions. Sometimes, you can even combine them: delegate a more complex task to AI while solving smaller subtasks with non-AI algorithms and technologies.
Resource sufficiency
Due to the complexity of their development, training, and testing, AI solutions are time- and money-consuming to build. You must have a clear view of the entire project and the scope of work to be done in order to make accurate time and budget estimates. And if your project’s resources are strictly limited, consider looking for ready-to-go AI solutions, such as pre-trained models and ready datasets that can be used in your product.
Related project
Developing and Supporting a CRM System for a Medical Transportation Company
Explore the success story of a medical transportation company that needed to upgrade its CRM system. Apriorit developers helped the customer’s team improve system security, UI, and adaptability, empowering faster customer service and business growth.
2. What resources will you need?
Depending on the task at hand, your AI-based solution can rely on different technologies, technical skills, and data. Your goal is to determine these core sets of data, skills, and technologies long before actual development begins. This is not an easy task, so you can delegate this decision to an expert team who will determine the scope of work for you.
Here’s what you need to pay special attention to:
- Quality and relevance of data for AI model training
- Collaboration with a skilled AI development team
- Collaboration with field experts
Let’s explore each of these aspects in detail.
Quality and relevance of data
The garbage in, garbage out principle works for any AI system and especially for those deployed in the healthcare industry. You need to determine the type and volume of data needed to build, train, and test your AI-based healthcare solution.
A quality dataset must meet several requirements:
- Include only data gathered from reliable sources
- Be properly labeled
- Contain no damaged, poor quality, or duplicated data
- Maintain patient privacy
- Be stored securely
If you have enough resources, you can try composing such a dataset from scratch. In other cases, you may use a ready dataset from a reliable source as a starting point and improve it. In both cases, you can turn to expert data scientists and AI engineers to help you prepare a quality dataset for your project.
Collaboration with a skilled AI development team
It’s best to form your own team out of experts with hands-on experience in building the type of AI solution you need. This team needs to include professionals familiar with the technologies most likely to be at the core of your solution. Let’s take a look at the most commonly used AI technologies in healthcare software.
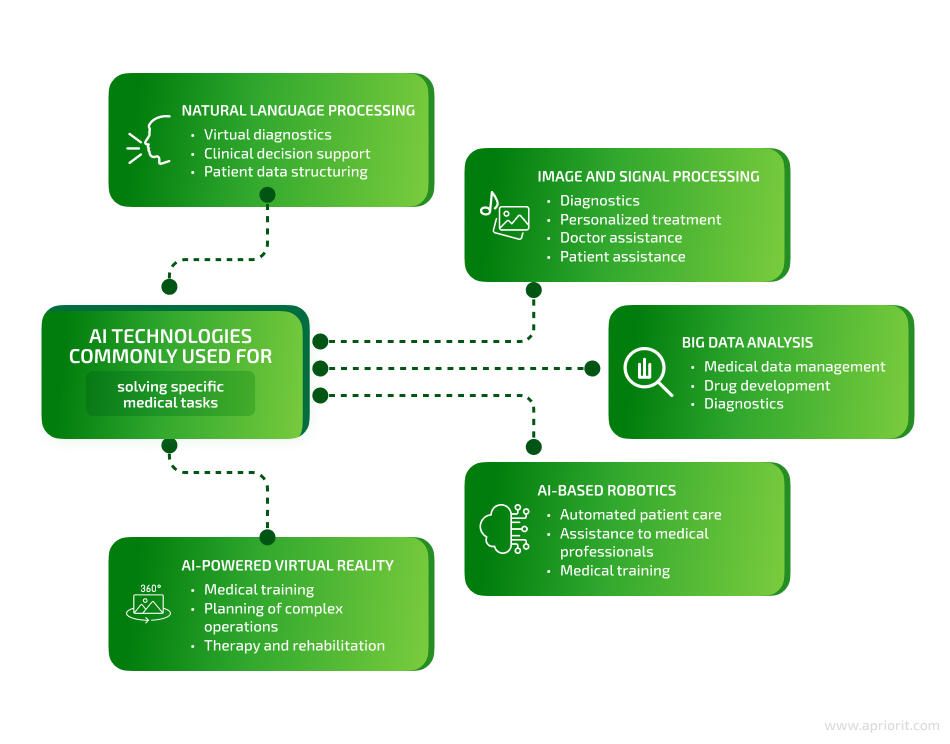
As you can see, aside from developers with AI expertise, you might need to engage specialists from other fields: data engineering, cybersecurity, DevOps, etc.
Collaboration with field experts
Form your team out of both AI and healthcare professionals, or at least make sure to consult with industry experts while working on your medical AI solution. Experienced clinicians can help your development team get a better understanding of industry needs, specifics, and relevant requirements as well as the particular problem your solution is supposed to solve. In some cases, medical professionals might even assist your team with technical tasks like labeling data.
3. What industry standards and requirements do you need to comply with?
Healthcare is a strictly regulated industry. However, there are not a lot of regulations when it comes to artificial intelligence and specifically its use in healthcare. Depending on the geographical reach of your solution, you might need to meet the requirements of both local and international laws, standards, and regulations.
United States
- FDA SaMD Regulations. If your AI solution is classified as Software as a Medical Device (SaMD), it may fall under the FDA’s regulatory purview. Non-compliance with the FDA’s SaMD regulations can lead to significant penalties, including product recalls.
- HIPAA. The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act mandates strict data privacy and security standards for healthcare providers and their business associates. Your AI solution must comply with HIPAA rules to protect patient health information. Failing to meet HIPAA’s data security and privacy rules can result in substantial penalties, with fines ranging from thousands to millions of dollars depending on the severity of the violation.
European Union
- GDPR. The General Data Protection Regulation imposes stringent data privacy and security requirements on organizations processing personal data of EU residents. Your AI solution must adhere to GDPR requirements to safeguard patient data. Non-compliance can lead to fines of up to €20 million or 4% of your company’s global annual revenue, whichever is higher.
- EU AI Act. In addition to the GDPR, the European Union has introduced the AI Act, a regulatory framework specifically designed to govern the development and deployment of artificial intelligence across various sectors, including healthcare. The EU AI Act categorizes AI systems by risk level, imposing stricter requirements on those deemed high-risk, such as medical AI applications. Compliance with the EU AI Act is essential for healthcare providers to ensure their AI systems meet the required safety, transparency, and accountability standards, protecting patient rights and maintaining regulatory approval.
Industry standards
- IEC 62304. This international standard specifies requirements for medical device software, including AI-powered solutions. Adherence to IEC 62304 ensures the safety and performance of your AI system.
- ISO/IEEE 11073. This group of standards provides a framework for communication between medical devices and systems, including AI-powered devices.
- ISO/IEC 27001. This standard outlines information security management best practices, which are essential for protecting sensitive patient data processed by AI systems.
You can ensure compliance with the help of thorough documentation, risk assessments, and constant monitoring of legal requirements. Your AI healthcare project might need to include legal experts and AI specialists who are well-versed in this field and its compliance requirements. Also, you need to regularly review and update your AI system to adapt to the changing legal landscape.
Conclusion
AI technologies have promising potential to improve the quality of healthcare services and automate daily processes for physicians. They also can empower medical professionals to make more accurate diagnoses and save more lives. If you are determined to make AI a part of your medical solution, you will need a skilled team of developers and AI experts who know all the nuances of the healthcare field.
At Apriorit, we have a team of passionate AI engineers with deep expertise in healthcare software development services. They’ll will gladly turn your ambitious ideas into real life-saving solutions. We can provide you with comprehensive AI consulting services, as well as with functionality that will improve the user experience and help you achieve your business goals. And our specialists put an emphasis on cybersecurity, which is a top priority for any healthcare solution.
Leverage the power of AI to enhance your software!
Partner up with Apriorit’s dedicated teams to develop a cutting-edge solution that will disrupt your market.



