The COVID-19 pandemic left us with hundreds of video conferencing solutions. Zoom, FreeConference, Microsoft Teams, and other apps have everything the average user needs — and more. But they aren’t good enough for enterprises, as they can’t securely handle sensitive data, support specific video conferencing equipment, and ensure low-latency communication.
In this article, we discuss how to build a video conferencing app like Zoom that is tailored for a specific industry or client. As a company with experience building various video conferencing solutions, we overview industry-specific requirements, must-have communication features, and cybersecurity implementations.
This article will be useful for leaders of software development companies that are looking into building custom video conferencing solutions and need a high-level overview of product requirements and key technologies, as well as experts in video conferencing app development.
Contents:
Increasing competition in the video conferencing market
The events of 2020 made us move most of our activities online. Whether we wanted to participate in a business meeting, see a doctor, or talk to a friend, we simply needed to launch a video conferencing application. This trend continued even after the COVID-19 pandemic: a lot of companies and employees decided to transition their activities to a remote model on a permanent basis.
Because of high demand, the video conferencing market continues to steadily grow. Precedence Research states that the global video conferencing market was worth US$6.65 billion in 2021 and was projected to be worth US$8.55 billion in 2023 and to reach US$10.67 billion by 2025.
The market is currently saturated with general-purpose software like Zoom and Google Meet. This software is mostly used by individuals and small to midsize companies. Enterprises often lean towards custom video conferencing software because it can provide specific features and capabilities they require: enhanced security, close to zero latency, support for industry-specific devices or software, advanced file storage, etc. In 2021, 86% of overall sales on the video conferencing market were secured by enterprises according to Precedence Research.
To deliver a solution that will be successful in the video conferencing market, consider focusing on industry-specific software tailored for a particular type of business.
Let’s take a look at the key benefits of creating a Zoom-like app and several examples of specific requirements for such applications.
Need a tailored solution to boost your business?
Choose Apriorit for custom application development that adapts to your unique challenges and drives your success.
Why build custom video conferencing software?
Developing custom video conferencing software is challenging, but it’s rewarding. Industries and organizations with non-trivial needs have at least three reasons to consider building a video conferencing app like Zoom:

Many organizations need more specific features from a video conferencing solution than simple video calls and messaging. Here are some specific requirements for such solutions:
| Industry | Use cases | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Finance |
|
|
| Healthcare |
|
|
| Education |
|
|
| Events |
|
|
| Music and cinematography |
|
|
Later in this article, we’ll take a look at features that implement the specific requirements mentioned above. For now, let’s overview some must-have features when creating a video conferencing app.
Core functionality for a video conferencing app
No matter your software’s target audience, you need to ensure your software is comfortable to use, compatible with popular devices and operating systems, and secure.
When making any Zoom-like video conferencing app, make sure to implement such features:

- User profile management. This feature includes user registration; setting up, editing, and deleting user profiles; changing user statuses; etc. The more options users have for managing their accounts, the better.
- Contact list. This list helps users find each other by username, email, company, city, or other search parameters.
- Video and audio call management. Video conferencing software usually supports both one-on-one and multipoint calls up to a certain number of users. Audio and video quality are the key parameters of a call. The software has to allow for scheduling and recording calls, sharing screens, and more. Also, users appreciate when conferencing software allows them to use masks and backgrounds during calls.
- Text messaging. Users need to exchange text messages both during and outside of calls. The software has to allow them to chat with each other, create group chats, and receive push notifications about new messages.
- File sharing. Users need to exchange files to conduct productive meetings. You can implement peer-to-peer file sharing (users store shared files on their computers) or copy shared data to a cloud or private server.
- Dashboards. Dashboards help software administrators analyze statistics on daily video conferencing use, the most common challenges, and possible improvements. You can augment dashboards with artificial intelligence (AI) capabilities to make software analyze data from dashboards and provide predictions automatically.
- Administration. Application administrators and call hosts should have control over call participants. For example, they should be able to mute and unmute participants, remove participants, and stop screen sharing.
- Cross-platform capabilities. To be able to connect users with various devices and operating systems, your video conferencing software should support various platforms like Windows, Linux, macOS, Android, and iOS.
- Convenient and inclusive interface. Video conferencing applications have to be easy to use on various devices for people with different backgrounds and capabilities. Creating user interfaces (UIs) that make your application accessible to everyone requires corresponding design skills and intensive testing.
- Scalability. When designing the software’s architecture and infrastructure, take into account possible needs to scale up or down in order to provide services to new customers without quality disruptions.
When implementing these must-have functionalities, make sure to customize them. Figure out which features your audience values the most and carefully balance the app according to their requirements. Here are several questions you can ask yourself to figure out those requirements:
- What are your audience’s key use cases for video conferencing?
- What sorts of files are your users going to share?
- Do users need specific dashboards?
- Do users require specific messaging capabilities like emojis or custom stickers?
- What’s more important for users: a stable connection, good video quality, or both equally?
- How many users are going to be on the average call?
After you’ve outlined the key features of your software, you can move to your audience’s specific video conferencing requests. In the next section, we’ll overview the eight most common functionalities and ways to implement them.
Read also
Ensuring Proper VoIP Call Quality of Your Audio/Video Conferencing Solution: Tips and Tricks
Learn how to enhance the performance of your audio and video conferencing solution. Our experts share the importance of sound clarity and an overview of available testing methods to help you significantly improve user satisfaction and maintain a competitive edge in the market.

Advanced video conferencing features
Making a video conferencing app with custom functionality is usually a complicated but rewarding process. Here are several examples of features you can implement in industry-specific solutions:
- AI-based video quality improvements. Video production companies use conferencing applications to record content. For example, the BBC recorded the award-winning series Staged via conference calls. Such series usually require bulky professional cameras to shoot. Using an AI-based video conferencing solution that can upscale video quality and broadcast it with low latency allows video production companies and other types of users to achieve professional video quality with minimum spending on equipment.
- Advanced noise suppression. A lot of popular video conferencing applications have noise reduction filters, but they aren’t good enough for professional audio and video recording. Software for such purposes needs noise suppression mechanisms that can cancel surrounding sounds without harming voices and musical instruments.
- Low latency. Latency and freezes in video conferences are generally annoying, but they can be especially disruptive in professional video conferencing. To deliver quality real-time conferencing, you need to develop specific communication protocols, implement streaming frameworks (GStreamer, Apache Storm, etc.), or even create custom drivers to handle audio and video streams.
- Advanced file storage system. Many organizations use video conferencing not only to communicate but to share materials. They need a system that stores data for a long time and allows them to manage and sort that data, configure access to shared files, etc. To work with such organizations, you need cloud-based or server-based software (we’ll describe implementation options later) with robust data storage and management options.
- Feature set for conducting webinars. Organizations that conduct webinars often need a specific set of configurations. Firstly, they need payment functionality to conduct paid webinars. Then, a webinar has to be scheduled, with the ability for participants to subscribe and get a notification. During the webinar, the speaker or administrator needs to be able to manage participants’ privileges, share their screen, create whiteboards, conduct polls, and so on.
- Integration with industry-specific software. There’s a high chance your clients use customer relationship management systems, enterprise resource planning systems, electronic health records management systems, and other industry solutions. They will appreciate the ability to integrate video conferencing into them. For example, a doctor may need to review patient records before a call, or a mortgage broker may have to analyze a client’s financial records before discussing mortgage options.
- Support for devices. Video conferencing software has to support corporate video conferencing hardware and specific user devices: professional cameras, microphones, mixing tables, virtual reality (VR) headsets, etc. Not all of those devices have drivers that allow them to be used for video conferencing. That’s why you have to foresee compatibility issues and implement support for such devices in your software.
- Support for electronic signatures. The ability to review and sign documents while video conferencing is particularly important for financial organizations, law firms, and institutions in the public sector. Electronic signatures are based on the digital signature encryption mechanism, which is considered an alternative to physically signing a document. Implementing this mechanism in your video conferencing software allows users to witness and sign documents and record the signing process as additional proof.
- VR integration. Hosting events in VR is getting more popular because of the pandemic and severe limitations on real-life gatherings. Events organizations stream concerts, festivals, and stage performances in the form of 360-degree real-time video. To do that, they require software capable of processing and streaming large amounts of data that supports PCs, smartphones, and VR headsets and provides high-quality audio and video.
When a client approaches Apriorit with a request to deliver a video conferencing app, one of our top priorities is outlining the set of general and specific features the client needs. This way, we save hours of development time and deliver relevant software to our client within the deadlines. We also ensure the security of user communications.
Let’s review key features to improve the protection of video conferencing software.
Read also
Building an Interactive Voice Response System with Twilio: Platform Overview
Apriorit experts discuss how to create an effective IVR system that meets your business needs. Explore how Twilio, a leading IVR platform, can revolutionize your communication strategies and improve customer interactions.
Features for secure communication
Popular video conferencing applications are widely known for suffering from cybersecurity issues. Zoom is infamous for its numerous security compromises like sharing video records with people outside the call, being unable to turn off the microphone after the call, and Zoom bombing. A vulnerability in Microsoft Teams allows hackers to execute code remotely and gain control over a user’s endpoint.
Because of such incidents, businesses that work with sensitive data look for more reliable communication solutions.
You can ensure strong protection of your software with the following features:
- End-to-end (E2E) encryption. This type of encryption protects data transmitted between two endpoints. The first endpoint encrypts the message and only the second endpoint can decrypt it. E2E is considered one of the most secure types of encryption, as no one in the communication chain (service provider, cloud provider, server, unauthorized intruder) other than the two participating endpoints can read the message. Keep in mind that this type of encryption has its limitations: it’s challenging to implement call recordings, facial recognition, noise reduction, or image improvements with E2E.
- Multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA is an additional access control measure that helps to verify the identity of a user trying to log in to software. MFA can verify a user with three categories of parameters: knowledge (credentials or additional questions), possession (phone or safety token), or heritage (fingerprints or other biometric data). Biometric MFA is the most reliable, but keep in mind that a user needs a fingerprint scanner, high-end microphone, or camera to pass this authentication.
- Smart contracts for data protection. Applying blockchain technology in video conferencing provides lots of security benefits: decentralized data storage, protected data processing and transfer, and user confidentiality. Also, it’s possible to gain extra marketing points for using cutting-edge technology or implementing blockchain-based monetization. However, blockchains have issues with processing vast amounts of data in real time (for example, streaming 4K video or sharing big files), administering corporate communications, scaling, and complying with regulations.
- Protected storage for shared files. Files shared by users are typically stored in the cloud or on-premises data centers. This data can be the target of hacking attempts or malware planted by a disgruntled employee. To secure your application and customers from such threats, make sure that your server runs firewalls, antivirus programs, sandboxes, and other cybersecurity solutions.
- Corporate and private domains. Private domains allow organizations to customize security and operational settings according to their needs. For example, they can allow access to the domain via invitation and create groups of users with configurable access rights.
- Robust privacy policies. Security policies allow software administrators to configure video conferencing software according to the needs of the organization or a particular meeting. For example, admins may need to enable or disable E2E encryption and file sharing, configure general user rights, and manage users that join private domains and groups.
When you’ve figured out the full feature set for your software, it’s time to discuss the way you’ll be implementing it with your development team. Let’s take a look at common ways to create a Zoom-like app along with their pros, cons, and use cases.
Read also
Third-Party API Integrations for Your Software: Benefits, Challenges, and Best Practices
Looking to enrich your application and improve user experience without full-scale development? With expert advice from Apriorit specialists, you’ll learn effective strategies to optimize third-party integrations and streamline development processes.

Four ways of implementing video conferencing applications
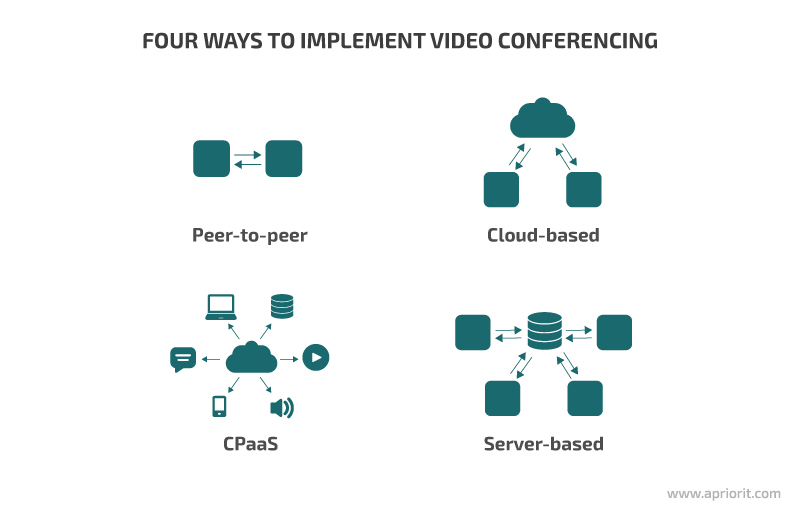
There are four major options for how to make an app like Zoom:
Peer-to-peer software
Peer-to-peer software routes video conferencing traffic between the endpoints of users participating in the communication. There’s no interaction with a server, cloud, or any other third party. Usually, such solutions are based on WebRTC, XMPP protocols, Jitsi, Peer’Em, and other communication software. To build a peer-to-peer solution, you’ll need to design, implement, and support the application itself, its infrastructure, and cybersecurity mechanisms.
Here are the key benefits of building peer-to-peer software:
- Secure communication. Since there’s no intermediary in the communication, it’s harder for a hacker to intercept or listen to traffic. If the communication is protected with E2E encryption, hackers have little to no chance to intercept it.
- High quality of one-on-one calls. User endpoints usually have no challenges in sending and interpreting communication data in direct communication. The only limitations here are the capacity of a user’s webcam and microphone.
When it comes to advanced multipoint communication, peer-to-peer implementation poses the following limitations:
- Unpredictable quality of multipoint calls. Call quality depends on the number of call participants, their bandwidth, and device limitations. For a developer, it’s challenging to manage and improve the quality of multipoint calls.
- Implementation of file sharing and call recording. Implementing these features is challenging since peer-to-peer software doesn’t use servers. Files shared by the user are available until the user renames or deletes them from the endpoint. Recording a call will use additional resources on a user’s endpoint.
- Little control over the conference. In peer-to-peer communications, developers can’t implement algorithms that improve audio and video quality.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Secure communication | Unpredictable quality of multipoint calls |
| High quality of one-on-one calls | Impossible to implement file sharing and call recording |
| Little control over the conference |
Cloud-based software
Cloud-based software uses communications platform as a service (CPaaS) or similar cloud solutions to deploy the server side of the solution and maintain the infrastructure. This type of video conferencing software is the fastest to deploy because the developer only has to create the client side and sign an agreement with a cloud provider. Examples of such providers are AT&T, Bandwidth, Infobip, and Twilio.
Hosting your video conferencing application in the cloud has the following benefits:
- Short time to market. Implementing cloud-based video conferencing apps requires less development effort compared with implementing peer-to-peer and server-based apps.
- Ability to process communication data. Before routing calls to user endpoints, the cloud service processes communication data. That means developers can manage the quality of calls, record them, implement data storage features, and more.
The disadvantages of this type of software are common for any cloud-based applications:
- Dependency on the cloud provider. Changing the cloud provider when you have already deployed and released your application can be challenging and painful.
- Limited scalability. You can’t use more server resources than the provider is able to provide. Also, scaling your software may lead to changes in cloud service pricing.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Secure communication | Unpredictable quality of multipoint calls |
| High quality of one-on-one calls | Impossible to implement file sharing and call recording |
| Little control over the conference |
Communication-Platform-as-a-Service (CPaaS)
Communication-Platform-as-a-Service (CPaaS) is a relatively new type of delivering a video conferencing application. Built on the principles of the Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) model, CPaaS solutions provide customers with APIs to add video conferencing capabilities to their own software.
Key benefits of delivering a CPaaS solution:
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Ability to focus on video conferencing features | Dependence on quality of APIs and SDKs |
| Flexibility of integrations | Dependence on the cloud provider |
| Cost-efficient development | Limited scalability |
- Ability to focus on video conferencing features. Since each customer can integrate a CPaaS solution into their corporate software, there’s no need to develop additional features like support for specific devices, digital signatures, etc. You can focus on delivering flawless and secure video conferencing and save your development efforts.
- Flexibility of integrations. For enterprise IT departments, deploying new software from scratch and reconfiguring infrastructure is always a challenge. Enterprises appreciate the chance to integrate new features instead of deploying entirely new software. Small and midsize companies, on the other hand, like to choose which features they need to integrate and not pay for functionality they don’t need.
- Cost-efficient development. The possibility to focus on developing core video conferencing features and leverage the advantages of cloud hosting greatly reduce spending on development and building hardware infrastructure.
Since CPaaS solutions are deployed in the cloud, they share the downsides of cloud-based video conferencing software. On top of that, they make a CPaaS provider dependent on the quality of APIs and SDKs. It doesn’t matter how good a CPaaS is if customers can’t properly integrate it into their software. You’ll need to spend a lot of time on development and quality assurance for every API and SDK you provide.
Related project
Developing Drivers for Low Latency Virtual Reality Headsets
Explore our success story of creating high-performance drivers that ensure seamless operation of VR devices for our client. Apriorit developers managed tp get the device to operate with 3–10 ms of latency and ~11 Gbps data transmission speed, resulting in a superior user experience.
Server-based software
Server-based software requires a dedicated media server to handle and redirect data streams during a call. This is the best implementation option for a custom video conferencing solution because it provides developers with the following benefits:
- Total control over the software and its data. As the only owner of both the server and client sides of the application, you can implement any features you need, protect your data with necessary cybersecurity mechanisms, add support for any devices, and scale according to your needs.
- High audio and video quality. You can enhance your media server with any video and audio improvement mechanisms discussed above to provide your clients with the best possible quality of communication. Also, you can scale video down according to users’ device capabilities to reduce bandwidth.
Here are the key challenges of creating a server-side application:
- The need for an expert development team. Since you have to implement each feature by yourself, you need a development team that’s up to this task. Based on your needs, the team may need to include AI and blockchain experts, embedded software and driver developers to ensure support for specific devices, cybersecurity engineers to design data protection, etc.
- Full responsibility for the software. In the software-based model, you don’t share the responsibility for the performance or security of your solution with a cloud provider or peer-to-peer communication protocol developers.
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Total control over the software and its data | Need an expert development team |
| High audio and video quality | Full responsibility for the software |
As you can see, each implementation model has major benefits and limitations. The choice between them should be based on your client’s needs, the abilities of the development team, and your project’s budget.
Conclusion
Although the video conferencing market is saturated, there is still room for highly protected and customized video conferencing solutions. That’s why many businesses consider developing software tailored to their industry and customers.
Building an app like Zoom means you need to:
- equip it with a robust set of video conferencing features to ensure a positive user experience
- protect data with cybersecurity mechanisms requested by customers or required for compliance with industry regulations and standards
- add specific features that help your customers work
- choose a suitable implementation model
At Apriorit, we have deep expertise in remote access and management solution development, video delivery, and cybersecurity, allowing us to produce video conferencing software that meets all your needs. Thanks to our experience in low-level driver development, we can also build all drivers and codecs necessary for handling different types of audio and video streams, as well as specific hardware.
Optimize your workflows and stay ahead of the competition
Partner with Apriorit’s skilled team to develop custom applications that meet your end business goals and boost customer experience.




