Key takeaways:
- In their search for answers to issues related to memory, performance, and compliance, automotive development leaders are slowly turning to Rust.
- With this language, developers can avoid many types of bugs and build solutions that are interoperable with C/C++ codebases and compliant with the latest vehicle functional and safety requirements.
- The automotive industry is already experimenting with Rust to build firmware for ECUs and microcontrollers, AUTOSAR integrations, ADAS components, and more.
- A limited ecosystem, lack of standardization, and a deficit of Rust experts are slowing down Rust adoption, but experienced development teams can find a way around these challenges.
Those who use Rust daily swear that it may just be the missing gear for automotive security. But is it?
Traditional programming languages — most notably, C and C++ — have long been the backbone of automotive software. Yet their vulnerability to memory errors and security flaws poses increasing challenges. Enter Rust — a modern language that promises memory safety, concurrency, and performance without compromise.
In this article, we explore how you can benefit from using Rust in automotive development projects, what Rust-based products already exist, and how Rust enables ISO 26262 and ISO/SAE 21434 compliance. We also take a look at Rust’s current limitations.
This article will be useful for technical leaders of automotive development companies, from vehicle manufacturers to Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, who are considering whether they should switch to Rust.
Contents:
- How does Rust improve automotive software development?
- What kinds of automotive solutions are built with Rust?
- How does Rust support automotive compliance?
- 1. Rust and ISO 26262
- 2. Rust and ISO/SAE 21434
- Limitations of Rust in automotive development
- Future of Rust in the automotive industry
- How Apriorit can help build automotive software with Rust
How does Rust improve automotive software development?
With the growing popularity of software-defined vehicles (SDVs), the requirements for automotive software are rapidly evolving and becoming increasingly complex. The cybersecurity, real-time performance, and reliability of automotive components matter now more than ever.
To satisfy legal and regulatory requirements, the majority of automotive software developers choose C/C++ — languages that offer low-level control, high code performance, and efficient resource consumption. They already have massive codebases with reliable, proven C++ code. However, this language also brings memory management challenges and issues with data races. Due to the limitations of embedded automotive software, fixing those issues after release (for example, with OTA updates) is expensive and risky due to recertification requirements and potential zero-day exploits before the patch lands. In these cases, C/C++ issues result in vehicle recalls, unsafe vehicle software, and penalties for non-compliance with automotive software requirements.
That’s why automotive development pioneers are slowly turning to Rust, some even calling it the future of automotive software. According to the 2025 State of Rust report, the number of automotive organizations using Rust increased from 0.3% in 2024 to 5.3% in 2025.
Here’s what automotive developers value in Rust:
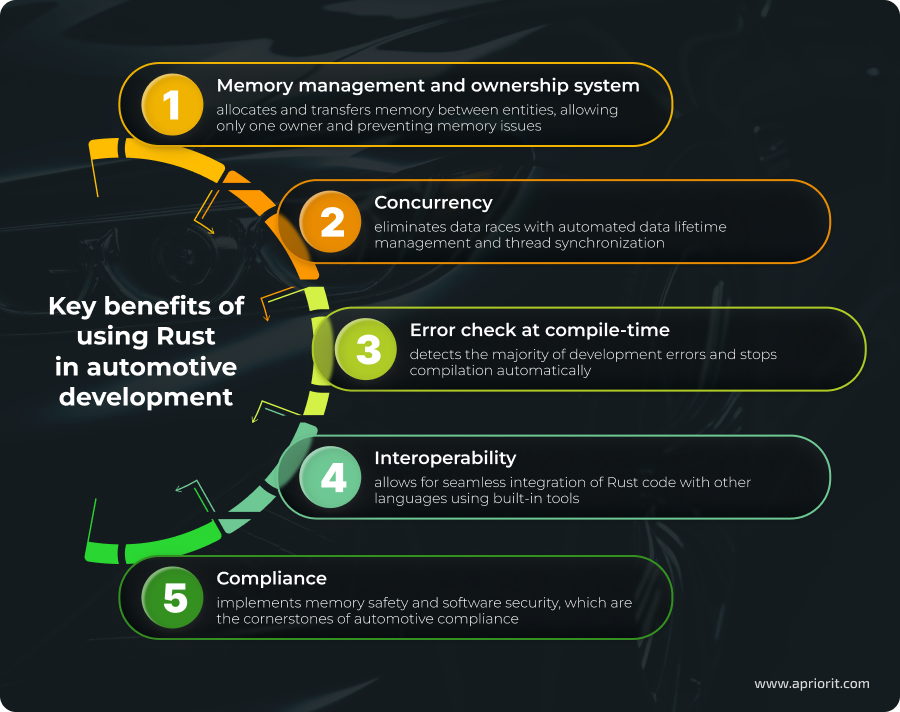
Rust’s key benefit compared to C/C++ that appeals to many automotive developers is unparalleled memory safety. This language automates the management of memory-related processes, prevents data races, reduces the risk of memory leaks, and prevents memory access issues. Rust is also good at preventing other types of errors and potential vulnerabilities by scanning code for errors during compilation.
Thanks to these features, Rust allows developers to build regulation-compliant software for tasks that C/C++ may struggle with. We’ll analyze how Rust supports ISO 26262 and ISO/SAE 21434 compliance later in this article.
Now, let’s assess the current use of Rust in the automotive industry by looking at real-life products powered by this language.
Want to benefit from Rust without the hassle of building an internal team?
Leverage Apriorit’s experience in building solutions for cybersecurity, automotive, and IoT with Rust.
What kinds of automotive solutions are built with Rust?
While we have yet to see a complex automotive solution fully developed with Rust, industry leaders are already experimenting with this language for specific software development tasks.
In most cases, they are using Rust for automotive software that powers SDVs, in which memory safety and real-time performance are critical. Here are a few examples:
Table 1. Rust applications in automotive
| Use case | Benefits of Rust | Companies using it |
|---|---|---|
| Memory-safe ECUs | – Improved memory safety – Lower risk of unpredictable behavior | – Volvo – Renault |
| ADAS elements | – Protection of hardware communications – Collection of vehicle performance data | – ETAS – Porsche |
| AUTOSAR integration | – AUTOSAR implementation with memory safety – Enforcement of industry standardization | – Vector – Elektrobit |
| SDV operating systems | – Efficient use of hardware resources – Improved overall vehicle security | – OxidOS – 42dot – Hyundai |
| Microcontroller firmware | – Compliance with ISO 26262 and other standards | – STMicroelectronics – Infineon |
Memory-safe ECUs
Electronic control units (ECUs) are the backbone of software-defined vehicles. They control a vehicle’s behavior, collect data about the driver and the vehicle’s surroundings, and ensure safe and enjoyable rides. Memory safety is critical for ECUs, and errors like buffer overflows and use-after-free can lead to unpredictable behavior or even safety hazards. That’s why companies that are known for their high safety standards, such as Volvo and Renault, are switching to Rust for ECU embedded software.
Elements of ADAS
Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) unite hundreds of ECUs and sensors into a data processing system designed to help a human drive safely and effortlessly. Some elements of ADAS, like data pipelines and hardware communication, are particularly sensitive to development errors and hacking attempts.
Software providers such as ETAS deliver Rust-based middleware systems to help developers design secure and fast ADAS communications. Automotive manufacturers also use Rust to build custom ADAS elements. For example, Porsche builds their own data collector framework with Rust. This language helps them avoid issues like unauthorized memory access and ensure the consistent use of physical units through data types.
AUTOSAR integration
AUTOSAR standards systematize software architecture for the automotive industry, helping developers seamlessly integrate third-party solutions into their systems. To ensure compliance with AUTOSAR principles, companies tend to use the C-based AUTOSAR Classic Platform.
Rust provides all the tools to bridge Classic and Adaptive AUTOSAR. In 2024, Vector and Elektrobit delivered toolchains for building Rust-based AUTOSAR-compliant software, helping developers integrate Rust code into existing C ecosystems. This way, automotive companies can both benefit from existing industry standardization and improve their product safety with Rust.
SDV operating systems
An operating system is a foundational layer of an SDV that manages hardware resources and enables safe, coordinated work of low-level systems. The operating system abstracts the underlying ECUs, processors, and sensors, allowing developers to deploy, update, and isolate applications efficiently.
Custom Rust-based operating systems like OxidOS and 42dot are entering the market. 42dot’s OS is expected to be a part of Hyundai’s new E/E architecture designed to enhance vehicle security and autonomous driving capabilities.
Apart from market-ready operating systems, automotive developers can rely on the Rust for Linux project to build custom drivers and implement non-safety-critical or mixed-criticality Linux systems. While still experimental, Rust for Linux is already used in several production-ready drivers with consistent security and performance.
Microcontroller firmware
Building high-level elements of an SDV system with Rust (such as the operating system and ADAS components) while low-level firmware is still C-based is like building a castle without a foundation. That’s why manufacturers such as STMicroelectronics and Infineon are starting to add Rust support for their microcontrollers.
Using Rust-native microcontrollers in SDV development helps automotive companies achieve strict compliance with new regulations like ISO 26262. It also saves development time, as there’s no need to build integrations.
These are only some examples of using for Rust in automotive software development. As you can see, developers use this language for diverse use cases, yet all of them pursue the same goal — building secure and compliant solutions.
In the next section, we examine how Rust allows automotive companies to achieve compliance with two common standards — ISO 26262 and ISO/SAE 21434.
Watch webinar
Rust in Cybersecurity: Capabilities and Prospects for System Programming
Join our experts as they discuss how Rust’s design principles help developers build secure, high-performance system software. Learn how Rust reshapes cybersecurity by preventing common vulnerabilities.
How does Rust support automotive compliance?
Automotive software requirements have undergone a significant transformation in recent years to address the growing complexity of connected and autonomous vehicles. These changes recognize that modern vehicles are essentially computers on wheels, requiring ongoing protection against cyber threats throughout their lifecycle.
New standards and regulations enforce mandatory cybersecurity processes and safety mechanisms for over-the-air software updates, vehicle-to-everything communications, data collection, and processing both inside and outside of an SDV. Additionally, since SDVs have started to manage drivers’ and passengers’ personal data, they have to be compliant with GDPR and similar laws and regulations.
The overall regulatory landscape now treats software as a critical component requiring continuous compliance monitoring rather than a one-time certification at production.
In our experience, building automotive software with Rust helps to adjust to that change. This language has every tool needed to adopt secure-by-design development and enforce functional safety at every stage of development.
Lidiia Mandrovna,
VP of Innovation and Technology at Apriorit
Since it’s impossible to review how Rust supports compliance with every automotive software development standard, in this article, we’ll focus on two key standards.
Rust and ISO 26262
ISO 26262 is an international standard that defines functional safety requirements for software-defined vehicles, establishing a comprehensive framework for the automotive development lifecycle from concept through decommissioning. The goal of ISO 26262 is to identify and mitigate random hardware failures and systematic software failures, thus improving vehicle safety.
Using Rust for development helps automotive manufacturers comply with ISO 26262 by:
- Eliminating undefined code behavior like memory safety violations, data races, and use-after-free errors that are characteristic of C/C++
- Supporting deterministic behavior and freedom from interference between software components through strict ownership rules and type boundaries
- Clearly separating safe and unsafe code blocks, allowing focused review efforts on critical sections that interact directly with hardware
- Limiting sources of functional safety failures with strict compile-time checks and lack of null and dangling pointers
- Integrating testing frameworks directly into the language ecosystem, simplifying the verification and validation activities required for ASIL compliance
Rust also has a chain of ISO 26262-compliant development tools that simplify implementation of the standard’s requirements. For example, the Ferrocene toolchain and HighTec compiler have achieved ISO 26262 ASIL D certification, meaning automotive developers can use them to build the most safety-critical environments.
Rust and ISO/SAE 21434
ISO/SAE 21434 is a standard that establishes cybersecurity engineering requirements for road vehicles throughout their lifecycle, addressing the growing threat landscape facing connected and software-defined vehicles. It focuses on protection against intentional exploitation through threat analysis and risk assessment (TARA).
Rust enables ISO/SAE 21434 compliance by:
- Providing audit tools and static analyzers to identify problematic code and third-party packages, facilitating software bill of materials (SBOM) creation and supply-chain risk controls
- Reducing the attack surface by making entire classes of exploits architecturally impossible, fundamentally changing the threat model during TARA activities
- Providing type-safe APIs for cryptographic operations and security-critical code paths, making it difficult to misuse security primitives or accidentally bypass authentication checks
- Supporting secure-by-default coding practices that align with the standard’s requirements for vulnerability prevention and a secure software development lifecycle
Thanks to its unique memory safety features and properties, Rust allows automotive developers to meet the strictest cybersecurity requirements. However, it’s not perfect for automotive — at least, not yet. Let’s see where Rust falls short.
Read also
Auditing the Security of a Connected Vehicle Communication System
Explore how our team reinforced a vehicle communication system by detecting security gaps, validating architecture robustness, and supporting compliance with safety standards.
Limitations of Rust in automotive development
Released in 2015, Rust is a relatively young language compared to the 30-plus-year-old C/C++. It still has many of the growing pains of a new technology, which can slow down development or at least require a lot of low-level expertise to navigate challenges.
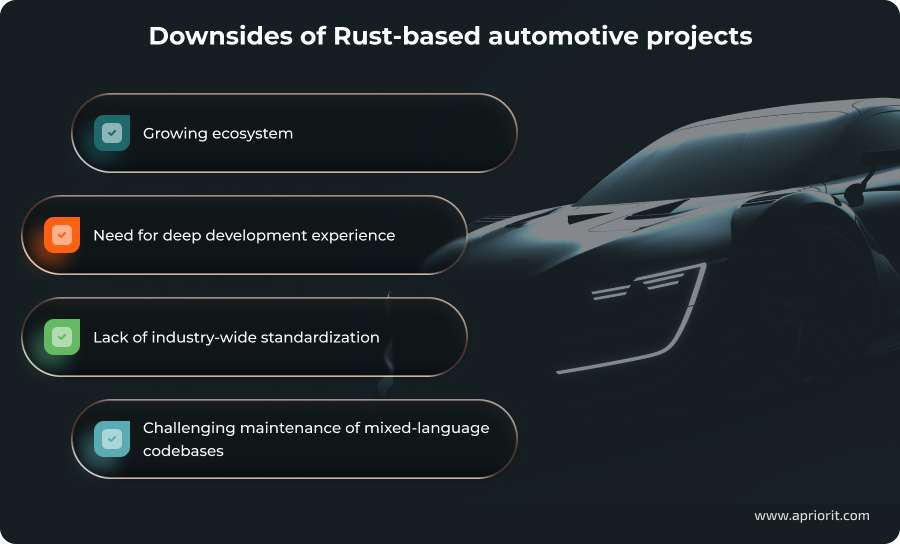
Growing ecosystem. Rust still lacks mature, well-tested tools for some development and testing tasks like metric evaluation, code coverage analysis, and tool qualification. Doing those tasks requires building custom Rust solutions or integrating C/C++ tools into your solution.
Need for deep development experience. As safe as it is, Rust isn’t a silver bullet for cybersecurity issues. It still requires expertise and development attention to catch issues that compilation rules may not detect.
Lack of industry-wide standardization. Compliance-approved automotive tools for Rust are only emerging now. Companies that choose to use this language need to find their own solutions to achieve compliance and high performance.
Challenging maintenance of mixed-language codebases. Rewriting a legacy C project into Rust can be too challenging and expensive. Companies that choose Rust will be forced to maintain both C and Rust expertise. While Rust provides tools for easy interoperability with other languages, it still requires correct and safe implementations, as well as performance optimizations along the way.
In our experience, building with Rust often means solving complex safety challenges at compile time rather than during testing. You’ll encounter unique issues that don’t have community solutions — yet.
However, you’ll end up with a safe and compliant product, which, in our opinion, is worth the trade-off.
Lidiia Mandrovna,
VP of Innovation and Technology at Apriorit
Future of Rust in the automotive industry: Are we there yet?
Rust promises to solve many challenges automotive developers are now facing, and those who have switched to this language swear by it. Does this mean Rust will become a default choice for automotive?
It’s hard to say when the change will happen, but automotive development experts agree on several things:
- Rust will continue to be used in combination with C/C++. The percentage of Rust code in automotive software will slowly increase. However, legacy C/C++ codebases will still exist. Also, companies already have C/C++ development expertise that they’ll continue to use for tasks that don’t require Rust.
- The Rust ecosystem will get richer. One thing that sets Rust apart from other languages is its passionate and tech-savvy community. As they continue building new tools and toolchains, finding the exact solution you need will get easier with time.
- Using Rust will lead to faster certification processes and time to market. Thanks to built-in compile-time checks and testing tools, Rust produces code with fewer bugs and cybersecurity issues. A development team with Rust expertise can use the advantages of this language to build solutions faster and make them compliant with regulatory requirements from the first development stages.
- Rust expertise will remain in high demand. With only 9% of development teams using Rust in 2025, finding skilled and available Rust developers will be a challenge. And the language’s steep learning curve and lack of standardization when it comes to automotive make it hard for companies to quickly build an internal Rust development team.
Although initial coding may take more time, Rust significantly shortens debugging and quality assurance processes, resulting in a faster overall time to market.
As Rust grows and becomes more common, this language will become easier for automotive companies to adopt. But those who want to take advantage of Rust’s memory safety and performance now can skip the tiresome process of growing Rust expertise internally and hire an outsourced software development team.
How Apriorit can help build automotive software with Rust
Building software for automotive isn’t just combining embedded and IoT software with cloud services — and at Apriorit, we understand the unique industry challenges.
Achieving compliance with TISAX, ISO 27001, and ASPICE helps us design, develop, and test secure and performant automotive software. And our Rust development team takes the lead on many automotive projects.
Working with Apriorit, you’ll get:
✅ Unique Rust expertise. Apriorit’s developers have years of experience building solutions with Rust and sharing their knowledge with the community in webinars and articles.
✅ Dedicated engineers with a security-first engineering culture. As a cybersecurity-focused company, we are fans of a secure software development lifecycle (SDLC). This helps us protect our clients’ solutions during the earliest stages of development.
✅ Proven track record of embedded and IoT projects. Feedback from our clients confirms that Apriorit development teams dig deep and solve challenging tasks in embedded and IoT development. We can deliver solutions that other teams are hesitant to approach.
✅ Experience in codebase migration and maintenance. Whether you plan on building new modules with Rust on top of your existing C/C++ software or migrating to a new language completely, Apriorit will help you navigate this process without delays and downsides.
With Apriorit at your side, you can be sure your automotive solution will be secure, performant, and compliant when it hits the market — exactly when and how you need it.
Ready to dip your toes into Rust development?
Let the Apriorit team guide you through Rust adoption and help you benefit from the capabilities of this language.
FAQ
Which major car manufacturers use Rust today?
<p>Several automakers (Toyota, Volkswagen Group, Volvo, Rivian) and suppliers (Bosch and Continental) are actively exploring or piloting Rust as a programming language for automotive software. </p>
<p>Most companies use Rust in R&D, tooling, or early-stage automotive software components rather than full production ECUs, but adoption is steadily growing across the industry.</p>
Can I use Rust alongside existing C/C++ automotive codebases?
Yes. Rust integrates well with C and C++ through FFI, allowing teams to incrementally introduce Rust without rewriting legacy systems.
How does Rust impact development costs and timelines for automotive software?
Rust typically increases time for project preparation and MVP development but reduces downstream costs. Over the entire lifecycle, Rust can shorten development timelines for safety-critical systems thanks to fewer defects and easier long-term maintenance.
How mature are Rust’s tools and libraries for embedded automotive systems?
Rust’s embedded ecosystem isn’t as mature as C/C++, but it’s growing quickly, with strong support for microcontrollers, HALs, and cross-compilation. Some types of tools, such as certified automotive toolchains and AUTOSAR-ready stacks, are still in development.
How does Rust perform compared to C or C++ under real-time constraints?
Rust’s performance is often comparable to C/C++ because it compiles to efficient native code without a garbage collector. In some cases, Rust works even faster than C/C++ code.
How do over-the-air updates benefit from Rust?
Rust improves OTA reliability by reducing memory-related failures and increasing software robustness. Its strong safety guarantees help prevent corrupted updates, undefined behavior, and security vulnerabilities. This results in safer, more predictable OTA rollouts.



