Cloud platforms have changed the way we build and manage IT infrastructure. With services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, teams can scale fast, store massive amounts of data, and create isolated environments for testing and development.
But with these benefits come new risks.
Misconfigured services, outdated credentials, and weak access controls can open the door to serious security threats. Many companies still rely on manual or fragmented scanning processes, which makes it hard to spot vulnerabilities in a timely manner. Add in multi-cloud complexity and compliance requirements and it’s clear that cloud security is a growing challenge.
That’s why at Apriorit we recommend focusing on vulnerability scanning for cloud-first services.
In the text below, we will:
- Walk you through common risk scenarios
- Show how tools like APIs, SDKs, and CLIs can help you detect misconfigurations and quickly respond to incidents
- Demonstrate how to implement a scanning system for AWS access key rotation
- Share additional cloud infrastructure security practices to enhance cloud vulnerability scanning
Whether you’re securing a product platform or managing a multi-cloud setup for corporate needs, this guide will help you improve visibility, reduce risks, and stay compliant.
This article will be helpful for product managers, development leaders, CISOs, and CTOs working on SaaS, PaaS, or cloud-native products who want to secure their solutions from vulnerabilities.
Contents:
- Security challenges in cloud solutions: 5 common scenarios
- How to establish vulnerability scanning for cloud infrastructure
- Practical example: Automated solution for verifying AWS access key rotation
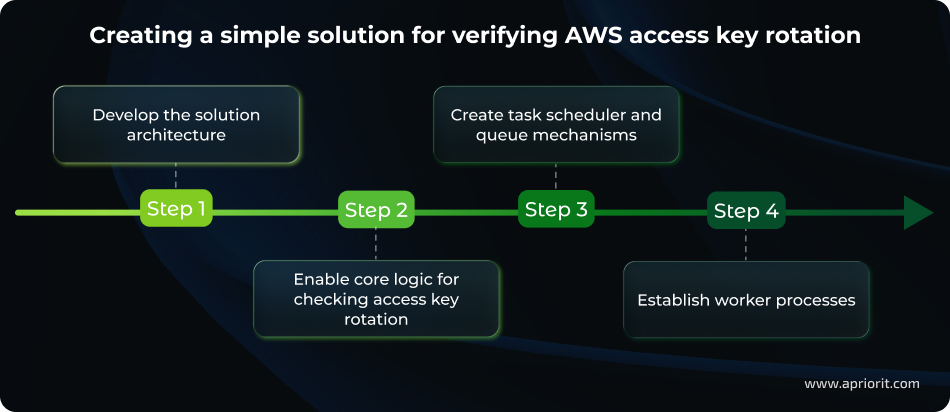
- 1. Develop the solution architecture
- 2. Enable core logic for checking access key rotation
- 3. Create task scheduler and queue mechanisms
- 4. Establish worker processes
- What’s next? Three cloud security practices to complement your vulnerability scanning efforts
- Develop and maintain secure cloud infrastructure with Apriorit’s professional help
- Conclusion
Security challenges in cloud solutions: 5 common scenarios
Most likely, your cloud product provides fine-grained control of access to resources, with individual rules for each user group. This helps you make sure that everyone has the necessary access rights to do their job.
However, such flexibility might lead to severe security issues. Consider the following scenarios:
- An employee leaves the company, but they retain access to systems. An administrator may forget to revoke access keys or remove the employee’s IP address from the allowlist.
- Long-term access keys like IAM keys, tokens, and service account passwords have never been used or remain active for a long time (for example, for more than 90 days). The risks of compromise increase significantly the longer keys exist, especially if there’s no key rotation.
- Attackers leverage the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) to gain account access, using brute force attacks, credential stuffing, or other attack methods.
Let’s take a look at a few of the typical risk scenarios within cloud infrastructure.
Looking to secure your corporate or product cloud environments?
Apriorit cloud and security experts are at your service. Whether you need a consultation, cloud security audit, or development of a custom feature, we’re ready to help.
Scenario 1: Delayed revocation of access rights
Say an employee with AWS access (EC2, RDS, etc.) leaves the company. If their credentials remain active and legitimate, this creates an opportunity for unauthorized access.
Below, we explore what could happen:
- With an automated access revocation workflow
- With a manual access revocation workflow
The problem with a manual workflow is that creating a ticket and manually revoking access can take some time, especially if an admin already has a long checklist of tasks and is completing them in the order they were received. A malicious actor might leverage this time gap to gain unauthorized access.
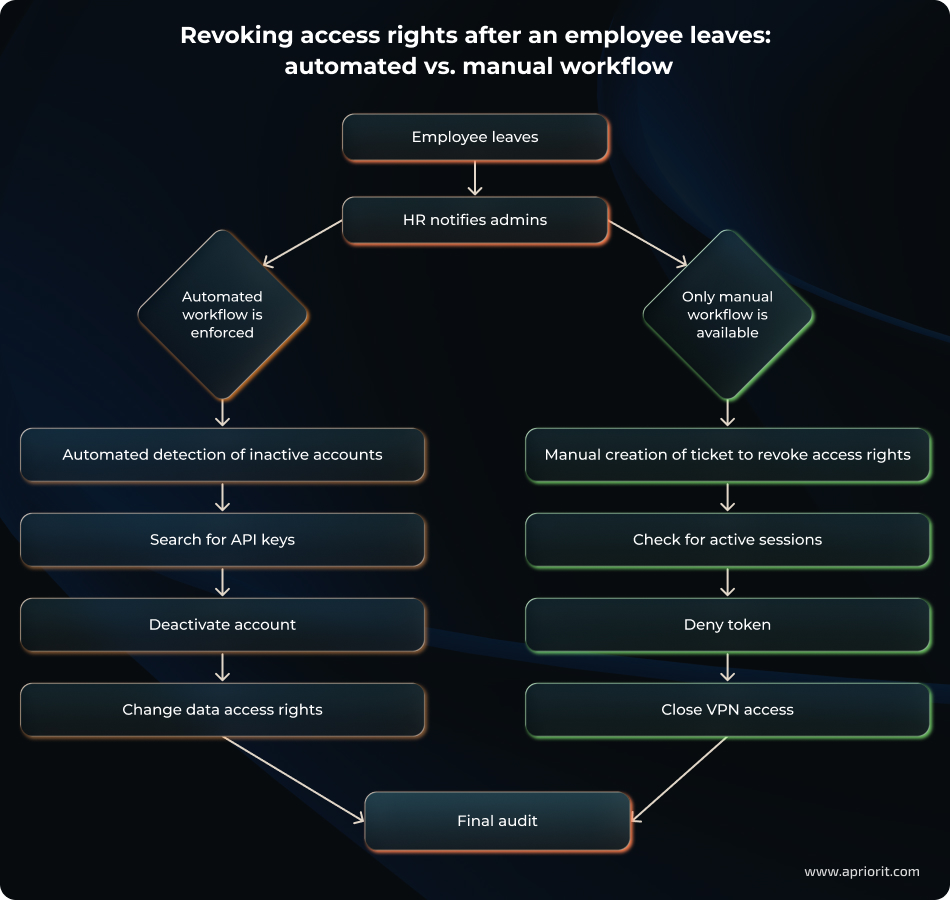
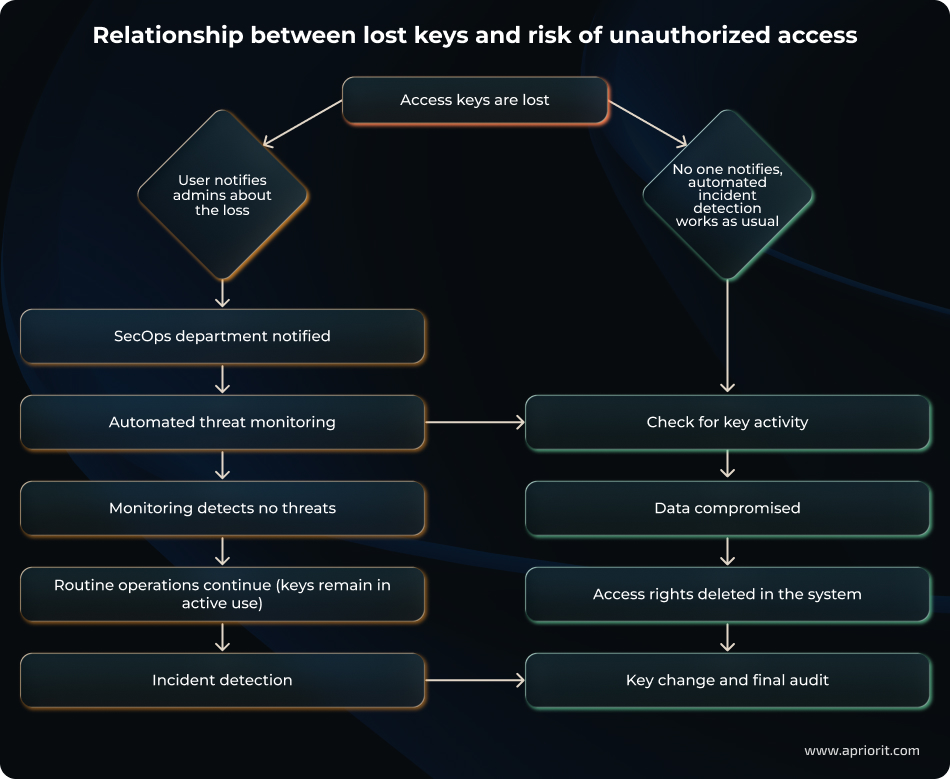
Scenario 2: Compromised access keys
If access keys are lost and no measures such as multi-factor authentication are in place, an attacker can exploit this situation to access data.
Imagine that a user has lost access keys. In this case, we might anticipate two scenarios:
- The user notifies the SecOps team, who launches an autodetection procedure to monitor for threats.
- With no notification from the user, automated incident detection systems work as usual until monitoring mechanics or audits detect an issue. In this scenario, the risk (and consequences of) a potential data breach will increase because of incident detection delays.
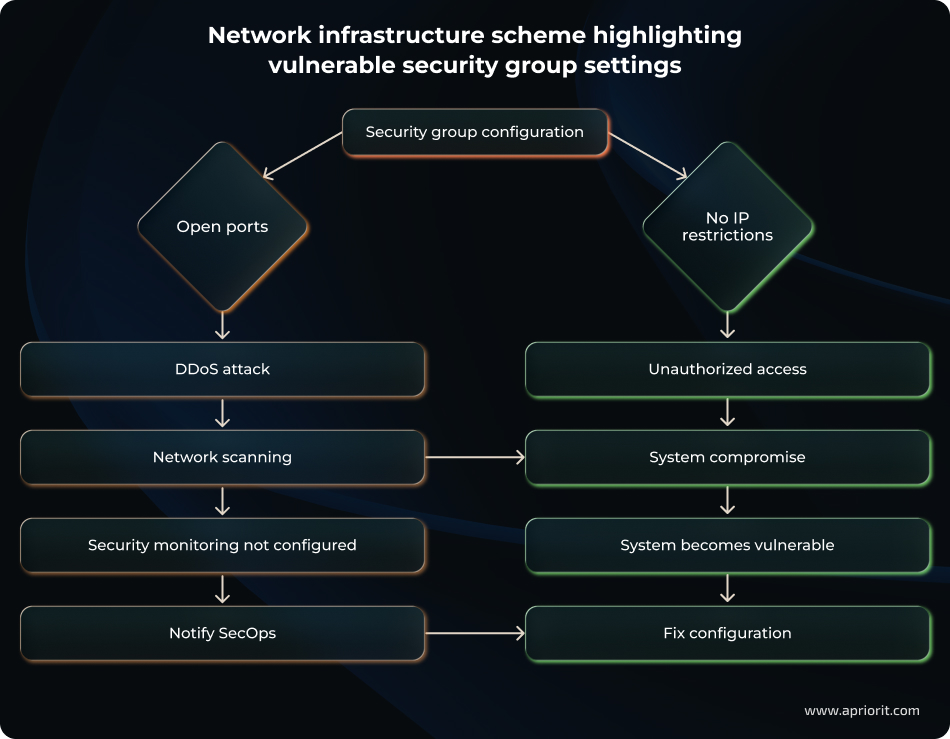
Scenario 3: Misconfigured network policies
Security groups represent another potential vulnerability, especially if they are incorrectly configured.
Let’s explore how a system might be harmed due to security group misconfiguration:
- If ports are open
- If no IP restrictions are enforced
In either scenario, the system becomes vulnerable to potential attacks. Such misconfigurations may allow for DDoS attacks or unauthorized system access.
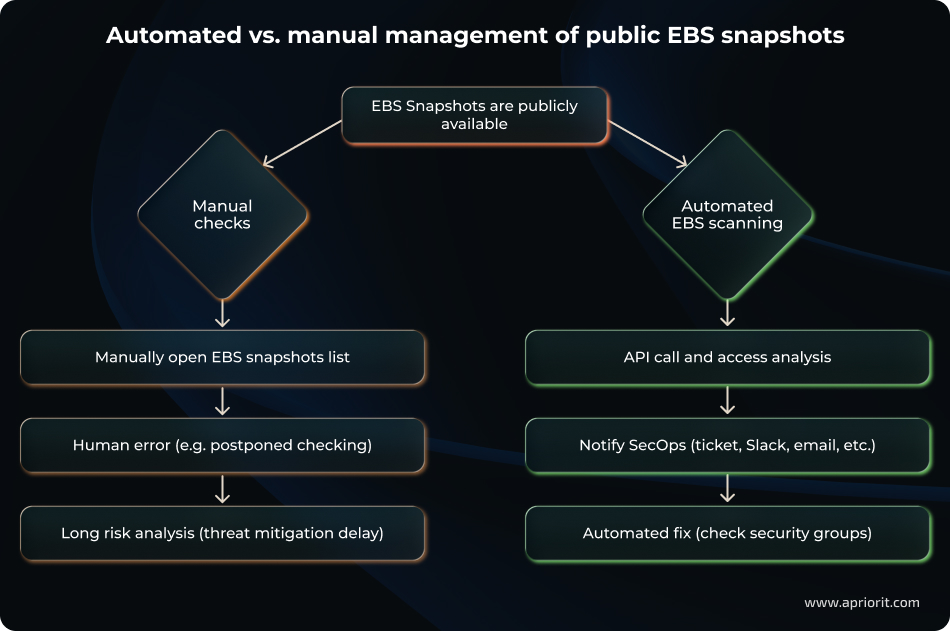
Scenario 4: Publicly available EBS snapshots for EC2
If an Elastic Block Store (EBS) snapshot for an Elastic Compute (EC2) instance is marked as public, its contents become accessible to all AWS users.
A publicly available EBS snapshot may cause a data leak, since attackers can restore data from the snapshot. That’s why snapshots should be either private or deleted.
Below, we show two possible ways of handling EBS snapshots:
- A manual workflow, in which checking security groups can be postponed due to a human error, delaying threat mitigation. In this case, your organization might face a data leak because of a missed vulnerability.
- An automated workflow powered by an EBS scanner, which helps mitigate an incident.
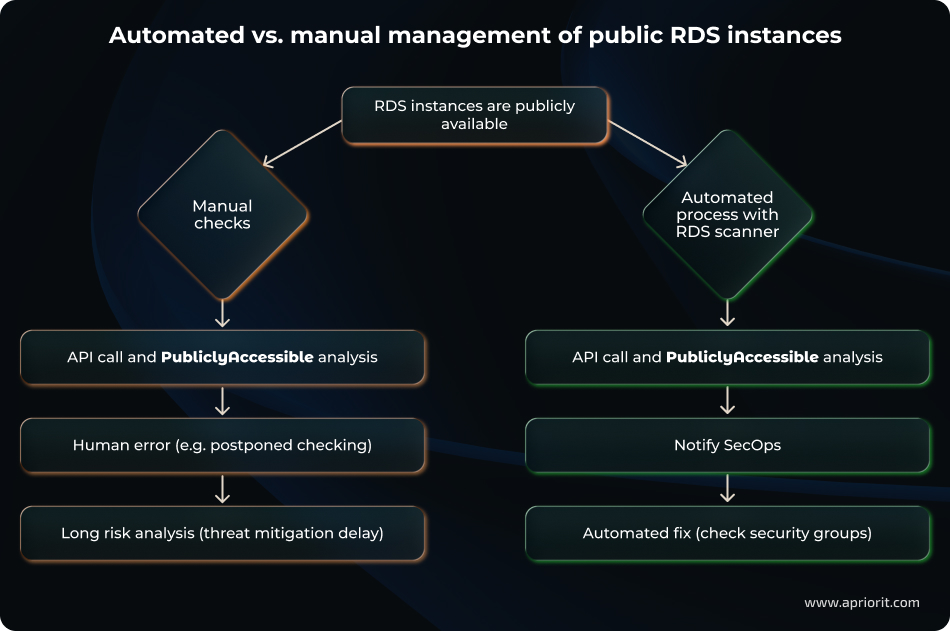
Scenario 5: Public access to RDS instance
If the PubliclyAccessible parameter for a Relational Database Service (RDS) instance is set to true, the database gets a public IP and DNS name. These, in turn, allow for unauthorized users to connect, potentially leading to data compromise.
This is why we recommend deploying RDS in private VPC subnets or restricting access to the security group rules.
Let’s explore two ways of managing the public availability of RDS instances:
- Perform manual checks, which are time-consuming and might lead to postponement of security group checking and delays in threat mitigation.
- Implement an automated process that enables the RDS scanner and helps your team mitigate incidents quickly and efficiently.
The list of risk scenarios could go on and on. However, you can already notice patterns like infrastructure misconfiguration and inefficient (or absent) automation that lead to security issues.
One way to detect and fix vulnerabilities in a timely manner is by introducing vulnerability scanning mechanisms. Let’s discuss why vulnerability scanning is important and how to implement a cloud scanning solution for vulnerability identification.
Read also
How to Effectively Audit AWS Infrastructure Security: Expert Tips for the Top 8 AWS Tools
Discover practical guidance for performing AWS security audits that reveal hidden gaps, validate your architecture’s resilience, and support continuous improvement of your cloud environment.

How to establish vulnerability scanning for cloud infrastructure
Vulnerability scanning for cloud infrastructure is the process of systematically identifying security weaknesses in cloud-based environments, such as misconfigurations, outdated software, and exposed services that attackers could exploit.
By implementing an automated cloud-based vulnerability scanning system, you team can:
- Verify access key rotation
- Check MFA availability for root accounts
- Detect excessive IAM policies
- Expose open or misconfigured security groups
- Flag publicly accessible resources (EBS / S3 / RDS)
- Monitor implementation of services like CloudTrail and GuardDuty
- Check for default encryption
The general workflow for enabling a vulnerability scanning system is the following:
- Plan the solution architecture and set up integration with the cloud provider.
- Define the list of security checks according to your requirements.
- Design the architecture: application server, task queue, notification system, etc.
- Develop and install the system.
- Configure the system’s integration with AWS: create a read-only user, set environment variables for passing access keys, integrate the AWS SDK according to official security recommendations.
- Perform a test run to verify that all modules work correctly.
- Set up logging to monitor errors and successful checks.
- Integrate notifications for quick response and issue resolution.
With key theoretical information in mind, let’s proceed to development. Since a comprehensive vulnerability scanning system is a huge project, for our practical example, we’ve decided to show you how to create a simple solution to automatically verify access key rotation.
Practical example: Automated solution for verifying AWS access key rotation
In this section, we’ll build a simple access key rotation verification mechanism for AWS using Node.js.
Below, we review the key architecture components, verification logic, and task distribution schemes in detail.
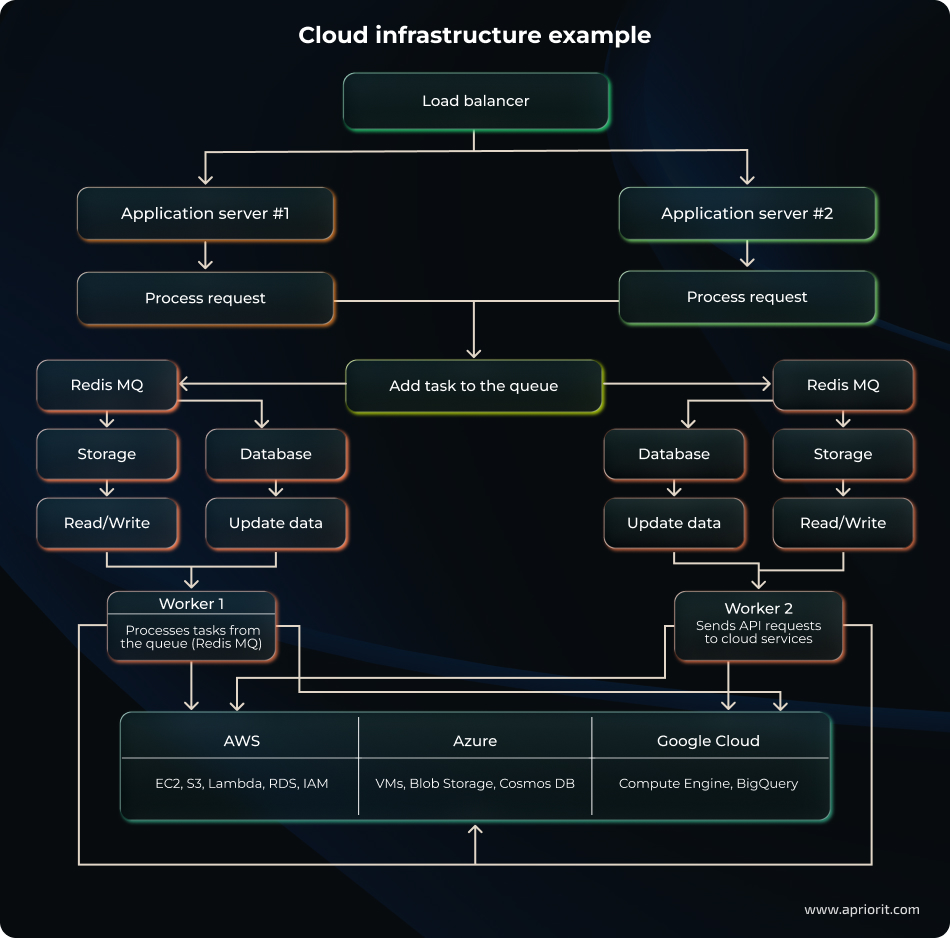
1. Develop the solution architecture
Let’s start with creating a general architectural scheme for the cloud infrastructure. Our architecture includes:
- Application servers that host the scanner logic and interacts with AWS via SDK
- Redis MQ, where tasks for checks are added to a scheduler queue via the cron scheduler
- Workers that process tasks from the queue in parallel, allowing the system to scale without overloading the AWS API
- Cloud services from AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud
2. Enable core logic for checking access key rotation
Now, we have to implement the logic for checking access key rotation.
The essence of the check is to:
- Retrieve a list of users
- Analyze key creation dates
- Identify outdated keys ー in our example, keys older than 90 days
Here’s how to implement an access key rotation check:
const ROTATED_DAYS = 90;
class AWSConfig {
constructor(awsAccessKey, awsSecretKey) {
this.AWS_IAM = null;
this.getIAM(awsAccessKey, awsSecretKey);
}
getUsersList = async () => this.AWS_IAM.listUsers().promise();
getListAccessKeys = async (userName) => {
const params = {
UserName: userName,
};
return this.AWS_IAM.listAccessKeys(params).promise();
};
accessKeysAreRotated = async () => {
const usersList = await this.getUsersList();
const response = await this.checkRotatedAccessKey(usersList);
return this.responseTemplate(response);
};
checkRotatedAccessKey = async (usersList) => {
try {
for (const user of usersList.Users) {
const accessKeysList = await this.getListAccessKeys(user.UserName);
const result = accessKeysList.reduce((accumulator, key) => {
const difDays = Math.ceil(Math.abs(new Date(key.CreateDate) - new Date()) / (1000 * 3600 * 24));
if (difDays > ROTATED_DAYS) return [...accumulator, {
user_name: user.UserName,
access_key: key.AccessKeyId,
}]
return accumulator;
}, [])
return result;
}
} catch (e) {
throw new Error('Fail to get rotated access keys');
}
};
}
module.exports = AWSConfig;3. Create task scheduler and queue mechanisms
Let’s implement a queue mechanism to ensure regular configuration audits.
We’ll use a cron scheduler to make sure tasks for checks are added to the queue.
We can enable task scheduler and queue logic using the following code:
const queueProducer = async (jobData) => {
try {
const { error } = validate(jobData);
if (error) {
Logger.error('Validation error in queueProducer', {
error: error.toString(),
jobData,
});
throw new Error(error.toString());
}
const queue = new Queue(QUEUE_NAME, { connection: CONNECTION_TO_REDIS });
const addedJob = await queue.add(
jobData?.jobName || 'defaultJobName',
jobData,
{
removeOnComplete: true,
removeOnFail: 5000,
}
);4. Establish worker processes
A worker should retrieve tasks from the queue and perform corresponding checks.
We also want our system to handle a large number of check tasks and execute them in parallel across multiple workers without overloading the system or exceeding AWS request limits.
Here’s code showing the essential logic of processing a key rotation check task:
const worker = new Worker(
QUEUE_NAME,
async (job) => {
await jobProcess(job);
},
{
connection: CONNECTION_TO_REDIS,
concurrency: JOBS_COUNT_FOR_ONE_WORKER,
}
);
worker.on('completed', async (job) => {
Logger.info(`Job ${job.id} completed`);
await onFinishedJob(job);
});
worker.on('failed', async (job) => {
Logger.info(`Job ${job.id} failed`);
await onFinishedJob(job);
});
const jobProcess = async (job) => {
const { jobName } = job.data;
try {
Logger.info('Start processing job.', logContext);
If (jobName === ‘AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ROTATED’) {
const aws = new AWSConfig(process.env.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, process.env.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY)
Const result = Await aws.accessKeysAreRotated();
console.log(result) // save it somewhere
}
Logger.info('Job completed successfully.', logContext);
} catch (error) {
Logger.error('JobProcess execution error');
}
};In these four steps, we’ve created a simple solution to automatically verify AWS access key rotation.
Note: Key rotation is just one of many checks necessary to secure a cloud service. To ensure comprehensive, automated cloud scanning for vulnerabilities, your project should include an extensive set of measures including encryption by default, MFA, and IAM policy checks.
Read also
Cloud Application Security Best Practices: Data Safety and IT Compliance Challenges
Strengthen your cloud environment with proven compliance strategies. Explore practical steps to reduce risks and align your infrastructure with key security standards.

What’s next? Three cloud security practices to complement your vulnerability scanning efforts
Even with solid vulnerability scanning systems in place, your cloud infrastructure is not 100% secure.
From Apriorit’s experience, it’s crucial to introduce practices that address different layers of cloud security in parallel to vulnerability scanning. Together, they will create a synergy effect, helping your team quickly detect misconfigurations, compliance violations, and vulnerabilities in cloud environments.

1. Establish a security-first mindset
To secure your cloud infrastructure, you must properly organize your security team and manage their approach to cybersecurity when developing and working with cloud infrastructure.
It is important to:
- Ensure strict adherence to the principle of least privilege so that each user only has access to necessary resources.
- Enforce MFA for all accounts, especially privileged ones.
- Conduct regular audits and monitoring of cloud infrastructure to promptly identify and eliminate vulnerabilities.
- Explore and follow recommendations from proven guidelines by the likes of NIST and CIS, as well as frameworks like the AWS Well-Architected Framework.
2. Automate validation of cloud services
Essential development tools like APIs, CLIs, and SDKs provide features for deep scanning of cloud service configurations without human intervention.
By enabling automated scanning systems, your team can:
- Retrieve up-to-date configuration data for cloud resources
- Compare settings against best practice templates: for example, the AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Generate reports on detected issues for quick remediation
For example, for AWS, your team can use the following tools:
- ListUsers, ListAccessKeys, and GetCredentialReport for identity and access management (IAM)
- DescribeSecurityGroups and DescribeSnapshots to check for open security groups and publicly available EBS snapshots for EC2
- DescribeDBInstances to check RDS instances
- GetPublicAccessBlock, ListBuckets, and GetBucketPolicyStatus to securely work with S3
- Config, Security Hub, Access Analyzer, CloudTrail, and GuardDuty to detect misconfigurations, suspicious behavior, and compliance violations
In our experience, clients who regularly conduct automated audits of their cloud infrastructure report reduced risks of compromised credentials. They also mention benefits like the ability to adjust configurations on the fly and the convenience of scalable checks due to parallel task processing.
Dmytro, Software Developer at Apriorit
3. Integrate CSPM and SSPM solutions
Modern systems like Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) and Service Security Posture Management (SSPM) help your team automatically analyze cloud service settings.
By enabling CSPM and SSPM solutions, your team gets:
- Continuous, real-time monitoring of changes in cloud configurations
- Automated detection of misconfigurations and potential vulnerabilities
- Integration with SIEM systems for centralized incident management
Popular examples of CSPM solutions include:
- Microsoft Defender for Cloud
- AWS Security Hub (+ Config)
- Google Cloud Security Command Center
- Wiz
- Prisma Cloud
Commonly used SSPM solutions include:
- AppOmni
- Adaptive Shield
- Valence or Grip for OAuth and third‑party risks
- Netskope SSPM or Zscaler SSPM if you already use Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
When developing, maintaining, and securing your cloud infrastructure, make sure to choose cloud engineering and cybersecurity professionals (like those at Apriorit) who have relevant expertise and experience.
Related project
Building AWS-based Blockchain Infrastructure for International Banking
Explore how our team delivered a fault-tolerant AWS-based blockchain environment, enabling our client to strengthen transaction reliability and support global banking workflows.

Develop and maintain secure cloud infrastructure with Apriorit’s professional help
Entrust your cloud security to experts who truly care.
With 20+ years of experience in software development and cybersecurity, Apriorit focuses on making each solution we build both efficient and protected.
Whether your project involves AWS, Azure, GCP, or a multi-cloud environment, our engineers will help you achieve your business and cybersecurity goals.
As a vendor with ISO 27001 and ISO 9001 certifications, we understand the importance and complexity of safeguarding digital solutions from various threats. Therefore, we use only proven approaches and tools to establish vulnerability management, cloud compliance, and data protection.
Apriorit teams are ready to help you with tasks of any complexity:
- Assist with cloud infrastructure management to improve visibility, security, and efficiency, helping you run your cloud ecosystem without interruptions or inefficiencies
- Optimize your cloud environments with proven engineering expertise and enhance the performance, data protection, and operational efficiency of your clouds
- Introduce relevant cybersecurity measures to detect misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and compliance gaps
- Adopt efficient DevOps practices to automate workflows, improve system reliability, and reduce errors
- Integrate security at every stage of the SDLC to strengthen cybersecurity posture, prevent vulnerabilities, and maintain compliance throughout the development lifecycle
If efficient cloud vulnerability scanning and threat detection are your priorities, then Apriorit is your partner of choice.
Conclusion
Maintaining reliable cloud infrastructure requires a systematic approach that includes both administrative measures and automated configuration scanning.
In this article, we showed only one possible way to secure your cloud environments ー by verifying access key rotation. Doing so helps you quickly detect deviations from best practices, remediate vulnerabilities in a timely manner, and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
To fully safeguard your cloud infrastructure, your team must use comprehensive approaches and cloud vulnerability scanning tools. For example, CSPM/SSPM solutions can give you real-time data on infrastructure status. Adding APIs, CLIs, and SDKs to the equation helps you perform deep configuration assessments and scale the verification process through parallel task processing.
Protecting cloud infrastructure is a challenging and complex task. That’s why you should consider involving professionals. Apriorit engineers have proven experience in cloud security engineering and auditing, as well as expertise in DevSecOps and secure SDLC implementation. We will not only help you enhance cloud security but also simplify and automate your workflows.
Ready to strengthen the security of your cloud infrastructure?
Apriorit will review existing configurations, integrate automated scanning tools, and build a continuous monitoring process that fits your business.



