Key takeaways:
- The quantum threat is approaching fast. Experts estimate that cryptographically relevant quantum computers could emerge as early as 2027–2030.
- Attackers are harvesting sensitive financial data today to decrypt it later using quantum methods.
- FinTech systems are high-value targets, making early post-quantum preparation essential to protect sensitive data, transactions, and customer trust.
- NIST has already approved the first PQC algorithms, but adopting them isn’t simple. Your software must be crypto-agile and architecturally ready to support these new standards.
Once quantum computers become powerful and widespread enough, they’ll be able to break the algorithms that FinTech companies use to safeguard user data. This will create both cybersecurity and financial risks that can devastate your business.
To prepare for this, FinTech leaders should start adapting their current systems for a fundamental transition to post-quantum cryptography (PQC) — a set of cryptographic algorithms that can withstand quantum attacks.
In this article, we explain what the quantum threat is, what assets are most at risk, and what action you can take today to prepare your FinTech business for the quantum future. This article is for technical and business leaders of FinTech companies who are looking for a clear strategy for a quantum-safe future.
Contents:
The quantum threat: what it is and when it will arrive
What is the threat?
Quantum machines promise to be significantly faster than classical computers in solving complex math problems behind today’s cryptography.
This means that once they are powerful enough and commonly available, quantum computers will be able to break the RSA encryption that protects everything from customer accounts and transaction data to digital signatures and proprietary FinTech algorithms. They’ll also compromise elliptic-curve cryptography (ECC), which is widely used in secure APIs, mobile payments, and blockchain protocols.
As a result, attackers will gain access to:
- Personally identifiable information (PII)
- Bank accounts and transaction histories
- Digital contracts and signatures
- Payment authentication systems
- Confidential trading or risk models
And while you may think there’s still time to get ready, the real threat is already here in the form of Harvest Now, Decrypt Later (HNDL) attacks.
Malicious actors are capturing encrypted data today so they can decrypt it later using quantum technology. If your business handles sensitive financial data that must remain secure for years or decades, this looming threat makes quantum readiness an urgent priority.
When do experts expect Q-Day?
Most organizations agree that quantum computers will be able to break today’s cryptography by 2030. McKinsey’s 2024 Quantum Technology Report suggests that Q-Day will be somewhere between 2027 and 2035.
NIST agrees, stating that classic digital signature cryptography will become obsolete by 2030 and be fully phased out by 2035.
It’s clear that the time for action is now. But what exactly should you do to protect your FinTech business?
Need to protect your FinTech product?
Get expert help from Apriorit and secure your customers’ data with bullet-proof encryption that’s ready for present and future threats.
The remedy: post-quantum cryptography
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is a set of cryptographic algorithms designed to resist quantum computers. Unlike classical encryption, PQC relies on highly complex mathematical problems that even quantum computers should not be able to solve.
PQC is the only way to protect digital systems from quantum threats, and governments around the world have issued timelines for PQC migration. One of the most specific timelines has been presented by the UK’s National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC), which has laid out three critical milestones for the banking and financial sector:
- By 2028 – Complete the discovery phase: identify all systems and services that rely on vulnerable cryptographic algorithms.
- By 2031 – Begin migration of high-priority systems to PQC.
- By 2035 – Complete migration across all systems, services, and products.
Finance is one of the sectors where PQC adoption is the most urgent and important, as financial software products handle extremely sensitive private data and financial transactions every day.
This means that you should adopt and integrate PQC across all systems where long-lived data or sensitive transactions are involved.
The commonly agreed-upon deadline for PQC migration is 2035. And in order to meet it, you need to start preparing now.
What FinTech systems should be protected with PQC?
It’s not necessary to apply PQC everywhere right away. Instead, you can focus on systems and data that need long-term protection or are most vulnerable to quantum threats. For FinTech companies, we recommend starting with:
- Transactions. Payment processing, transfers, and settlements must be encrypted with quantum-safe methods to prevent interception or manipulation.
- Digital identity & authentication. Digital signatures and certificates must be updated to resist quantum attacks that could otherwise allow identity spoofing.
- Blockchain & digital assets. Cryptocurrencies, NFTs, and smart contracts rely on public-key cryptography, which quantum computing could easily break.
- Data storage. Archived transaction records, user data, and compliance logs must be protected against Harvest Now, Decrypt Later attacks.
- Communications. APIs, messaging systems, and internal infrastructure should transition to PQC to ensure confidentiality and integrity.
Aside from choosing what data and systems to secure, it’s important to use the right PQC algorithms to protect them.
What quantum-safe algorithms are available now?
The U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has already approved a core set of PQC algorithms. They include:

- ML-KEM (FIPS 203) — A key encapsulation mechanism based on CRYSTALS-Kyber, designed for efficient quantum-safe encryption. This standard is intended for general encryption, as it’s quite fast and features relatively small encryption keys for easy exchange between parties.
- ML-DSA (FIPS 204) — A digital signature algorithm based on CRYSTALS-Dilithium, offering strong security with practical performance.
- SLH-DSA (FIPS 205) — A stateless hash-based signature algorithm based on SPHINCS+, intended as a cryptographic fallback.
NIST is also evaluating FALCON and HQC for future inclusion, but these algorithms will act as backups to the three main standards. NIST mathematicians urge organizations not to wait for backup algorithms and to start adopting the three available algorithms right now.
While it’s a good idea to start implementation, adopting PQC isn’t as easy as just replacing old algorithms with new ones. In the next section, we explore the hidden complexities of PQC adoption and explain what FinTech organizations need to prepare for.
Read also
Preparing Your Software for Post-Quantum Cryptography: A Practical Guide to Crypto-Agility
Get your organization ready for the quantum future by adopting crypto-agility ー a key strategy for integrating quantum-safe algorithms without major disruptions.

The challenge: what to consider before implementing PQC
Many FinTech organizations are holding off on PQC adoption — and that’s understandable.
With forecasts still placing quantum computing a few years out and headlines often lacking specifics, it’s easy to feel like there’s time. It’s also common to assume that swapping in quantum-resistant algorithms will be as simple as a routine software update.
In reality, the transition is likely to involve complex technical and compliance challenges. But the good news is that these challenges have solutions.
Table 1. Challenges in implementing post-quantum cryptography and their solutions
| Challenge | Main issue | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Algorithm immaturity | Lack of real-life testing may hide some algorithm vulnerabilities | Start with approved algorithms and design crypto-agile systems to support future alternatives |
| Performance tradeoffs | PQC increases resource use and may slow down systems | Optimize architecture, use hybrid cryptography, and match algorithms to use cases |
| Implementation complexity | PQC may be incompatible with legacy systems | Update infrastructure, begin with non-critical systems, and focus on crypto-agility |
| Compliance challenges | Standards and regulations are still evolving | Monitor regulatory updates and ensure cross-team alignment for future compliance |
| High implementation cost | Transitioning to PQC requires major investments | Run pilot projects, adopt cloud or upgradeable infrastructure, and build capacity proactively |
1. Algorithm immaturity
You may ask: Is algorithm immaturity still an issue given that NIST has already approved and standardized three algorithms? This is a good question.
Although the chosen algorithms have been rigorously reviewed, their long-term robustness has yet to be tested. Unlike classical algorithms like RSA or ECC, quantum-resistant algorithms haven’t been field-tested in real conditions, as quantum computers haven’t reached their full potential yet.
Will algorithms like ML-KEM or ML-DSA still protect FinTech systems as quantum computing evolves? PQC is an emerging technology, and it needs more time and tests in real-world conditions to show its true power, as well as its true weaknesses.
NIST also realizes that future advancements in quantum computing may reveal weaknesses in the currently approved algorithms, so they’re developing backup standards like HQC.
The solution
Start preparing your fintech product for post-quantum cryptography right now. They can already provide enough protection to shield your FinTech data from HNDL attacks. In the section below, we provide actionable steps for realistic PQC adoption.
However, to successfully support the change of cryptography, your system has to be flexible and crypto-agile. We’ll talk more about how to implement crypto-agility in your software below.
2. Performance tradeoffs
PQC is naturally more complex than traditional cryptography, with longer keys and more intricate mathematical problems. This results in PQC consuming more computing power, energy, and memory. In short, PQC may make your FinTech system slower.
This means that PQC may not work on your existing hardware, which is especially problematic for embedded systems or IoT devices. The hardware of devices like payment terminals, banking tokens, and ATM machines will likely need to be redesigned to handle complex algorithms.
The solution
To counter the performance issues that come with adopting PQC, your team will have to design an architecture that optimizes memory use and accommodates multiple PQC algorithms. This may come with the need to upgrade your hardware or cloud storage to efficiently run encryption and decryption tasks.
You can also adopt a hybrid approach, using both classical and PQC algorithms in your system, to preserve performance and backward compatibility while still adding another layer of protection.
Choosing appropriate algorithms based on a specific use case can also significantly improve your system’s performance: for example, you can use ML-DSA for general signatures but use Falcon when compact signatures are more important.
3. Implementation complexity
The efficiency of quantum-resistant algorithms depends not only on their inherent strength, but also on how well they’re integrated into your system. New PQC protocols may be incompatible with existing environments and communication protocols.
Because PQC algorithms haven’t been widely integrated and tested yet, it’s hard to assess how compatible they are with current FinTech systems. Moreover, some current FinTech software still uses outdated, legacy technologies that lack flexibility to support PQC algorithms.
Integrating PQC into these legacy infrastructures will require you to update your system, modify or refactor code, and test it rigorously.
The solution
Again, it’s vital that your current systems are up to date and use modern technologies that support the latest algorithms. If you still use outdated tech, focus on the crypto-agility of your system first.
Your team may start integrating post-quantum cryptography algorithms in non-critical systems to understand how well your software handles them, then gradually extend the implementation to more critical components.
Additionally, you can use a hybrid approach to maintain the security of your system while adopting new algorithms.
Read also
How to Integrate Post-Quantum Cryptography Algorithms into Your Software: A Practical Guide
Get hands-on insights into integrating post-quantum cryptography in real-world software solutions. Protect your sensitive data from potential quantum attacks with PQC.

4. Compliance and regulatory challenges
Compliance with PQC requirements presents a major hurdle. The regulatory landscape is still evolving, with standards from bodies like NIST and ISO still in development. Although you can already start implementing PQC, you must be able to adjust your integrations once standards are finalized and enforced.
In the FinTech industry, regulators will demand PQC adoption in areas like Know Your Customer, data privacy, and transactions. This means that once government bodies catch up, FinTech companies can expect a wave of regulatory updates.
Certification for cryptographic systems adds another layer of complexity when adopting PQC. While there are no dedicated PQC certifications yet, FinTech organizations relying on standards like FIPS 140-3 or ISO/IEC 19790 may need to re-certify their cryptographic modules once post-quantum algorithms are introduced.
Given that PQC algorithms are still relatively new, this process is likely to be resource-intensive and subject to evolving regulatory expectations.
The solution
To stay ahead, your organization should take a proactive stance and monitor regulatory updates. A dedicated compliance team is vital to track standards and coordinate the legal, security, and IT departments to ensure that regulatory standards are accurately reflected in your software.
5. High implementation cost
Transitioning to post-quantum cryptography involves updating and replacing software, upgrading hardware, and conducting extensive testing and staff training — which means it’s costly. This is especially true for FinTech organizations with legacy systems that require additional investments to solve compatibility issues.
Ongoing costs include expenses for security audits and regular patches if standards or requirements change.
The solution
To optimize costs, your FinTech organization can run pilot projects and learn more about the implementation costs and hurdles. It’s also a good idea to invest now in upgradeable infrastructure so that your technical debt doesn’t grow further.
Where possible, transition to cloud infrastructure, which offers more flexibility and scalability than on-premises systems.
Now that we’ve discussed challenges and solutions, let’s look at actual steps you can start taking today to prepare your FinTech system for a post-quantum transition.
The strategy: 6 realistic PQC transition steps to take now
Currently, no regulations explicitly mandate immediate PQC adoption. However, several frameworks already call for FinTech companies to assess their quantum risks and plan for crypto-agility. Below is a practical step-by-step strategy, adapted from the Swiss Financial Innovation Desk (FIND) roadmap, that you can follow today to get ready.
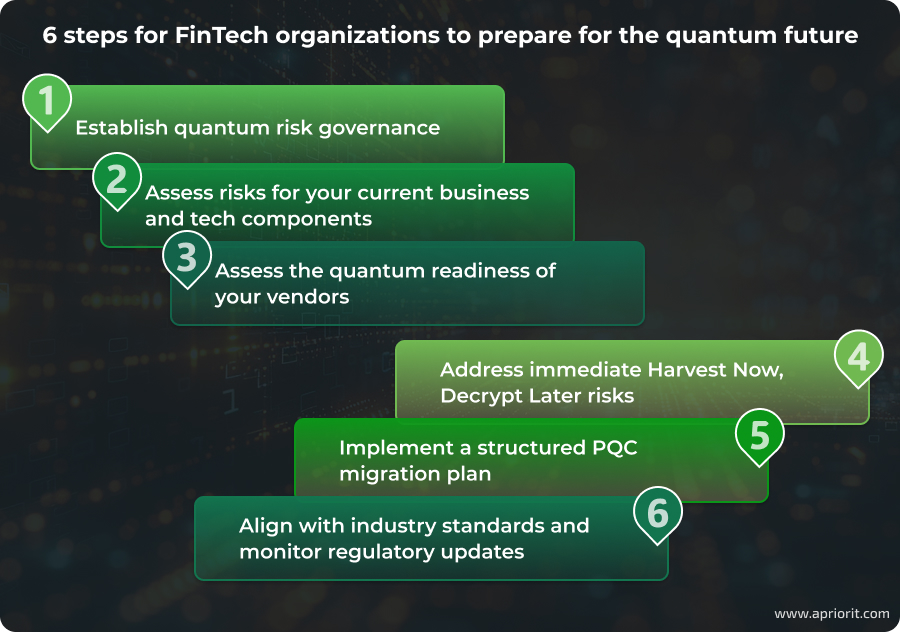
Step 1. Establish quantum risk governance
Start by assigning ownership. Form a cross-functional task force or working group that includes stakeholders from security, compliance, IT, and business teams. This group will be responsible for coordinating all PQC-related activities, tracking regulatory changes, and aligning the migration strategy with broader risk management objectives.
Consider engaging external consultants with expertise in post-quantum cryptography and regulatory compliance. Their guidance can help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure your migration strategy is future-proof and audit-ready.
Actionable tip: Embed quantum preparedness into your organization’s existing governance and risk frameworks rather than treating it as a separate initiative.
Step 2. Assess current risks
Conduct a thorough cryptographic inventory to identify where encryption is used across your systems, applications, and third-party tools. Determine which cryptographic mechanisms will be vulnerable to quantum attacks and map them to critical business processes.
As a result of this inventory analysis, you’ll get a Cryptographic Bill of Materials (CBOM) that will help you and your team navigate the current state of your cryptography. A CBOM should include items like:
- Cryptographic algorithms and key lengths
- Dependencies
- Compliance with cryptographic standards
- Cryptographic certificates and their expiration dates
- Security protocols and policies
Your CBOM should be regularly updated to serve as a relevant reference for all members of your team involved in updating your system.
Actionable tip: Prioritize systems that store long-term sensitive data or are part of mission-critical transaction flows — these are most at risk from Harvest Now, Decrypt Later attacks.
Read also
Cybersecurity in FinTech Solutions: What to Watch Out For and How to Respond
Learn how to navigate security in complex FinTech applications by protecting entry points in your software. Explore the key security measures to safeguard your user data and maintain your reputation.

Step 3. Assess the quantum readiness of your vendors
Prevent further technical debt by updating your procurement criteria to include quantum readiness. Any new software or hardware you purchase should support crypto-agility, or at least provide a clear roadmap to PQC compliance.
Actionable tip: Audit your cloud providers, payment processors, and other critical partners for PQC readiness. Ask vendors about their support for PQC standards (such as NIST FIPS 203–206) and whether their products support cryptographic upgrades without replacing the entire system.
4. Address immediate Harvest Now, Decrypt Later risks
Encrypting sensitive data with vulnerable algorithms today means it could be exposed tomorrow, once quantum computers are available. To counter this, prioritize securing long-term sensitive data now with quantum-safe or hybrid cryptography.
Actionable tip: Use hybrid encryption methods that combine classical and PQC algorithms to protect data in transit and at rest while maintaining backward compatibility.
5. Build cryptographic agility into your system architecture
Before you experiment with integrating PQC into your software, it has to be crypto-agile. This means your software architecture should allow for replacing or upgrading cryptographic algorithms without overhauling the entire infrastructure.
Without this flexibility, migrating to PQC — or any new cryptographic standard — will be time-consuming and costly.
Actionable tip: Audit your current cryptographic architecture to identify hard-coded algorithms or rigid implementations. Refactor such components to support replacing cryptography methods without disrupting critical services.
6. Align with industry standards
Multiple frameworks either explicitly or implicitly require FinTech companies to start planning for a quantum transition:
- PCI DSS 4.0 requires organizations to maintain crypto inventories, monitor quantum threats, and develop a strategy to address them.
- SWIFT Customer Security Programme and ISO/IEC 27001 mandate risk-based cybersecurity, implicitly including preparation for quantum threats.
- The EU’s NIS2 and DORA require organizations to keep encryption mechanisms up to date, which includes staying ahead of quantum vulnerabilities.
- SWIFT CSP and EMVCo are advising financial firms to start planning now for PQC migration.
- ISO/IEC 27001 requires assessing evolving threats — including quantum computing — to ensure the continued security of cryptographic controls. Therefore, organizations that are compliant with ISO/IEC 27001 must consider a future transition to PQC algorithms as part of their cybersecurity planning.
Actionable tip: Ensure that quantum transition roadmaps align with your migration timelines, and regularly monitor emerging regulations. It’s important to track regulatory updates from bodies like NIST, ISO, SWIFT, and cybersecurity agencies in countries and markets where you operate.
By following this roadmap, FinTech companies can move beyond passive awareness. In the next section, we’ll discuss how Apriorit can help you prepare for post-quantum cryptography (PQC) integration and brace for quantum threats on your own timeline.
Related project
Evaluating Smart Contract Security for Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Explore how Apriorit performed an in-depth audit of a client’s smart contract. Our recommendations helped the client mitigate risks, enhance security, and maintain customer trust.
The solution: get quantum-ready with Apriorit
Moving from classical to post-quantum cryptography is a complex, multi-step process. At Apriorit, we help FinTech companies navigate this journey, using our 20+ years of experience in cybersecurity and constantly growing knowledge of advanced technologies. Here’s what our team can do for you at each stage of your PQC readiness journey:
- Evaluate your software’s cybersecurity posture. Our security experts will conduct a thorough audit of your software to identify where classical cryptography is used, assess current vulnerabilities, and evaluate your exposure to future quantum threats. As a result, you’ll get a detailed cryptographic inventory, risk profile, and tailored recommendations for transitioning to PQC, giving you clarity on where to start and how to prioritize upgrades.
- Design and implement a crypto-agile architecture. We design and develop a future-proof cryptographic architecture so you can swap algorithms, benefit from hybrid encryption, and gradually migrate to PQC. We can build a crypto-agile system from scratch, or migrate your legacy software to its future-ready version without disrupting your services.
- Enhance your encryption methods. Our engineers integrate hybrid encryption and upgrade vulnerable components to more secure configurations using modern cryptographic libraries. For you, this means stronger protection of long-term sensitive data, particularly against HNDL attacks.
- Integrate NIST-approved algorithms into your product. Our cybersecurity developers have already gained experience in implementing post-quantum cryptography algorithms that are already approved by NIST. With Apriorit, you can pilot PQC implementations into parts of your system to get practical experience and cut future migration times.
Conclusion
For FinTech companies, the quantum threat is no longer a distant concern — it’s rapidly approaching. It’s important to start preparing now to protect customer data, secure financial transactions, and maintain compliance and your reputation.
Transitioning to post-quantum cryptography is a complex process. It may involve auditing your cryptographic systems, upgrading software and hardware, or even rebuilding key components from the ground up. Apriorit can guide you through every step to ensure a smooth and effective migration, helping you invest in changes that truly strengthen the cybersecurity posture of your FinTech software.
Apriorit has the expertise to help you move confidently toward a quantum-secure future by:
- Auditing your existing systems to identify cryptographic vulnerabilities
- Developing a migration strategy for legacy software
- Implementing NIST-approved PQC algorithms
- Building a crypto-agile FinTech solution from scratch
Deliver protected FinTech with confidence!
Get a dedicated partner with a security-first mindset to build a compliant, reliable, and future-ready FinTech solution.




