The use of unapproved software and hardware often puts an organization’s entire network at risk. System administrators are supposed to discover and manage shadow IT elements, but doing so becomes more and more challenging. In 2021, only 22% of organizations needed to ask for approval from IT teams to purchase any application according to the 2021 Digital Readiness Survey by ManageEngine.
Wide adoption of cloud services and switching to remote work makes it easy for users to deploy software of their choice. IT teams must adapt to this new reality and figure out new ways to discover, manage, and even benefit from shadow IT.
In this article, we take a look at the main security challenges of shadow IT, how it differs from business-led IT, and what can be done to detect and mitigate the risks of shadow IT. This article will be useful for project leaders and CIOs who want to secure their organization’s network from shadow IT.
Contents:
Hiding in the shadows
What is shadow IT? Basically, it’s any IT system, hardware, or application that’s deployed and used without the approval of the corporate IT department. In some cases, personal devices including cell phones and USB devices may also be considered part of shadow IT. The most common examples of shadow IT are popular cloud services like Dropbox and Salesforce and commonly used messengers like Slack and WhatsApp.
The most common reasons people turn to shadow IT are:
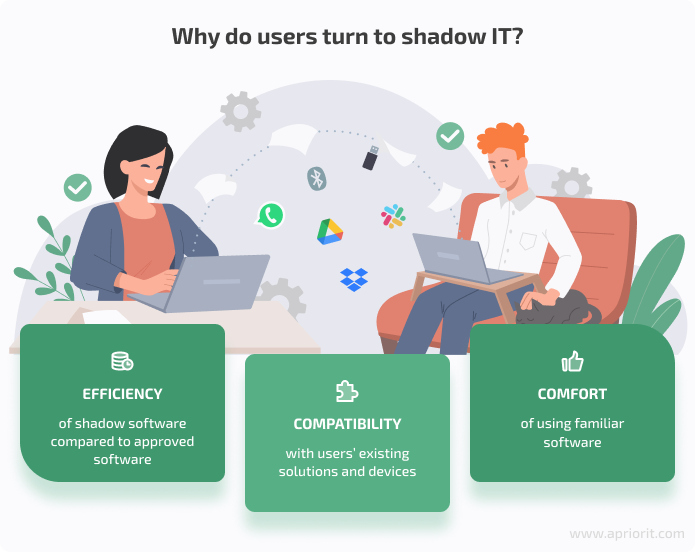
Even though shadow IT often seems helpful to end users, it poses a serious threat to enterprises. The main threat hides in its unaccountability — you can’t effectively manage something that you don’t even know exists. As a result, both the security and performance of the entire network are put at risk.
Let’s see what shadow IT risks are:

- Unmanaged security vulnerabilities. Software that wasn’t approved by the IT department may have unpatched vulnerabilities, security errors, vulnerable libraries, etc. Such software can create numerous weak spots that hackers may use for compromising a system and stealing sensitive business information. Since IT administrators don’t know about these vulnerabilities, they can’t manage the security risks of shadow IT.
- Data loss. An IT department can’t create backups for software and data they don’t know is present in the network, while shadow IT users typically don’t think (or know) that backups are necessary. As a result, there’s always a significant risk of losing sensitive data.
- Data and resource silos. An enterprise usually has a way of handling and storing its data with approved solutions. Yet users create their own data management systems with shadow solutions that consume additional resources to maintain and store additional data records, thus creating data silos.
- Increased IT costs. If employees prefer to use software and devices other than the ones approved, it means that the organization’s investments in IT aren’t paying off, and there’s a better way to use those finances.
- Compliance issues. Most businesses have various regulations, laws, and industry standards they need to comply with. The presence of unmanaged software makes it much harder for a company to meet compliance requirements. Non-compliance can lead to data breaches, costly penalties, and loss of customers.
Although shadow IT brings lots of risks, an organization can still benefit from unapproved software. Let’s discuss how your organization can turn the tables in the next section.
How can you benefit from shadow IT?
The appearance of shadow IT indicates that employees find approved solutions inefficient, uncomfortable, or both. Shadow solutions can be more productive and cost-effective than already deployed tools. And with the mass adoption of cloud services, there’s no chance you can get all shadow IT under control. But you can benefit from it by turning it into business-led IT.
Business-led IT is an IT management approach that allows employees to use the software and hardware they need without approval from the IT department. Employees only need to notify IT administrators about the products they have chosen to use.
Shifting to business-led IT provides organizations with several benefits:

Despite the benefits of the business-led approach, it doesn’t eliminate the key risks from shadow IT activities: the possibility of data loss and unknown security vulnerabilities. Also, keep in mind that the success of business-led IT relies on the openness and security awareness of users. If users don’t report shadow software, an IT department might never know about it.
40% of IT professionals admit to using unapproved technologies themselves despite the risks.
The Upside of Shadow IT Revealed report by Entrust
Even if you decide to adopt business-led IT for your enterprise, you still need to know whether there are applications and devices in your network that are unaccounted for. In the next section, we talk about popular solutions for detecting and mitigating security risks of shadow IT.
Throwing light on shadow IT
There are four major approaches to dealing with unapproved software and cloud applications. Which to choose depends on your organization’s management style and available resources. Let’s take a look at each of the options:
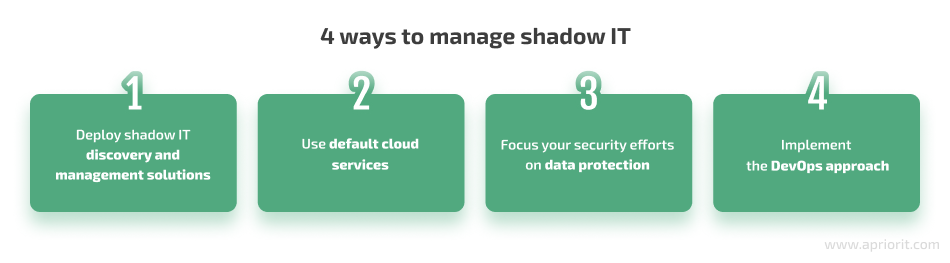
1. Deploy shadow IT discovery and management solutions
You can detect shadow IT with IT asset management (ITAM) systems. These systems gather a detailed inventory of hardware and software running in your organization’s networks. Based on this information, you can analyze how different assets are used.
When choosing or building custom ITAM software, pay attention to these four parameters:
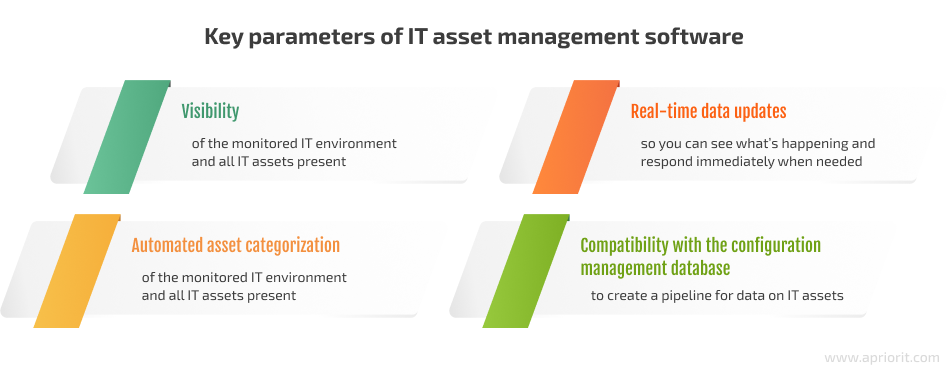
There are three types of ITAM solutions:
- Agent-based solutions work well when you need to gather inventory information from remote endpoints or devices that aren’t constantly connected to the network, such as laptops.
- Agentless tools work best for performing non-intrusive monitoring and analysis of critical assets.
- Cloud-based IT asset inventory systems are used for monitoring and auditing the use of cloud solutions. An example is Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASBs).
CASBs are popular tools for discovering shadow IT risks in the cloud. They can identify cloud services and applications in use by analyzing logs from firewalls, proxies, and endpoints. These solutions give a high level of visibility over what devices are connected to the network as well as who can access sensitive data and store it in the cloud.
Some CASBs also provide the opportunity to put cloud services used in business-led IT into read-only mode. This way, users can still view the contents of these applications but can’t add data to them.
To cover all of your enterprise’s networks with asset management software and access CASBs, you’ll probably need to deploy several solutions and integrate them with each other as well as with your existing IT systems.
2. Use default cloud services
Large cloud service providers (CSPs) offer additional solutions for detecting and managing shadow IT in the cloud. They are useful for organizations that deploy all of their network in one or several clouds.

Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is a service for monitoring and auditing the use of cloud services. It can discover applications, files, and users in a company’s cloud environment, including third-party applications connected to it.
Microsoft Azure has an agent-based Azure Active Directory Cloud Discovery tool in its Premium edition. The agent captures such data as headers, URLs, and metadata for HTTP/HTTPS connections to discover cloud applications used within an organization, identify people who use them, and provide detailed information for further analysis.
Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers two similar services — AWS Cloud Discovery and AWS Application Discovery Service. They help users discover accounts, applications, data centers, and relationships between instances in AWS environments. Both services can be used for free in small networks.
3. Focus your security efforts on data protection
At the end of the day, it’s sensitive data we want to protect from risks caused by shadow IT. Instead of discovering all elements of shadow IT in your network, you can focus on data monitoring and protection. This way, you will monitor all interactions with data regardless of the way your users access sensitive information.
Here are the key data protection practices you can adopt:

Ensure data retention. Most records stored by an enterprise have an expiration date; in other words, the organization has to preserve these records for a certain period of time. The storage period is usually defined by cybersecurity standards and regulations as well as company-specific operations. A data retention policy helps to unify, classify, and manage sensitive data and define rules of its storage and disposal.
With this policy in place, you can focus your cybersecurity efforts on protecting the records your organization really needs. Also, you can reduce the risk of data leaks simply by reducing the number of sensitive records.
Encrypt sensitive data. Encrypting records at rest and in transit allows you to make sure that sensitive data will be secure if uploaded to shadow software or leaked. To interact with encrypted data, a user needs a public or symmetric key and a decryption algorithm.
The most common data encryption protocols are AES, TLS/SSL, and RSA. They provide an adequate level of protection while not taking too long to cipher data.
Manage users’ access to data. Security vulnerabilities created by shadow IT may serve as an entry point for hackers, who can infiltrate your network and steal sensitive data unless you have an access control system in place. Such a system defines which users can interact with which resources and denies access requests from all other users.
Access control systems often include authentication services like multi-factor authentication to verify user identities. Multi-factor authentication helps security systems positively identify users by their credentials, biometrics, or additional confirmation via a smartphone before providing access.
Trace all data movements. Since shadow IT implies moving data to unapproved services and software, it’s important to be able to monitor and trace all your sensitive records. Data loss prevention software can help you with this task.
Knowing where your sensitive data is stored, how it’s managed, and when it’s transferred outside the protected perimeter eliminates the need to discover all shadow IT elements. Instead, you can focus on data movements and configure rules to automatically block transfers outside the protected environment.
4. Implement the DevOps approach
DevOps is an approach that combines software development and operations practices into a single streamlined process. It allows enterprises to boost productivity, reduce the time needed for incorporating new solutions, and break down the silos between development, testing, and operations.
A DevOps approach helps organizations build a pipeline for continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) during software development and make sure this pipeline consists of only useful software, tools, and services.
Adopting DevOps to mitigate shadow IT has several major benefits:
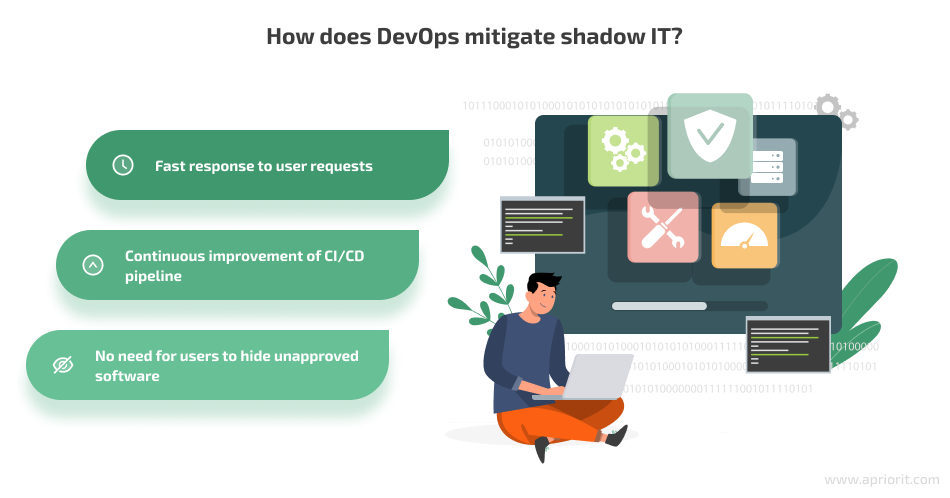
Since DevOps allows for a faster response to requests from end users and helps companies implement new solutions easily and effectively, this approach can be viewed as one of the most effective ways to solve the problem of shadow IT.
DevOps eliminates the need to use shadow IT by making it easier for end users to officially implement new software and technologies needed to do their jobs better and faster. Organizations that embrace DevOps can turn shadow IT into part of their IT infrastructure without compromising performance or security.
Keep in mind that DevOps can mitigate the appearance of shadow IT only when the whole enterprise adopts this approach. Otherwise, the teams that didn’t adopt DevOps may create even more shadow IT elements to keep up with DevOps-oriented teams.
Conclusion
The use of unmanaged software and cloud services can pose a serious threat to any company by compromising the security of its network and creating performance and compliance issues. There are at least three ways of solving this problem: by implementing an effective IT asset inventory and management system, focusing on data protection, or moving to DevOps.
At Apriorit, we have teams of professionals experienced in building effective network management solutions, cloud infrastructure, and DevOps processes. Reach out to start shedding light on shadow IT and improving your network!




