Key takeaways:
- Implementing a microservices architecture brings many benefits, including the ability to scale individual services, improved resilience, and high flexibility.
- Building efficient microservices requires thorough preparation for specific challenges, including high maintenance costs and the need to define clear service boundaries.
- To enhance the overall efficiency and performance of microservices, consider key microservices trends, such as event-driven architectures and AI.
- Robust infrastructure, fault-tolerant design, and sufficient observability allow you to create a resilient and secure solution that meets your business demands.
Despite the obvious advantages of a microservices architecture, not all businesses are rushing to rebuild their solutions. Key factors that may hold your organization back from choosing microservices include instant growth in operational overhead as microservices expand, an increasing cyberattack surface, and insufficient service observability.
So, are the benefits of migrating to microservices worth the risk? Does every solution need a microservices architecture? What should you consider before implementing microservices?
In this article, you will get answers to these questions, discover challenges that may emerge during the development process, and find expert tips on implementing a secure and reliable microservices solution.
This article will be helpful for CTOs, product managers, and engineering leads who are thinking of building a new microservices solution or modernizing the architecture of an existing solution.
Contents:
- Business benefits of a microservices architecture
- Challenges of implementing a microservices architecture
- Core microservices trends for 2026
- Achieving balanced microservices: tips and considerations
- Apriorit’s client success story: Migrating a monolithic SaaS solution to microservices
- How Apriorit can help you develop and implement microservices
- Conclusion
Business benefits of a microservices architecture
The software architecture you choose before starting development or migration will define your product’s long-term stability. The right choice of architecture must ensure not only your software’s functionality but also its scalability, maintainability, and security.
When we talk about a microservices architecture, we mean an approach to breaking a complex system into small, modular, and loosely coupled services, where each service is responsible for a specific business function. Such modularity lets you develop, deploy, and scale individual services independently and on demand.
Microservices autonomously manage their logic and data, communicating over the network mainly through standardized API calls. This enables loosely coupled integration so that changes to one service have a minimal impact on others.
Using a microservices architecture helps you build flexible solutions that provide a broad spectrum of business benefits, such as:
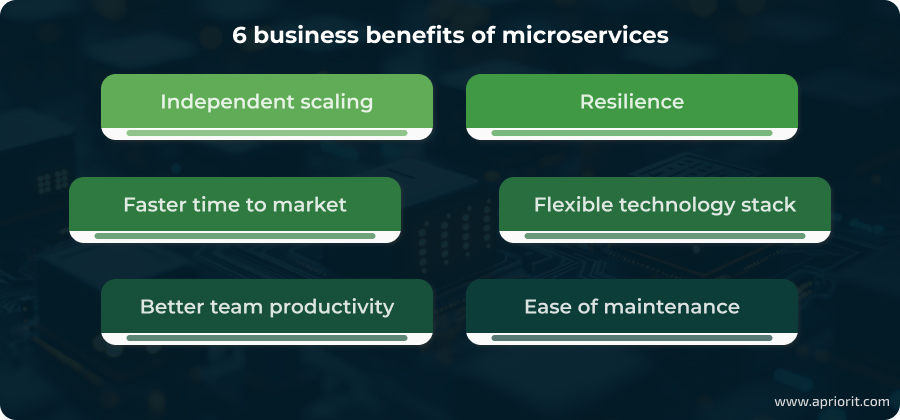
- Independent scaling. Since every service handles a distinct business function, you can independently scale up a service that is experiencing significant load without affecting other services. This allows for optimizing resource use along with reducing costs.
- Resilience. The fault-tolerant design of microservices prevents the whole system from crashing if one service fails. Moreover, microservices can be designed to auto-scale and auto-recover in an emergency. All of these factors ensure the entire solution’s resilience and seamless operation even when separate components face issues.
- Faster time to market. The autonomy of every microservice allows your team to develop, test, and release different components independently and concurrently. Each team can deploy its own microservices without waiting for any other teams. This allows you to significantly shorten release cycles and promptly provide updates and new features to your customers.
- Flexible technology stack. As you can build and maintain every service independently, your team can choose the technology stack best suited to a particular service’s requirements and goals. This flexibility lets you and your team experiment with different technologies and stay on top of industry trends.
- Better team productivity. When building microservices, you can engage small teams focused on developing separate services. This can help improve code quality and increase development speed.
- Ease of maintenance. The modularity of microservices allows your team to make fixes and updates to one service without affecting other services. As a result, you can resolve issues and respond to users’ demands faster, enhancing the loyalty of existing customers and attracting new ones.
When is it crucial to implement a microservices architecture?
Consider using microservices in the following cases:
1. Legacy app modernization
Breaking down outdated monolithic software into smaller and more manageable services lets you develop your solution incrementally and adopt different technologies when updating different parts.
2. Complex multi-component solutions
A microservices architecture allows for autonomous development of independent components without impacting the entire solution’s stability and performance.
3. Data-intensive apps
Microservices help you handle different data stores and processes at the service level, improving data management and enhancing the protection of sensitive data within a particular service.
4. Solutions requiring real-time data processing
Implementing microservices lets you efficiently manage fluctuating data volumes due to independent scaling and the possibility of allocating additional resources for a particular service to optimize its performance.
5. Resilient and fault-tolerant software
When an app’s troubleproof operation is pivotal, implementing microservices with a fault-tolerant design can ensure reliability.
As we know, every top-notch solution is a result of precise preparation. Such preparation involves thorough analysis and mitigation of potential risks before launching product development. In the next section, we explore what the main challenges are when implementing a microservices architecture.
Want to implement a resilient microservices solution?
Reach out to Apriorit specialists who have vast expertise in developing microservices-based solutions of any complexity.
Challenges of implementing a microservices architecture
Before deciding to use a microservices architecture, it’s important to clearly understand the difficulties that may occur during development and weigh all the pros and cons.
Based on our vast experience developing software with monolithic, microservice, and hybrid architectures, we will share the most typical challenges you can face when implementing a microservices-based solution — and possible ways to address them:
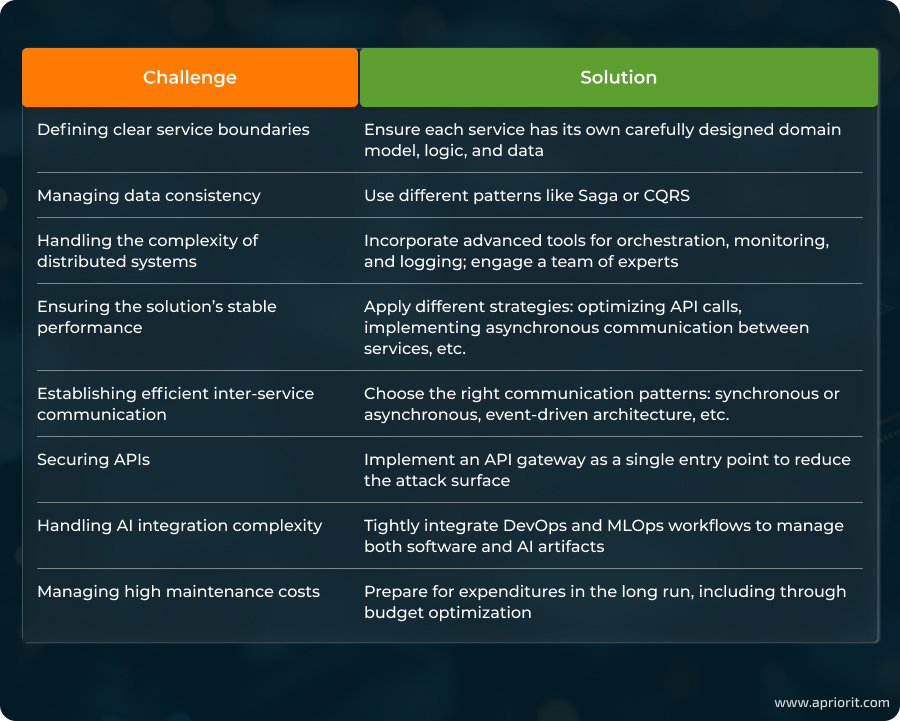
Defining clear service boundaries. Every microservice needs to have a well-defined scope and responsibility. Poorly defined boundaries cause tight coupling, data inconsistencies, and deployment difficulties. To define clear boundaries, ensure that each service has its own carefully designed domain model, logic, and data. This will allow you to minimize dependencies.
Managing data consistency. Unlike monolithic applications that typically use a single database for all transactions, every microservice typically has its own database that is isolated from all others. But such decentralization makes maintaining the consistency of data sources difficult. Architectural patterns such as Saga or CQRS can help you manage eventual consistency and coordinate distributed transactions.
Handling the complexity of distributed systems. The components of microservices solutions are independently deployable services (with separate data stores) that communicate over networks. Keeping track of hundreds of such services introduces operational, communication, consistency, and management overhead. To run the system successfully, you need to incorporate advanced tools for orchestration, monitoring, and logging. You also need to engage a team of specialists with deep knowledge of microservices.
Ensuring the solution’s stable performance. Since microservices often communicate through API calls over the network, each call adds latency that can cause delays. In turn, these delays increase overall application response times. You can apply different strategies to address performance and latency issues, from optimizing API calls to implementing asynchronous communication between services.
Establishing efficient inter-service communication. For building scalable, resilient, and maintainable systems, it’s crucial to establish efficient communication between services.
To do so, you need to choose the right communication patterns to match your solution’s demands. Depending on your needs, these may vary from synchronous or asynchronous communication to an event-driven architecture.
Securing APIs. APIs expose functionality and mainly serve the purpose of allowing microservices to communicate. But every API can also be a potential entry point for attackers. One way to secure APIs is by implementing an API gateway — a centralized entry point that lets you enforce authentication, authorization, and rate limiting, thereby decreasing the attack surface.
Handling AI integration complexity. Before integrating AI, it’s crucial to consider that the CI/CD pipeline has to accommodate not only microservices deployment but also AI model lifecycle management. This includes AI model training, retraining, versioning, and data governance. Handling AI integration complexity requires tightly integrated DevOps and MLOps workflows to manage both software and AI artifacts.
Managing high maintenance costs. Maintaining a broad microservices environment on a stable level requires significant investment in observability tools, CI/CD pipelines, and DevOps tooling. Moreover, maintenance costs increase with the rise of API endpoints that need version support, testing, and synchronized deployment. It’s essential to be ready for such expenditures in the long run and search for ways to optimize your budget. For example, you can carefully choose tools based on your solution needs and prioritize their integration into your product.
Considering these challenges during the discovery phase will help you build a resilient and balanced microservices solution.
Despite the obvious difficulties of implementing and managing microservices, they continue to evolve and to enhance the scalability, security, and overall efficiency of software solutions. Let’s look at the main trends that drive microservices adoption.
Read also
Effective Load Testing for Golang Microservices: A Practical Guide
Explore a guide on how to design and run load tests for Golang microservices and how to analyze performance results.
Core microservices trends for 2026
Like any mature technology, microservices have a range of downsides that stimulate the constant search for possible solutions. Here are some of the key trends aimed at enhancing the performance and security of microservices:
- Event-driven architecture. Incorporating an event-driven architecture (EDA) into microservices makes them more dynamic and responsive due to asynchronous communication. This enables services to respond to business events in real time, leading to better performance and flexibility. An instant response to events makes EDA ideal for IoT, real-time analytics and monitoring, financial systems, and other use cases.
- Serverless computing. The use of serverless computing has increased due to its auto-scaling capabilities, which can lead to decreased operational overhead. In addition, having a cloud provider manage infrastructure lowers maintenance costs, as you pay only for execution time and resource consumption. Serverless computing is best suited for event-driven and highly scalable systems with unpredictable loads, or when minimizing operational complexity is crucial.
- Service mesh technology. The evolution of service mesh technology enables its use in microservices as an infrastructure layer to manage and monitor inter-service communication. Service mesh adoption allows for automated service discovery, load balancing, advanced traffic management, traffic splitting, enhanced security, and observability.
- Zero-trust security. Adopting a zero-trust security approach involves treating the entire microservices environment as untrusted and applying security controls at the level of individual services and their interactions. The key principles of this approach are verifying every request, encrypting all communication, and implementing least privilege and time-bound access. Together, these practices deliver a high level of security in a dynamic environment.
- AI technology. Incorporating AI technology enhances microservices automation. AI models continuously analyze logs, metrics, and traces from microservices to detect anomalies or potential failures early. This helps improve system reliability and enables predictive maintenance. Moreover, AI helps predict traffic patterns and resource demands, triggering dynamic scaling of individual microservices ahead of load spikes to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
In the next section, we explore what to consider when implementing microservices and provide tips from Apriorit experts that you can use to facilitate the development process.
Achieving balanced microservices: tips and considerations
If you’re implementing a microservices architecture, there are certain details you need to consider when planning product development:
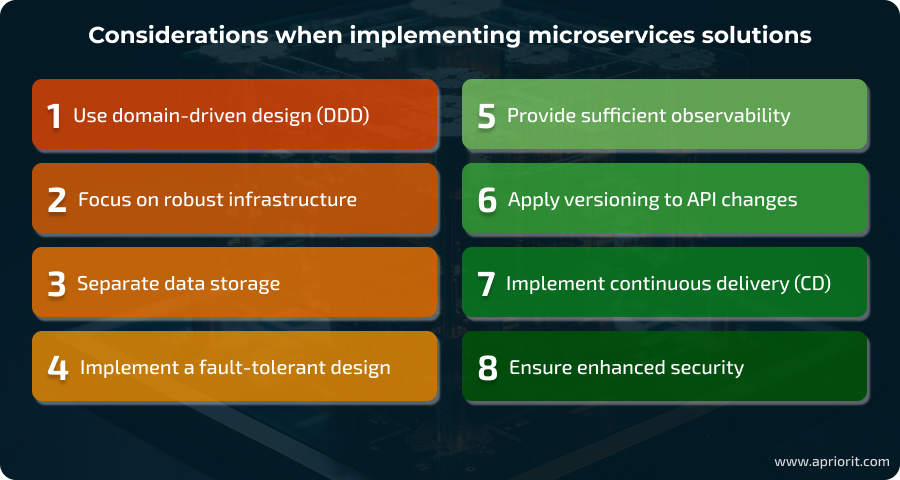
1. Use domain-driven design (DDD)
The DDD approach focuses on breaking down complex systems into software components for specific business domains. Designing microservices around the bounded context lets you define clear boundaries and responsibilities for each service. This approach ensures that each microservice contains logic and data specifically related to its business domain, allowing for building highly adaptable and flexible solutions.
Apriorit expert tip: Engage domain experts, developers, product owners, and business analysts to get a deep understanding of the business domain. Then, break down the domain into subdomains representing distinct business capabilities and define bounded contexts for these subdomains. Each designed microservice will operate within a specific bounded context.
2. Focus on robust infrastructure
Robust infrastructure enables microservices to achieve agility, scalability, and innovation while effectively managing operational complexity. A poorly designed microservices hosting platform will decrease a solution’s resilience.
Apriorit expert tip: Consider providing infrastructure fully suited for microservices solutions. For example, using containerization or cloud services will help you allocate resources for each service dynamically on demand; implementing automatic recovery and health checks will maintain the system’s reliability; supporting CI/CD pipelines, automated testing, and automated deployment will speed up release cycles and reduce the risk of downtime.
3. Use separate data storage
Separate data storage allows each microservice to manage its own data independently and eliminates the tight coupling caused by shared databases. Thus, changes to one service’s data schema will not impact other services. Moreover, microservices often have different data models, access patterns, and query needs. Separate storage allows each microservice to optimize its schema and queries for its domain without compromise.
Apriorit expert tip: While implementing separate data storage, it’s important to consider and address various challenges. For example:
- Implementing queries that demand data across multiple databases requires additional API composition layers or data replication.
- Using different database technologies requires working with different experts and tooling.
- As a microservices solution evolves, there can be a need for database schema changes. This requires careful versioning and migration strategies to avoid breaking changes and downtime.
4. Implement a fault-tolerant design
Ensuring fault tolerance in microservices-based solutions is crucial, as the failure of one service can cascade and bring down the entire system. Implementing a fault-tolerant design allows for failure isolation. In this case, only the affected service is impacted, preventing system-wide downtime.
Apriorit expert tip: To ensure fault tolerance, you can apply different design principles, including the following:
- Circuit breakers let you monitor an operation’s health and prevent calls to a failing component.
- Graceful degradation maintains core and essential functions even when some system components fail or encounter issues.
- Replication is the process of duplicating data or the system state across multiple nodes or instances. If a node fails, replicas provide uninterrupted access to data.
- Load balancing automatically reroutes traffic to other healthy instances, maintaining uninterrupted service availability if one instance fails.
5. Provide sufficient observability
Successfully managing the complexity of the distributed system requires ensuring a proper level of observability. Observability delivers the visibility and insights needed to effectively understand, monitor, and troubleshoot microservices solutions.
Apriorit expert tip: To achieve or enhance service observability, you can integrate logging for records analysis, metrics to measure the system’s performance, tracing to track requests across the distributed system, and health checks to monitor a service’s availability to handle requests.
6. Apply versioning to API changes
Changes to APIs can break existing clients if they expect an older interface. API versioning allows for incorporating new features or changes without impacting users of earlier API versions. It also lets your team update services on demand, maintaining multiple API versions simultaneously.
Apriorit expert tip: To ensure effective API versioning, you can follow rules such as these:
- Select a versioning strategy, such as URL path versioning or header versioning
- Avoid modifying or removing existing endpoints without versioning
- Document API versions properly
- Remove deprecated API versions after the transition time only
- Automate testing to validate all supported versions
7. Implement continuous delivery (CD)
Continuous delivery allows each microservice to be built, tested, and deployed independently. This speeds up development cycles and time to market for new features and updates.
Apriorit expert tip: To implement CD for microservices:
- For each microservice, create an isolated CI/CD pipeline for building, testing, and deploying.
- Use an orchestration platform such as Kubernetes for deployment, scaling, and rollback.
- Implement progressive delivery techniques like blue-green deployment or canary releases.
8. Ensure enhanced security
The decentralized nature of microservices and the network-based communication between them increases the attack surface. Every microservice API creates a lot of potential entry points for attackers, while network communication channels can be vulnerable to interception or man-in-the-middle attacks.
Apriorit expert tip: To provide robust protection, follow cybersecurity best practices. These include:
- Encrypting all data and communications between microservices
- Ensuring strong authentication and authorization
- Implementing secure API gateways with strict access control
- Delivering regular security updates
- Performing penetration testing
Now, let’s see how Apriorit experts helped our client build a microservices SaaS solution and how we can help you implement reliable microservices.
Read also
From Concept to Implementation: Building Robust Microservices with Node.js
Find best practices for developing Node.js microservices, including a detailed implementation guide.

Apriorit’s client success story: Migrating a monolithic SaaS solution to microservices
A large US-based provider of property management software decided to replace their monolithic SaaS solution with one that was agile and based on microservices. Their aim was to facilitate the implementation of new features and, as a result, attract new customers.
A dedicated Apriorit team worked on three key stages of the project:
- Project discovery stage — Our BA elicited requirements and prepared the documentation required to launch development.
- Backend development stage — This was focused on integrating the database, creating different models for connecting microservices and communicating with the platform front end, and finally implementing microservices.
- Frontend development stage — This stage was devoted to building the client side of the solution’s web interface.
The new SaaS platform we built has an updated design that offers better scalability, easier code maintenance, and an improved user experience.
Moreover, migrating to microservices helped our client not only enhance the product’s scalability but also level up the flexibility of the platform’s architecture and simplify the process of adding new features.
How Apriorit can help you develop and implement microservices
Whether you need to outsource full-cycle development of microservices or only some tasks, we will be glad to provide the following services:
- Custom web application development. We can help you develop flexible and secure web platforms of any complexity from scratch.
- SaaS software development. Our team provides a full range of SaaS software development services to deliver efficient and scalable solutions that meet your business needs.
- Cloud computing and virtualization development. Our research and development teams can offer you multiple virtualization-related services, including network and operating system virtualization.
- Backend development services. We provide fully functional backend services, which involve custom backend development, legacy backend modernization, backend refactoring, and more.
- DevOps services. Our experienced DevOps specialists can help you ensure stable, high-quality delivery processes and develop high-load and high-performance solutions.
- Solution security. We have 20+ years of experience in cybersecurity and adhere to the principles of a secure SDLC for every project. This means that we know how to secure your solution effectively, considering the nuances of your industry.
- Maintaining solutions after release. Our specialists will assist your team in keeping your solution safe and stable by providing support and maintenance services after solution deployment.
Conclusion
Implementing a microservices architecture makes complex and highly distributed systems flexible so they can support changes and innovations while ensuring stability in an emergency.
However, building a resilient and balanced microservices solution requires considering and thoroughly preparing for the peculiarities of microservices development.
Whether you want to outsource the whole development process or just non-trivial tasks, a team of Apriorit experts is ready to help you develop microservices-based solutions in any language that fits your goals and your existing infrastructure.
Looking for experts in microservices?
Partner with Apriorit to build a top-notch and secure microservices solution!
FAQ
What’s the difference between microservices and monolithic architectures?
Microservices and monolithic architectures differ mainly in their structure and management. Monolithic apps are built as a single unified codebase and deployed as one unit, which is best for small, simple solutions. Microservices are independent services that can use their own technologies and can be deployed and scaled separately. They are ideal for complex, highly distributed systems.
What security practices are essential in a microservices architecture?
<p>Key security practices for microservices include using secure secrets managers to store credentials and tokens, applying centralized authentication and fine-grained authorization, and encrypting all data in transit with TLS. To ensure container security, you can use minimal trusted images, scan for vulnerabilities, and avoid running containers as root.</p>
<p>Also, it’s essential to secure API gateways, collect logs and metrics to detect issues, regularly perform automated security testing, and adopt a zero-trust architecture to minimize risks.</p>
What tools and frameworks are recommended for managing microservices in 2026?
Recommended tools and frameworks for managing microservices in 2026 include:
<ul class=apriorit-list-markers-green>
<li>Development frameworks like Spring Boot and Spring Cloud (Java), Micronaut, Quarkus, Express.js (Node.js), Django and FastAPI (Python), and Go kit (Go)</li>
<li>Monitoring and observability tools such as Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack, and Jaeger</li>
<li>Service mesh tools like Istio, Linkerd, and Consul Connect</li>
<li>Orchestration tools include Kubernetes and Orkes Conductor</li>
<li>Testing tools such as Postman, Pact, Cypress, and ACCELQ</li>
</ul>
What are the key design principles of a microservices architecture in 2026?
Key design principles of a microservices architecture in 2026 include:
<ul class=apriorit-list-markers-green>
<li>Single responsibility. Each microservice focuses on one business function.</li>
<li>Loose coupling. Services are mostly independent, with minimal dependencies possible.</li>
<li>Domain-driven design. Services are built around business domains with clear boundaries.</li>
<li>API-first design. APIs are designed before implementation for consistency and reusability.</li>
<li>Decentralization. Teams have autonomy over development, deployment, database choice, and technology stack.</li>
<li>Containerization. Services are packaged and deployed in containers.</li>
</ul>
What are the ways to handle communication between microservices?
Handling communication between microservices mostly involves two main communication styles:
<ul class=apriorit-list-markers-green>
<li>Synchronous communication. Services call each other’s APIs directly and wait for a response before continuing. You can use different patterns to implement synchronous communication, such as API gateways, service discovery, or load balancing.</li>
<li>Asynchronous communication. With this style, services communicate by sending messages without waiting for immediate responses. Asynchronous communication patterns include message queues.</li>
</ul>
<p>The best choice of communication style will depend on the solution’s tasks and business needs.</p>
How much does it cost to implement a microservices solution?
<p>Implementation costs depend on different factors, such as the solution’s complexity and whether you want to build a solution from scratch or modernize a monolith system. In any case, developing microservices requires significant initial investment in team restructuring, additional infrastructure, migration, and much more.</p>
<p>And as the microservices solution grows, its maintenance costs will grow too. That’s why it’s essential to conduct a cost–benefit analysis to confirm the worthiness of such investments. Apriorit specialists can help you estimate implementation costs and, if required, offer alternative solutions.</p>




