Key takeaways:
- AI-powered medical imaging systems are best suited for augmentation-first workflow improvements, such as in triage, measurement automation, and quality enhancement.
- In medical imaging AI systems, data governance, validation strategy, and lifecycle monitoring are just as critical as the model itself.
- From the start, the architecture, documentation, and update governance of your AI system should be designed with privacy, security, and compliance requirements in mind.
- Common failure points for AI-powered medical imaging solutions are unstable performance and domain shifts when encountering unseen data.
Clinical usability, explainability, reliable security, and transparent governance.
These are today’s expectations for medical imaging systems powered by artificial intelligence (AI), and they are challenging to meet. Development teams need to take care of a variety of tasks, from designing and implementing new features to actually integrating them into existing solutions.
This article is aimed at development teams who are under pressure to integrate AI features into medical imaging products while navigating realities that don’t appear in demos. In particular, we’ll discuss how to handle uneven data quality, generalization across scanners and sites, privacy constraints, and compliance expectations that impact everything from documentation to post-deployment monitoring.
You’ll learn:
✔ Where AI delivers the most measurable impact in medical imaging workflows
✔ What commonly halts implementation and leads to expensive rework
✔ How to help your team deliver a product that meets both clinical and market requirements
Contents:
- What is medical imaging?
- Why invest in AI-powered medical imaging?
- Common use cases for AI-enhanced medical imaging
- The impact of AI on medical imaging
- Challenges of AI implementation for medical imaging
- How to engineer an AI medical imaging system: Advice from Apriorit experts
- Build a competitive medical AI system with Apriorit
What is medical imaging?
Medical imaging is a generalized term referring to a set of technologies used to visualize internal body structures for diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of different diseases.
Various technologies provide medical professionals with specific information on areas of the body or systems being studied. There are three main types of medical images:
- X-ray–based images such as radiography, fluoroscopy, and computed tomography (CT)
- Ultrasound images and videos
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans
Medical imaging supports decision-making across various domains — essentially, anywhere clinicians need objective visual evidence to plan or verify care, such as in oncology or for image-guided interventions.
Now, let’s determine if you should consider investing in custom medical imaging AI software or enhancing existing systems with AI.
Want to turn your AI investment into measurable business value?
Our consulting experts will assess your needs, define clear objectives, and guide you through every step of your AI journey.
Why invest in AI-powered medical imaging?
Market forecasts highlight the potential of AI-powered medical imaging:
- MarketsandMarkets forecasts that the AI in medical imaging market will grow from roughly $1.5B in 2024 to $4.5B by 2029, at a 23% CAGR.
- Grand View Research estimates the global AI-based medical imaging market at $1.36B in 2024 and forecasts a 34.67% CAGR increase by 2033, with the market size projected to reach $19.78B.
If you’re building a product roadmap (or evaluating whether to invest at all), it helps to treat market sizing as a signal rather than a single source of truth. Market vision is also different from analyst to analyst: some operate in software-only vs. full-stack categories, while others consider diagnostic vs. operational tools.
Despite the differences in numbers, a common trend emerges: buyers are actively seeking scalable imaging workflows, creating a clear niche in the market for AI-powered healthcare solutions.
The reason behind this is simple:
Demand for imaging is rising faster than the capacity of clinical teams and current workflows can absorb.
Every year, medical organizations generate massive volumes of medical imaging data. For example, according to an NHS England report [PDF], between April 2022 and March 2023, over 45 million imaging tests were reported in England alone.
At the same time, the industry faces significant talent shortages. In the UK, the Royal College of Radiologists’ 2023 workforce census reports that demand for CT and MRI scans increased by 11% in 2023, while the clinical radiology workforce expanded by 6.3%. This widening gap translates into backlogs, delayed treatment decisions, and mounting pressure on medical professionals who must not only process all that data efficiently but also be able to move it safely between devices and systems: from scanners to picture archiving and communication systems (PACSs) to radiology workflows and electronic health record (EHR) systems.
Addressing this imbalance between supply and demand is exactly where AI comes into play. Let’s see what this may look like in practice and analyze the key use cases for and advantages of AI in medical imaging.
Read also
Starting a New AI Project: 12 Questions to Assess If You’re Ready
Avoid common pitfalls when launching an AI project by learning what really matters at the planning stage. Set up your AI project for success with expert recommendations on strategy, data readiness, and resource allocation.
Common use cases for AI-enhanced medical imaging
To keep your product highly competitive, it’s essential to make sure it covers the most relevant use cases.
Generally, there are three high-level use cases for AI in medical imaging and diagnostics:
1. Image analysis
When talking about image analysis, we’re referring to multiple operations: detection, segmentation, measurement, tracking, and so on. AI algorithms detect and localize findings, segment structures of interest, and compute measurements such as diameter, area, and volume. Some algorithms can be used to track those structures across frames or over time.
For example, in one of our previous projects, the Apriorit team worked on automating follicle detection and measurement in ultrasound images.
Our client, a US-based infertility clinic, needed to speed up and standardize the evaluation of ultrasound videos for ovarian follicles. Their workflow required therapists to repeatedly pause videos, manually mark follicles, and measure their dimensions, which was both time-consuming and unscalable.
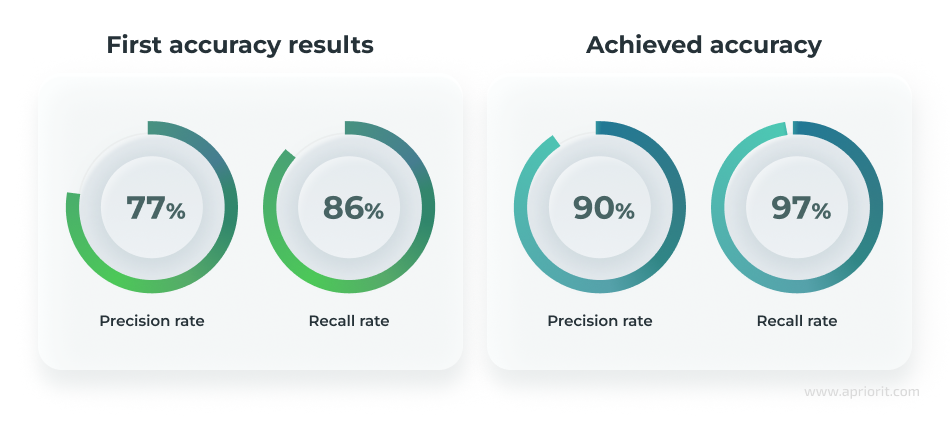
The Apriorit team developed an AI-based system that automates the processing of ultrasound videos, detecting, segmenting, and measuring ovarian follicles with up to 90% precision and a 97% recall rate.
Related project
Building an AI-based Healthcare Solution
Explore details of how our team delivered an AI-based healthcare system that addressed complex technical challenges and supported more efficient and reliable medical workflows.
2. Quantitative feature extraction
Extracting quantitative features from medical images is the special focus of radiomics. And this is where AI can efficiently assist medical professionals.
Radiological images contain quantitative data that is hard or impossible to detect during a standard visual evaluation. But when executed with the help of AI-enhanced radiomics, such evaluation can provide significant data-driven support to complex tasks such as estimating prognoses and predicting therapy response.
An article published in the journal Clinical Oncology highlights that when enhanced with AI, radiomics enables medical professionals to better predict tumor behavior and treatment response in specific contexts.
In particular, AI-powered radiomics systems can help extract specific features from radiological images (including texture, shape, and intensity patterns) and precisely measure them. At the same time, scientists are warning about the importance of validation on external heterogeneous datasets for such AI systems to ensure reliable, unbiased results.
3. Image enhancement and reconstruction
Another critical area of AI application in medical imaging covers operations like image denoising, artifact reduction, resolution improvement, and image reconstruction. All of these operations are unified by a single goal — to get maximum valuable medical insights from existing medical images.
For example, a 2024 publication in the European Journal of Radiology highlights that the use of deep learning reconstruction enables medical professionals to improve noise reduction and potentially support dose reduction while maintaining diagnostic utility.
Read also
Applying Deep Learning to Classify Skin Cancer Types
Explore a practical example of using deep learning for skin cancer classification and learn what it takes to build AI solutions that balance accuracy, scalability, and medical data constraints.
The impact of AI on medical imaging
AI can serve as an augmentation measure, enabling clinical teams to spend more time on high-judgment work and reduce friction in repeatable steps. We’ll analyze the potential of this technology in two parts: benefits and use cases.
Let’s start with examining key benefits of AI in medical imaging:
1. Shortened time to decision
AI can help healthcare professionals make critical decisions faster while ensuring they are clinically validated. In particular, AI can help prioritize urgent findings, pre-fill measurements, and speed up routine steps that often slow clinicians down during peak workloads. For example, an AI-triage study of chest CT pulmonary angiography exams reported a reduction in turnaround time for pulmonary embolism-positive tests from 68.9 to 46.7 minutes during work hours. Clinical AI triage research published in the Cureus Journal of Medical Science also suggests potential reductions in triage time and improvements in decision support.
AI-powered medical imaging systems can also highlight likely urgent studies, allowing radiologists to review them much earlier than during manual processing.
2. Improved reporting consistency
In many imaging workflows, the main bottleneck is the manual, repetitive work of outlining structures, measuring diameters and areas, and consistently documenting these findings.
When measurements, lesion descriptions, or follow-up recommendations vary across readers, sites, or shifts, it creates uncertain baselines and makes tasks like longitudinal tracking more challenging. AI helps address these issues and improve reporting consistency by transitioning clinical documentation from subjective, free-text narratives to standardized, structured formats that rely on objective data and specific medical terminology.
As a result, AI creates repeatable, structured outputs, ensuring that the same clinical question is answered in the same format, using the same measurement logic, and reliably across sites and cases.
3. Expanded use of existing imaging data
While healthcare organizations already possess billions of medical images, they hardly use all that data to its full potential.
AI can process existing data to generate new diagnostic and clinical insights. For example, it can analyze scans that were initially taken for unrelated clinical reasons to identify incidental signs of other diseases.
When applied to radiomics and quantitative imaging approaches, AI can extract patterns that support prognosis and treatment planning, thus improving the prediction of outcomes and treatment responses in specific contexts.
Additionally, by analyzing existing patient data across multiple institutions, AI helps identify broader trends in public health, disease prevalence, and risk factors that would be impossible to coordinate manually.
4. Ability to use lower-dose ionizing radiation imaging
In modalities like X-ray and CT, where ionizing radiation is involved, AI-assisted reconstruction and denoising techniques can help preserve diagnostic image quality at lower radiation doses.
This can enable medical professionals to obtain images of the same or even higher quality when using low-dose scans. It can also eliminate the need for repeated imaging of dose-sensitive populations.
These benefits of using AI in medical imaging can introduce significant improvements for both healthcare providers and patients.
Yet, while aiming to achieve these benefits, your engineering team will likely face numerous challenges. In the next section, we discuss which ones your team should prepare for in advance.
Read also
Benefits of AI in Healthcare: How to Enhance Your Software and Improve Patient Care
Learn how AI solutions can assist medical professionals in handling complex data, improving accuracy, and optimizing daily operations while meeting strict healthcare requirements.

Challenges of AI implementation for medical imaging
AI imaging projects rarely fail because a model doesn’t work.
They stall when teams underestimate three intertwined challenge vectors:
- clinical adoption
- regulatory and business risks
- engineering challenges of medical data and deployment
The right way to treat these risks is as design inputs. After all, in medical imaging, how you build and operate the system often matters just as much as the model’s benchmark score.
Let’s take a look at the key challenges your development team should be aware of and prepared for:
1. Clinical adoption and human factors
Integrating AI capabilities into an existing system can create friction if it disrupts how clinicians work or if the output generated by AI is difficult to interpret, validate, and override. This lays the groundwork for a number of issues:
- Lack of trust. If clinicians can’t quickly understand what the model is seeing, they may mistrust it and deliberately ignore its recommendations.
Patients may also mistrust AI-assisted medical procedures if they are unsure about how AI-driven decisions are made and who validates them. If left unaddressed, this issue may significantly impact adoption.
- Concerns about skill atrophy. Automating repetitive tasks with the help of AI raises two major concerns: overreliance on AI and degradation of clinician skills.
Outputs from AI systems still need to be validated by humans to critically assess their quality and prevent end users from falling victim to automation bias. For development teams, this creates a challenge of determining the right stages for human review.
At the same time, clinicians may hesitate to work with AI systems, fearing that with less first-hand experience, their skills will gradually degrade.
- Risks of misdiagnosis. Setting explicit responsibility boundaries within AI-assisted medical workflows is a true challenge. There’s always a risk that AI may misinterpret the provided data and suggest an incorrect diagnosis and an unsuitable treatment plan. And even when AI is positioned as decision support, it still influences the prioritization and attention of clinicians.
2. Regulatory and business risks
Ideally, compliance requirements should be the basis for data governance, validation strategies, documentation streams, and post-market monitoring of your product’s performance from day one. However, this is where creators of AI-assisted medical imaging software encounter several challenges:
- Vague regulatory requirements. AI technology evolves faster than laws and regulations possibly can. Depending on the specifics of your product and the geography of your operations, you may need to account for various legal and regulatory requirements. The most common include the FDA’s Good Machine Learning Practice (GMLP) guiding principles for US businesses and the EU AI Act for businesses selling their solutions in the EU. Identifying which requirements are mandatory today and what emerging demands you should proactively prepare for is what your team may struggle with the most.
- High model governance demands. Healthcare is a highly regulated industry, so it’s only natural that adoption of AI in this sector will also be strictly governed. For example, the European Commission categorizes AI-based software intended for medical purposes as potentially high-risk, with specific and strict requirements for risk management, data governance, transparency, and human oversight. This places additional pressure on project teams, who must precisely plan the implementation of corresponding functionality and implement it in a timely manner.
- Privacy and security constraints. Imaging pipelines interact with sensitive data and protected health information (PHI) both in transit and at rest. Without well-established privacy-preserving workflows in place, there’s a risk of devastating data leaks and privacy violations, which in turn can harm your business’s reputation.
3) Data and engineering challenges
AI-assisted medical imaging solutions are highly dependent on the data they’re being fed, so development teams should be aware of:
- Data quality and quantity. To deliver reliable, high-quality outputs, AI systems require sufficient volumes of high-quality, properly labeled data. Getting and normalizing enough relevant data can become a serious bottleneck for your development team, especially when working on cases that involve less prevalent medical conditions or underrepresented subgroups.
For example, when Apriorit worked on a deep learning model for classifying skin lesion images, our team had to deal with a significant lack of relevant and properly pre-processed medical data. To address this challenge, we applied data augmentation techniques to increase the volume of available data for model training while maintaining the required quality and relevance metrics. But since augmentation can’t replace genuine data diversity, we also took extra measures to ensure that our augmented data would not cause model overfitting.
- Bias and fairness. Providing unbiased and fair treatment to every patient is a crucial ethical concern for the adoption of AI in healthcare. However, deep learning models and imaging datasets can encode systematic bias through site-specific protocols, demographic skews, device differences, label noise, and leakage between training and test splits. Unfortunately, bias in datasets and algorithms is often difficult to detect without a disciplined evaluation.
- Domain shift. Even when trained on a high-quality, well-balanced dataset, a model can experience domain shift, failing to properly handle the gap between training data and previously unseen real-world information. As a result, models that perform well in one hospital can degrade when acquisition protocols, scanner vendors, or patient populations change.
- MLOps complexity. When delivering an AI medical imaging product, your team needs to implement efficient machine learning operations (MLOps) practices. These typically include reproducibility, audit logs, versioning and rollback mechanisms, continuous learning with prevention of catastrophic forgetting, curriculum learning for new classes, backward compatibility, drift monitoring, and retraining governance. Without these, you can’t safely update models and maintain their performance over time. However, establishing efficient MLOps workflows is a challenging task that requires domain expertise and niche skills that many engineering teams lack.
Handling these challenges requires thorough planning. To help your team narrow their focus to what’s really important, we’ll move to analyzing key requirements to meet and activities to include in every stage of medical imaging AI software development project.
Read also
Challenges in AI Adoption and Key Strategies for Managing Risks
Gain insights into strategic and operational challenges of AI adoption and learn how organizations can turn complexity into measurable value with the right planning and execution.

How to engineer an AI medical imaging system: Advice from Apriorit experts
Building an accurate and reliable AI-powered medical imaging solution means balancing clinical relevance, regulatory discipline, and engineering realities, often under tight timelines and budget constraints.
Before we analyze how to plan the development process, let’s highlight the key characteristics of an efficient and reliable AI-assisted medical imaging system:
Table 1: Key characteristics of a reliable AI medical imaging system
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | An AI model should deliver accurate and verifiable outputs, even when faced with real-world data variability. |
| Transparency | Your AI system should be able to clearly communicate why it produced a particular output. |
| Clinical relevance | The model’s output should have a measurable impact and be tied to a specific workflow step, such as triage, quantification, or follow-up tracking. |
| Security | Your system should have appropriate security controls at different levels, including model artifacts and logs that may contain sensitive traces. |
| Auditability | Your solution should include detailed and structured documentation, such as model versions and change history, to support traceability and auditability. |
Human oversight | Your model should have reviewable outputs, allow for easy discovery of errors, and provide a defined feedback path for disagreements. |
Wondering how to plan these requirements into the development process for your system? Let’s look closer, stage by stage.
While at a high level, the engineering workflow for such a solution is rather standard, there are specific tasks your team needs to pay attention to at every stage of the process.
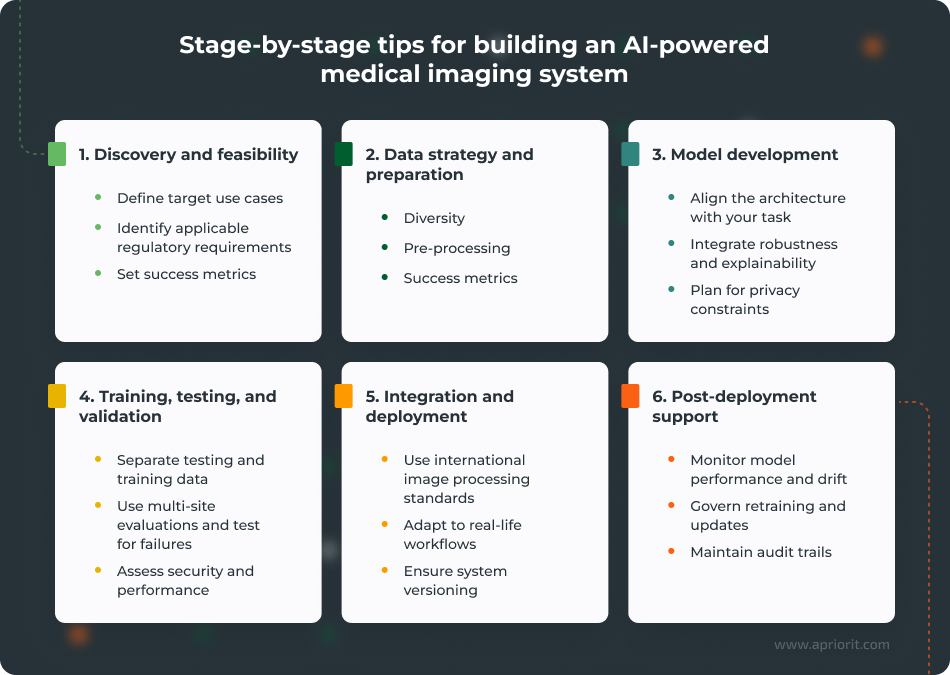
1. Discovery and feasibility
At this stage, it’s crucial for your team to define the clinical job and the regulatory posture of your future system.
You can start by translating a clinical goal into an engineering target:
- Define intended use and workflow position. Is this triage, decision support, measurement automation, or reconstruction enhancement? The intended use will dictate the required evidence, UI design, and risk controls.
- Align with regulatory pathways and outline what compliance requirements your system should meet. Look at both industry and location-specific regulations, standards, and guidelines, and prioritize mandatory requirements early on. You can start by assessing requirements of HIPAA, the GDPR, the NIST AI Risk Management Framework, the FDA, and the EU AI Act.
- Set measurable success metrics early. Include clinical metrics (e.g., time-to-decision, measurement variability reduction) and model metrics (e.g., sensitivity at a fixed false-positive rate), plus operational metrics (latency, uptime).
2. Data strategy and preparation
Next, your team needs to build reliable, well-balanced datasets for your system. Here’s what they need to pay attention to the most:
- Plan for diversity and representativeness. If the model will be deployed across multiple sites, you need data that reflects differences in scanners, protocols, populations, and artifacts. Plan where to get that data from and how to cover a lack of it in advance.
- Properly pre-process your data. At this stage, you need to take care of properly labeling your data, handling class imbalances in it, as well as normalizing and properly documenting your data pipelines. Operations like data labeling, de-identification, and dataset splits must be reproducible and auditable.
- Treat privacy requirements as architectural constraints. Implement privacy-preserving approaches, such as strong anonymization, federated learning, and log data lineage, to harden the security of your system and enhance auditability.
3. Model development
Your team needs to choose architectures that match the task and plan for maintenance from the start. The goal is to ensure robust and predictable performance under variation. To achieve this, your team needs to:
- Pick task-aligned patterns. Account for parameters such as inference time requirements, memory footprint, and required accuracy levels when choosing the appropriate architecture. For example, transformer-based architectures such as UNETR or nnU-Net often show better results on medical imaging benchmarks than other architectures. For detection tasks, region-based detectors are a commonly used option.
- Integrate robustness and explainability early. Make sure to incorporate fitting robustness (artifact handling, augmentation strategies, calibration) and interpretability (GradCAM, integrated gradients, attention maps, counterfactual explanations) techniques while planning your model architecture. Also, account for domain expert reviews and assess the explainability of model outputs.
- Engineer for reproducibility. Track the versions of your training datasets, hyperparameters, and environment details that are crucial for maintaining stable performance and understanding the reasons behind performance changes between releases.
4. Training, testing, and validation
Training and validation should mirror the deployment conditions of your AI system, which means that your team needs to:
- Separate testing and training data. To ensure your model’s stable performance and high accuracy in real-world scenarios, it’s crucial to test it on previously unseen data. To achieve this, you need to separate training data from testing data and use an external validation dataset at post-training stages.
- Use multi-site or multi-scanner evaluation where the product scope requires it. This is especially important since the performance of AI models tends to degrade when protocols and populations shift.
- Test failure modes intentionally. Evaluate by subgroups (device types, acquisition settings, demographics where available), and quantify uncertainty.
- Test security and performance both before and after release. Inference services and integration points must be tested for latency, reliability, and basic hardening before planning deployment.
5. Integration and deployment
Even excellent models fail when they can’t be operationalized, so it’s vital for your team to make the delivered AI system actually fit into clinical systems:
- Integrate into imaging infrastructure using established standards. DICOM is central to how imaging information is stored and exchanged, and integration requirements should be defined early to avoid building a sidecar tool that clinicians won’t be able to adopt.
- Design for actual workflows. Where does the AI output appear? How does it impact triage queues or reporting? How can a clinician validate it quickly? Plan integration and deployment with these questions in mind to meet the actual needs of your system’s end users.
- Operationalize versioning and rollback. If you can’t trace which model version produced a result or roll it back safely, then you don’t have a production-grade system yet.
6. Post-deployment support
Even after successful deployment, your system needs continuous monitoring and maintenance:
- Monitor model performance and drift. Track outcome proxies, data drift indicators, and model confidence behavior to maintain high accuracy of your model’s outputs over time.
- Govern retraining and updates. Define who approves updates, what triggers retraining, what validation is required, and how system changes are communicated to end users.
- Maintain audit trails. Keep logs of decisions, model versions, and incidents in a way that supports compliance audits and internal quality management.
As you can see, the use of AI in medical imaging and the engineering of such systems requires a structured approach. You need to combine deep domain knowledge with readiness to adopt innovative approaches and solve non-trivial problems. And if your team needs assistance with addressing particular tasks or lacks niche skills, you can always work with a reliable technical partner such as Apriorit.
Read also
How to Build a Secure and Resilient GenAI Architecture: Key Considerations and Best Practices
Learn how to architect generative AI solutions that meet security expectations while remaining scalable and flexible for future growth and evolving threats.

Build a competitive medical AI system with Apriorit
In healthcare, an AI initiative is mostly judged by whether it delivers safe, reliable outcomes inside real clinical workflows while staying compliant and defensible.
That’s why the choice of technical partner matters. You need a team that can build not only the model but the whole system around it, from data governance and security controls to validation discipline and integration patterns that protect patient trust and support clinical adoption.
With over 20 years in the market, Apriorit brings the security-first engineering expertise and deep domain knowledge your project needs. Here’s what we can help you with:
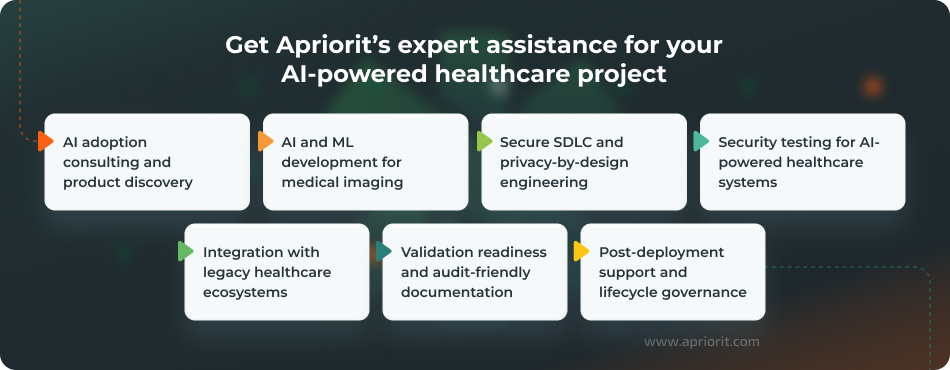
AI adoption consulting and product discovery — If your team lacks clarity on where AI fits in medical imaging, we will help you define intended use cases, success metrics, evidence expectations, and a phased roadmap.
This early work reduces the risk of failure later on, preventing you from building a technically impressive solution that doesn’t align with real-life needs.
AI and ML development for medical imaging — Our team can enrich your project with deep expertise in medical computer vision and help you build and integrate an efficient AI model. We can provide expert assistance with tasks ranging from creating a dataset strategy and training pipelines to validation.
Secure SDLC and privacy-by-design engineering — AI-powered medical imaging systems move sensitive data through pipelines, integrations, logs, and model endpoints. We ensure high-level security of this data by implementing relevant requirements and secure SDLC practices to reduce security and compliance risks early.
Security testing for AI-powered healthcare systems — Apriorit’s cybersecurity experts will help your team identify vulnerabilities across AI-enabled APIs, integrations, and infrastructure. We’ll also validate that security controls match your system’s deployment model and the sensitivity level of the data it works with.
Integration with legacy healthcare ecosystems — Innovative AI solutions are often supposed to operate as part of larger legacy healthcare systems. If this is your case, we will help you ensure seamless integration of new AI-powered capabilities into your system without compromising its performance, security, and reliability.
Validation readiness and audit-friendly documentation — Healthcare AI requires more than functional quality assurance (QA). We help teams establish reproducible testing, traceability, and documentation practices that support audits and compliance expectations, all to help you meet compliance requirements and pass audits with minimal effort. Apriorit’s delivery practices include an ISTQB-aligned QA process and project documentation practices designed to support regulatory compliance.
Post-deployment support and lifecycle governance — We help teams operationalize monitoring, incident response planning, model/versioning governance, and safe update workflows. This can prevent possible performance drifts and keep your model adaptable to continually expanding data sources, tasks, and security threats.
Whatever task you have in mind, you can discuss it with one of our experts and we’ll plan the optimal execution path together.
Looking for end-to-end AI and ML expertise?
Work with our team to build, train, and deploy models that fit your data, goals, and technical environment.
FAQ
What are the most common applications of AI in medical imaging?
<p>Most production deployments fall into three buckets:<p/>
<ul>
<li>workflow triage and prioritization</li>
<li>measurement and segmentation automation (feature quantification and tracking)</li>
<li>image quality enhancement and reconstruction (denoising, artifact reduction)</li>
</ul>
<p>Some systems may target only one of these applications, while more complex solutions may address a combination of them.<p/>
How does AI improve diagnostic accuracy in medical imaging?
<p>AI-powered systems can enhance diagnostic procedures by detecting and processing early signs of diseases that are often missed during standard visual evaluations of medical images.<p/>
<p>AI can automatically quantify disease markers such as tumor size, lesion volume, and tissue density. By accurately measuring these parameters over time, AI can also help clinicians track disease progression or response to therapy with high precision.<p/>
<p>However, to enable these improvements, an AI system should be trained on substantial volumes of high-quality, relevant data and fine-tuned regularly after deployment.<p/>
What are the main challenges of implementing AI in medical imaging?
<p>The challenges your team will most likely encounter when working on an AI-based medical imaging system include:<p/>
<ul>
<li>Finding enough quality, relevant, and properly labeled data</li>
<li>Implementing proper data privacy and security measures</li>
<li>Ensuring compliance with strict regulatory requirements</li>
<li>Meeting transparency and explainability requirements for your AI model</li>
<li>Seamlessly and safely integrating new AI-powered capabilities with legacy systems</li>
<li>Maintaining high accuracy, performance, and security of the model post-deployment</li>
</ul>
<p>To tackle these challenges, you may need to involve outside technical professionals with niche expertise in healthcare and cybersecurity engineering.<p/>
Does AI in medical imaging comply with HIPAA, FDA rules, and the EU AI Act?
<p>Most international, local, and industry-specific compliance requirements don’t prohibit the use of AI in medical imaging solutions. However, they pose strict requirements on such systems, as they work with PHI and sensitive personal data.<p/>
<p>Specific requirements for your system will depend on factors like the types of data it processes and the geography of your business operations. However, there are several universal factors to pay attention to:<p/>
<ul>
<li>Traceability and documentation, including data provenance, model versions, and validation evidence</li>
<li>Output transparency and human oversight, especially for life-critical operations</li>
<li>Lifecycle management, with established practices for monitoring performance and managing model updates over time</li>
</ul>
What technologies are used to build AI medical imaging solutions?
<p>Some of the key technologies your team will need to work with when building an AI medical imaging solution include:<p/>
<ul>
<li>Computer vision models for detecting, segmenting, and classifying tasks</li>
<li>Data pipelines for normalization, labeling, and versioning</li>
<li>Integration standards and infrastructure, such as DICOM-based imaging workflows</li>
<li>MLOps for monitoring, rollback, and controlled updates</li>
</ul>
How can I integrate AI into an existing imaging platform?
<p>Integrating AI capabilities into an existing imaging platform is a complex task that usually includes these steps:<p/>
<ul>
<li>Defining where AI outputs appear in clinical workflows</li>
<li>Deciding how clinicians confirm or override outputs</li>
<li>Implementing versioning and audit trails for your model</li>
<li>Validating latency and reliability under real-world load</li>
</ul>
<p>If you’re integrating your AI solution into hospital imaging environments, it’s also important to ensure standards-driven interoperability, which commonly involves ensuring support for the DICOM standard.<p/>



