Key takeaways:
- Traditional rule- and signature-based solutions often fail to detect zero-day attacks.
- Anomaly detection helps cybersecurity products better address previously unknown threats.
- Choosing fitting techniques and models is crucial for efficient anomaly detection.
- An anomaly detection solution should be flexible, integrable, and highly secure.
Today’s cybersecurity products are good at detecting known threats. But is this really enough?
Hackers keep coming up with sophisticated attacks. They look for and exploit previously unknown vulnerabilities, targeting their victims’ sensitive data and valuable assets. To answer this threat, cybersecurity vendors need to enhance their products with advanced capabilities. Specifically, they need anomaly detection.
This article covers the fundamentals of anomaly detection in cybersecurity, from core techniques and capabilities to key challenges and development best practices. This information will be helpful to cybersecurity product leaders who are considering anomaly detection as the basis for a new product or want to enhance their existing cybersecurity platform.
Contents:
- What is anomaly detection?
- Key anomaly detection methods
- Why embed anomaly detection in your cybersecurity solution?
- How does anomaly detection work?
- Popular anomaly detection tools and their capabilities
- Challenges of anomaly detection in cybersecurity
- Best practices for building anomaly detection solutions
- Implement efficient anomaly detection with Apriorit’s help
- Conclusion
What is anomaly detection?
Anomaly detection, also referred to as outlier or novelty detection, is the process of identifying events and behavioral patterns that significantly deviate from established norms.
Given this definition, what is anomaly detection in cybersecurity? In the realm of cybersecurity, the main goal of anomaly detection remains the same (to identify deviations from the norm), but the focus is on detecting and flagging potential indicators of malicious activity and misuse.
Usually, anomaly detection systems work with time-series data and classify detected deviations into one of three categories:
- Point anomalies — Typically, a single event that deviates from the established norm. This can be a late-night user login or a sudden spike in the volume of transferred data.
- Contextual anomalies — An event that only becomes an anomaly under specific circumstances. A typical example is a fund transfer performed outside regular operating hours.
- Collective anomalies — A series of events that may each look legitimate on its own but collectively form a suspicious pattern. This can appear as a series of low-volume data exfiltration incidents detected across the network.
However, not all anomalies are necessarily threats.
Some anomalies, while unusual or unexpected, can still represent completely legitimate events and behaviors.
Key anomaly detection methods
To identify anomalies, cybersecurity solutions rely on various techniques:
Statistical methods identify any points that fall outside the range of the established baseline. Such anomaly detection techniques in cybersecurity are best suited for fast triage. They require precise and stable metrics and can be prone to false positives.
Read also
Statistical Methods for Anomaly Detection in Cybersecurity Solutions: Balancing Cost and Efficiency
Discover how statistical anomaly detection methods can enhance your data-driven systems. Learn what statistical anomaly detection techniques will help you identify deviations, optimize monitoring, and strengthen overall system performance.

Machine learning (ML) models can establish a baseline based on training data from various sources, including user activity, system processes, and event logs. In contrast to statistical methods, ML models are better suited for working with complex anomalies that require analysis of multiple data points. Depending on the available data and system complexity, cybersecurity vendors can use unsupervised, supervised, or semi-supervised machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies.
Deep learning techniques use neural networks to spot anomalies in large and complex datasets. The most common examples of deep learning algorithms used for anomaly detection are autoencoders and long short-term memory (LSTM) networks. They are especially helpful when working with unstructured and sequential time-series data, but they require substantial computational resources and careful tuning of hyperparameters.
Graph-based methods model data entities and their relationships as nodes and edges. Most suitable for systems operating on highly structured data, these methods allow for detecting complex abnormalities in multi-stage operations and processes while accounting for the broader context. They are commonly used to detect fraud in financial transactions but can also be applied to identifying cybersecurity anomalies.
While these techniques can be used separately, most of today’s solutions combine several of them to balance the coverage of different types of anomalies, increase the interpretability of results, and better control false positives. For instance, some user and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) tools use both statistical and machine learning methods to speed up anomaly assessment and increase detection accuracy.
Since anomaly detection is a complex process, implementing it requires significant investment. So, it’s only natural for cybersecurity vendors to question whether they need to add such functionality to their products.
Want to stay ahead of evolving attacks?
Partner with Apriorit to develop custom anomaly detection capabilities that ensure early warning, minimize downtime, and improve overall security performance.
Why embed anomaly detection in your cybersecurity solution?
To keep pace with the increasing speed of cyberthreat development, you must adopt advanced technologies and approaches — among them, anomaly detection.
Previously, cybersecurity products relied on signature- and rule-based approaches to detect potential threats. Over time, these approaches became less and less efficient, failing to properly handle things like:
- Zero-day attacks with no known signatures to monitor for
- Stealthy attacks that mimic typical (and legitimate) behavior patterns
- Encrypted malicious traffic that can’t be inspected appropriately
- Gradually evolving lateral movements and insider threats
In contrast to rule- and signature-based systems, anomaly detection doesn’t rely on prior knowledge of threats but looks for deviations from the established norm. This allows cybersecurity systems enhanced with anomaly detection capabilities to catch threats that systems relying on legacy methods can’t.
Here are some of the results you can expect when you invest in an anomaly detection feature for your cybersecurity product:
- Layered defense — Offer your customers a multi-layered defense, with advanced features complementing and enhancing traditional threat detection methods.
- Adaptive security — Bring flexibility to dynamic cloud and hybrid environments where static rules can’t ensure the desired level of data and operational security.
- Increased visibility — Make it easier for your end users to spot and stop complex threats, including lateral movements, data exfiltration, and behavioral drift.
- Product competitiveness — Position your product in the same league as market leaders and differentiate it from those offering limited, often outdated threat detection capabilities.
Now that you understand the potential gains from enhancing your cybersecurity product with anomaly detection features, let’s explore in depth how this process actually works.
How does anomaly detection work?
We can split the process of identifying and handling an anomaly into five major stages:
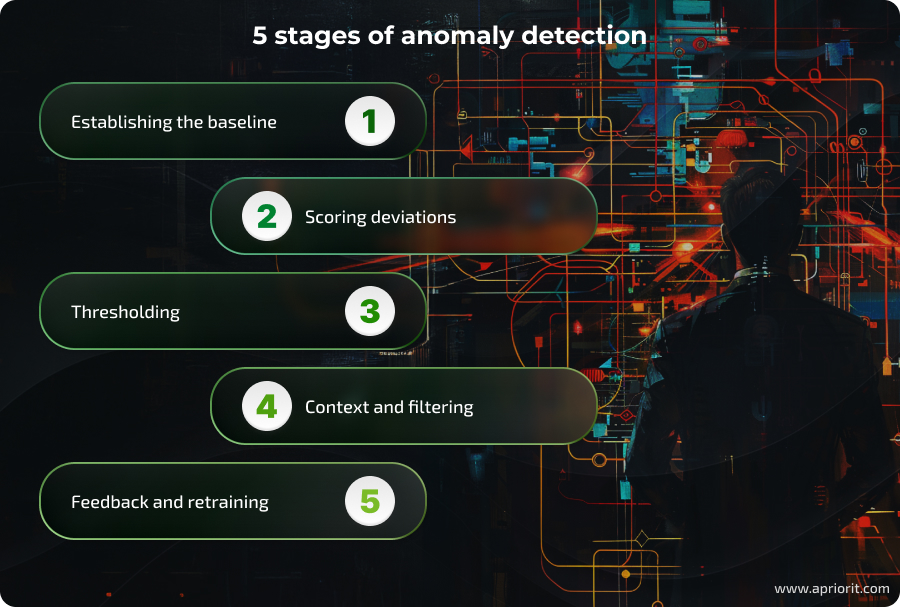
1. Establishing the baseline — Using previously gathered representative data, the system learns statistical norms and behavioral patterns in order to establish a baseline profile. Your go-to technologies here can range from traditional statistical models and clustering to advanced AI/ML models.
2. Scoring deviations — The system calculates a score for every event or data point, defining how far it deviates from the previously learned norm.
3. Thresholding — If the calculated score is outside the normal range, the system flags it as an anomaly. In more advanced systems that use adaptive thresholding, anomalies are ranked by severity and potential impact rather than a binary cutoff.
4. Context and filtering — To increase detection accuracy, the system can use correlation rules and cross-check the flagged anomaly with other signals, including parameters like user role, asset criticality, and time of day.
5. Feedback and retraining — The model uses labeled feedback to retrain and adapt over time, reducing potential drift and minimizing both false positives and false negatives.
While the process itself seems straightforward, you need to carefully plan which capabilities to include in your product. A good starting point for such planning is evaluating the functionality of leading tools in the market.
Read also
How to Use Data Visualization and AI-Powered Knowledge Graphs to Enhance Your Cybersecurity Product
Turn complex threat data into clear insights. Learn practical visualization techniques to identify anomalies, monitor attack trends, and improve decision-making.
Popular anomaly detection tools and their capabilities
The global anomaly detection market is projected to reach $14.5 billion by 2030, showing impressive 16.5% growth over just seven years. Key players offer sophisticated, cross-industry solutions, while some vendors choose to target specific sectors like finance or healthcare.
To find the right niche, it’s important to understand what capabilities are currently in high demand and identify key competitors to watch. Below, we cover some of the most essential capabilities offered by market leaders.
User and entity behavior analytics (UEBA) helps to identify risky abnormalities in the behavior of users or devices. Often AI- or ML-driven, UEBA is particularly effective at detecting insider threats and account takeovers.
You can find UEBA capabilities in products such as Splunk and IBM QRadar.
Network behavior anomaly detection (NBAD) and network detection and response (NDR) allow for identifying anomalies in network traffic. These features and tools help prevent incidents such as data exfiltration, command-and-control traffic, and reconnaissance.
Common market examples include Cisco’s Secure Network Analytics solution and Progress Flowmon’s ADS.
Cloud anomaly detection focuses on cloud configurations, workloads, and accounts, looking for suspicious events and behavior patterns.
Leading service providers often offer their own solutions for anomaly detection in the cloud, but their capabilities can vary significantly. For example, AWS GuardDuty uses machine learning algorithms to identify suspicious events in your AWS environment, while Google Cloud’s Security Command Center provides anomaly detection capabilities for securing service accounts and virtual machines.
High-fidelity telemetry provides the raw data that anomaly detection features depend on. For example, network traffic analyzer Zeek uses detailed network logs to build baseline profiles.
While it’s relatively easy to determine what capabilities are trending by looking at competitors’ products, doing so won’t help your team predict possible development challenges. Let’s talk about key risk factors to pay attention to if you decide to start working on an anomaly detection tool.
Read also
Telemetry in Cybersecurity: Improve Security Monitoring with Telemetry Data Collection (+ Code Examples)
Improve your security visibility with telemetry data. Get expert insights on how to collect and process system metrics to detect anomalies, trace attacks, and strengthen cybersecurity defenses.

Challenges of anomaly detection in cybersecurity
There are several issues your team will need to watch out for when implementing an anomaly detection feature or solution. Here are the most significant:

False positives and false negatives — Whether your solution alerts end users of things that don’t require human intervention or doesn’t alert them of critical issues, either scenario is disturbing. In the first case, your customer’s security team will have to deal with extreme alert fatigue and will waste time on processing low-priority incidents. In the second case, your product will fail to accomplish the task for which it was initially deployed. Either way, it increases the risk of not detecting a serious incident in time.
Noisy, incomplete data with weak labeling — To deliver highly accurate results, anomaly detection tools need vast volumes of high-quality, properly labeled, and preprocessed data. However, most systems and tools that feed data to anomaly detection models generate incomplete timestamps, noisy telemetry, and inconsistent schemas. This degrades the accuracy of the model’s forecasts and increases the risk of false positives and false negatives.
Lack of specific training datasets — Publicly available datasets lack relevant industry- and operation-specific data. With ML- and AI-driven anomaly detection in cybersecurity, models trained on generic datasets often underperform in production. Due to the lack of representative data, they simply can’t detect patterns and flag incidents unique to a particular type of traffic, system operations, and user behavior.
Interoperability with third-party tools — Cybersecurity solutions like SIEM, SOAR, and XDR often serve as the main data sources for anomaly detection tools. They generate large volumes of heterogeneous security data (such as logs, alerts, and behavioral signals) that have different formats but need to be processed by a single engine, often in real time. Unless that data is initially formatted according to the requirements of the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework, your team will have to put extra effort into normalizing it.
Model drift monitoring — Over time, the initially established baseline may need to adapt to changing factors like workforce shifts, seasonality, and installation of new apps. This makes it difficult to maintain high detection accuracy and keep deployed models adaptable.
Explainability and transparency — Black-boxed models create space for opaque forecasts that are hard or impossible to explain. If unaddressed, the lack of explainability can compromise the trustworthiness of anomaly detection results and raise compliance-related concerns.
Adversarial attacks — The model itself can be a target of an attack. Hackers can poison training data or shift the baseline over time by slowly introducing multiple benign anomalies, thus masking attacks as normal activity. They can also try to reverse engineer or misconfigure the system, or execute evasion attacks.
Regulatory and privacy constraints — Anomaly detection tools handle vast amounts of highly sensitive data, such as personally identifiable information and geolocation metadata. Your team will need to pay special attention to properly implementing robust regulatory and compliance requirements to maintain data security and privacy, especially when working with black-boxed third-party models.
These are, of course, only the most universal challenges of anomaly detection that your team should be prepared for. In the next section, we offer several best practices for building a reliable and efficient product.
Watch webinar
The Power of AI in Behavioral Analysis for Cybersecurity
See how AI transforms security operations through advanced behavioral analysis. Learn from experts how intelligent algorithms identify hidden patterns, predict attacks, and reduce incident response times.
Best practices for building anomaly detection solutions
Delivering a reliable, secure, and compliant cybersecurity solution with anomaly detection capabilities requires thorough planning that accounts for multiple factors. Below, we list some of the key practices for your team to implement when working on anomaly detection functionality.

1. Build with compliance and integrations in mind — Start planning the most impactful aspects before you even start building your anomaly detection solution. For example, explainability is a critical concept covered by several AI development frameworks and regulations, including the EU AI Act. To make sure your model is explainable, your team can either look for a suitable white-box model or increase the transparency of your black-box model by deploying explainable AI tools like SHapley Additive exPlanations (SHAP) or Local Interpretable Model Agnostic Explanation (LIME).
Depending on the types of anomalies you want your solution to identify, you may want to consider different detection methods. Your team’s goal should be to combine them in a way that cuts implementation costs while maintaining high detection accuracy.
Finally, make sure your team works with widely accepted data standardization frameworks, such as the Open Cybersecurity Schema Framework. This will help you simplify the integration of third-party services and enhance threat analytics.
2. Design for flexibility and adaptiveness — Static baselines can only be efficient under very specific conditions. For most anomaly detection solutions, building flexible and adaptive baselines is a must.
At the same time, your team needs to plan for possible model drift and compromise by malicious actors. To do this, your team should schedule regular model retraining and automate the detection of model drift, especially when it comes to AI-based anomaly detection in cybersecurity.
3. Limit data and system access — To keep the system and data properly secured, rely on a privacy-by-design approach when building your anomaly detection solution. Enforce least privilege within critical systems and minimize the amount of data your tool can process and store.
To ease future compliance efforts, make sure your tool generates audit-ready decision logs.
4. Strengthen both data and model security — Have your team implement input validation mechanisms to secure your anomaly detection model from injection attacks. To ensure the model is well-secured, run additional security tests or perform penetration testing on the most critical elements of your solution.
In-house expertise may not be enough to successfully identify which practices your project requires — and to implement them efficiently. For sophisticated tasks, you may need the assistance of seasoned professionals.
Related project
Custom Cybersecurity Solution Development: From MVP to Support and Maintenance
Our client wanted to protect sensitive data, meet regulatory requirements, and ensure business stability in a high-risk digital environment. Apriorit helped them achieve all these goals with a custom-built cybersecurity platform.

Implement efficient anomaly detection with Apriorit’s help
Building anomaly detection into a cybersecurity solution requires more than selecting the right algorithm. It demands custom engineering across data, integration, scalability, and compliance layers. Apriorit can help you with all that and more.
With over 20 years of experience in cybersecurity, we have successfully delivered projects of varying complexities, ranging from minor feature integrations to comprehensive cybersecurity platform development and support.
You can entrust us with:
- Custom cybersecurity development to design, implement, test, and support a custom anomaly detection module, features, or a standalone solution that will differentiate you in the cybersecurity market.
- Network management tasks ranging from telemetry processing to behavior analysis to ensure your anomaly detection solution can gather, normalize, and process high volumes of security data and signals while maintaining low-latency inference.
- Penetration testing aimed at validating and improving the protection of your anomaly detection engine against potential threats and adversarial attacks. We can also assist you with security audits, supporting your internal security assessment efforts or helping your team prepare for future compliance audits.
- External API integration of any complexity to help you expand the capabilities of your product securely and efficiently. Our specialists can also design a custom API to enable and improve your product’s integrability.
- AI and machine learning engineering tasks to ensure that your anomaly detection solution relies on an interpretable and adaptive ML model that can stay reliable and deliver accurate results even under increased load.
Working with Apriorit, you can quickly enhance your engineering team with rare skills and valuable domain expertise, ensuring you deliver a quality and competitive product even within strict deadlines.
Conclusion
Demand for anomaly detection capabilities continues to rise across markets and is especially gaining traction in the cybersecurity domain.
With comprehensive anomaly detection in place, cybersecurity vendors can offer their users broader visibility and a stronger defense against zero-day threats while reducing alert fatigue.
However, delivering such a solution requires extensive planning and unique technical expertise. Partner with the Apriorit team to overcome the challenges that prevent your project’s success.
Is your security solution ready for tomorrow’s threats?
Let Apriorit’s engineers and security experts help you strengthen your product’s defenses and meet compliance goals.
What is the difference between anomaly detection and threat detection?
<p>Anomaly detection searches for any deviation from the norm, whether it’s an unusual data point, event, or action. Not all anomalies are necessarily dangerous.</p>
<p>In turn, threat detection focuses on identifying events and activity patterns that match the profiles of known attacks.</p>
<p>These two approaches often complement each other within the same cybersecurity system, expanding visibility across both known threats and zero-day attacks.</p>
Which anomaly detection technique is best for enterprise cybersecurity solutions?
<p>There’s no universally efficient technique for anomaly detection. You need to choose the most suitable one depending on the type of data your solution works with and the types of anomalies you want to detect.</p>
<p>For example, UEBA-based tools are best suited for identifying insider threats and behavioral anomalies, while time-series models are more effective for detecting low-and-slow patterns.</p>
<p>Apriorit specialists can help you choose the technique that is most suitable for your product. Reach out to discuss the details.</p>
How can anomaly detection be integrated into existing SIEM or SOAR platforms?
<p>To integrate anomaly detection capabilities into an existing SIEM or SOAR solution, you can use dedicated APIs, special connectors, or ready-to-use modules.</p>
<p>If off-the-shelf anomaly detection solutions cannot meet your needs and expectations, consider building a custom tool tailored specifically to the data pipelines and workflows of your target platform.</p>
How can you reduce false positives in anomaly detection systems?
<p>False positives — as well as false negatives — can have a severe impact on the efficiency of security teams using your product. To improve alert quality, you can implement adaptive baselines instead of relying on static ones, use contextual correlation with other signals to cross-check triggered alerts, and extract domain-specific features.</p>
<p>Another important factor to consider is model drift detection and fine-tuning, which should be regular and preferably automated activities.</p>
What trends will shape the future of anomaly detection in cybersecurity?
<p>To stay on top of the latest trends, cybersecurity vendors who work on anomaly detection products should pay attention to:</p>
<ul>
<li>Graph-based approaches for detecting anomalies in user–device–asset relationships</li>
<li>Growing scalability and real-time data processing requirements</li>
<li>Increasing adoption of ML and AI models with high resistance to evasion and poisoning attacks</li>
<li>Multimodal approaches that combine different logs, telemetry, and behavioral signals for more accurate anomaly detection</li>
<li>Rising demand for transparent and explainable AI models</li>
</ul>
How does anomaly detection support compliance initiatives?
<p>Anomaly detection systems can log what data triggered an alert, making it easier to prove transparency and traceability of outputs. With proper configurations, such systems can also support data minimization standards.</p>
<p>All of this will help you meet the requirements of such frameworks and regulations as SOC 2 and the GDPR.</p>
<p>At Apriorit, we already have relevant experience and will gladly assist you in building highly accurate anomaly detection tools that fully meet your international, regional, or industry-specific compliance requirements.</p>



